Many times we hear about rotation and reciprocation as rival movements and feel like we have to choose one or the other. In reality both are very important and helpful […]
 Rotation and Reciprocation: Synergy not rivalry
Rotation and Reciprocation: Synergy not rivalry
Many times we hear about rotation and reciprocation as rival movements and feel like we have to choose one or the other. In reality both are very important and helpful […]
 FAST RETREATMENT & APICAL BLOCKAGE
FAST RETREATMENT & APICAL BLOCKAGE
The field of endodontic retreatment is wide and the cases are variable according to the mishaps included. This article will deal with a short filling which was condensed despite having […]
 Non-surgical endodontic treatment of large periapical lesions
Non-surgical endodontic treatment of large periapical lesions
This article showing the method of using non-setting calcium hydroxide in case with large periapical lesion .
 Endodontic Surgery: A Conservative Solution in Some Cases for Preserving Natural Teeth
Endodontic Surgery: A Conservative Solution in Some Cases for Preserving Natural Teeth
A patient recently visited our clinic with a complaint of persistent pain in the upper right lateral incisor. Upon examination, we discovered a granuloma at the root of the affected […]
 RESTORATIVE OPTIONS FOR ENDO TREATED TEETH - GAINING FERRULE
RESTORATIVE OPTIONS FOR ENDO TREATED TEETH - GAINING FERRULE
In this article i am going to show an option for the ferrule gaining for badly destructed teeth.
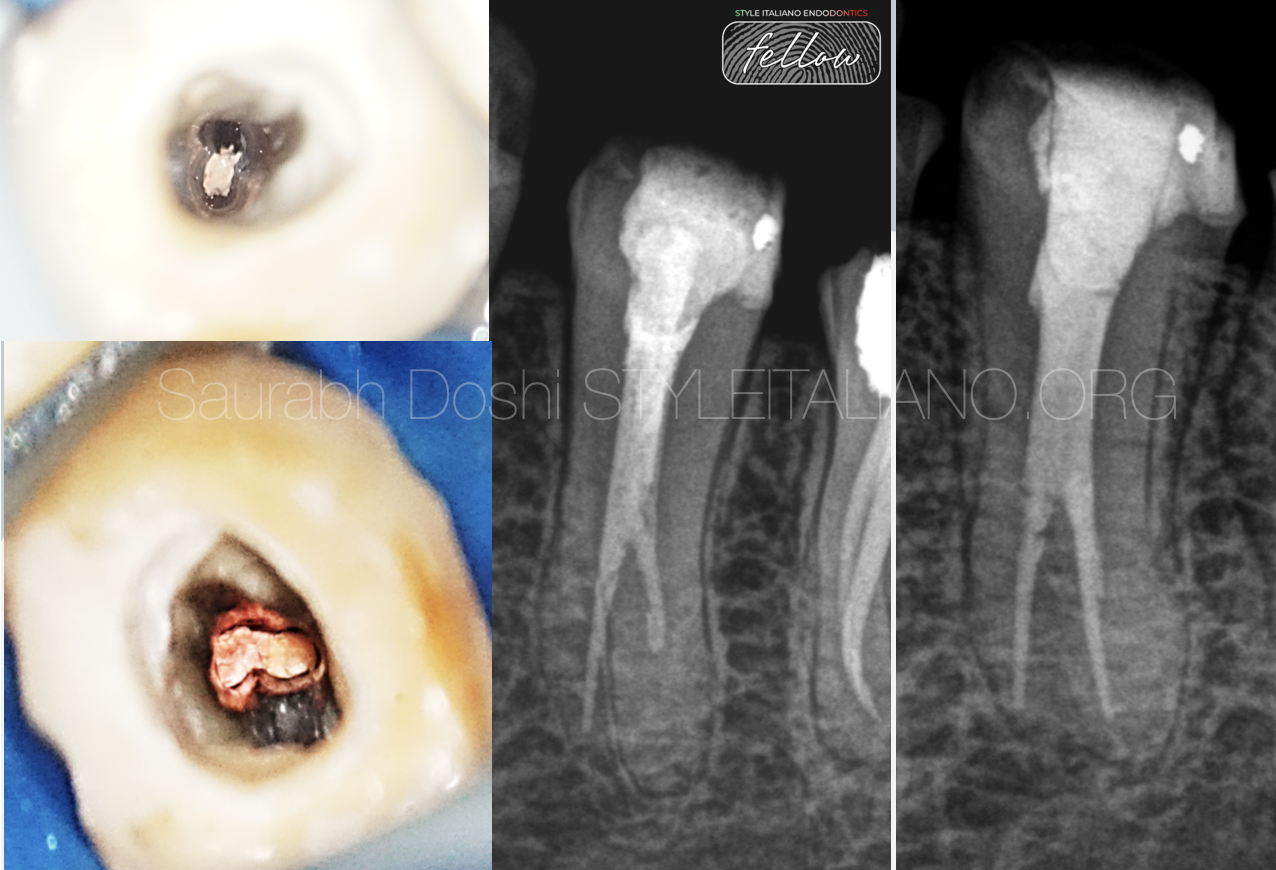 Selective Root Canal Re-Treatement of Lower Left Pre-Molar
Selective Root Canal Re-Treatement of Lower Left Pre-Molar
In retreatment cases , the clinician has to deal with many mishaps such as underfilled, missed and obstructed canals as also with iatrogenic damages as separated instruments and perforations. Underfilled […]
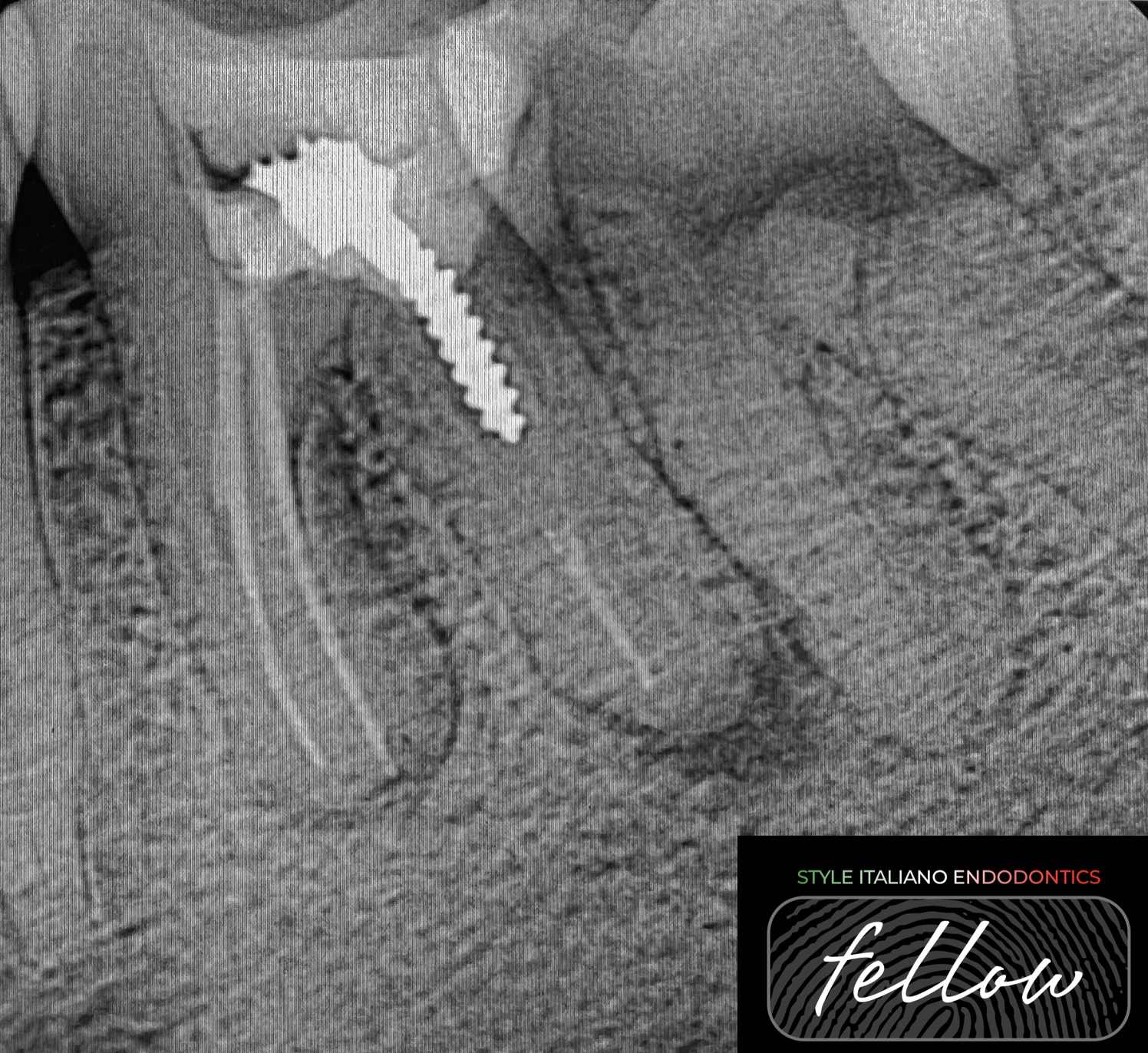 Retreatment case: metal post removal and deep splitting canal
Retreatment case: metal post removal and deep splitting canal
There are four options for managing a tooth with posttreatment disease: do nothing, extraction, nonsurgical retreatment, or surgical treatment. Avoiding treatment may result in the progression of disease and continued […]
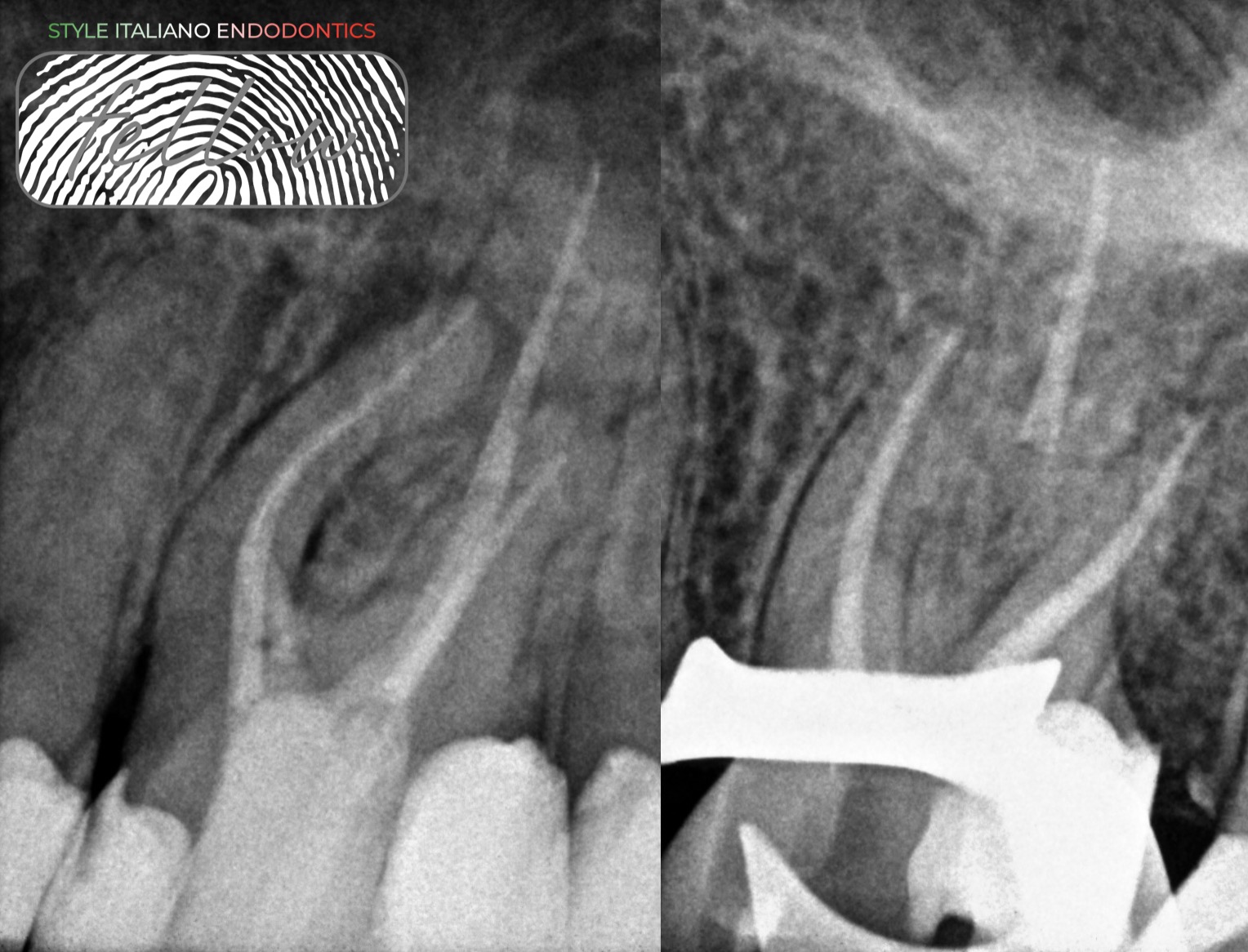
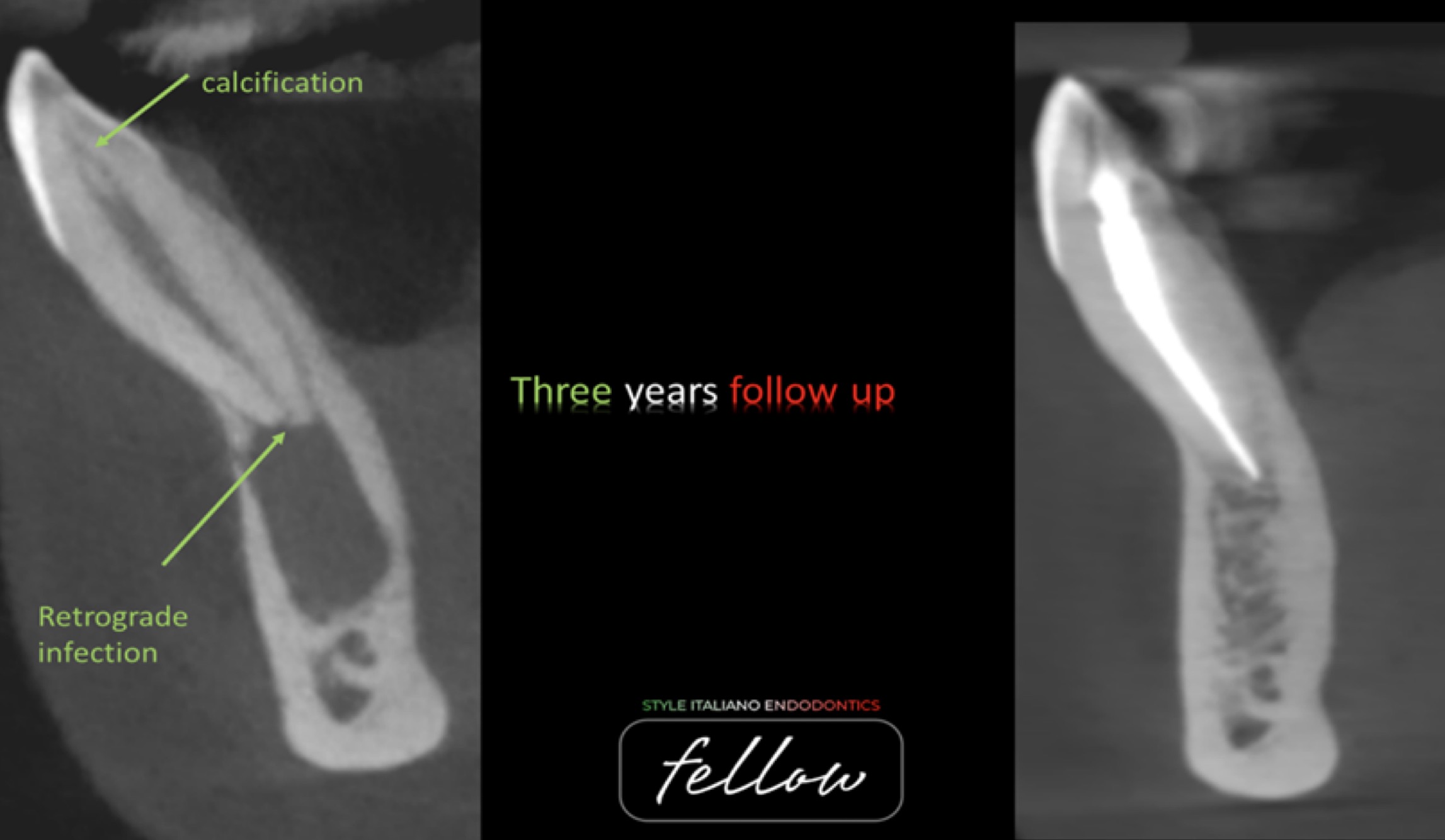
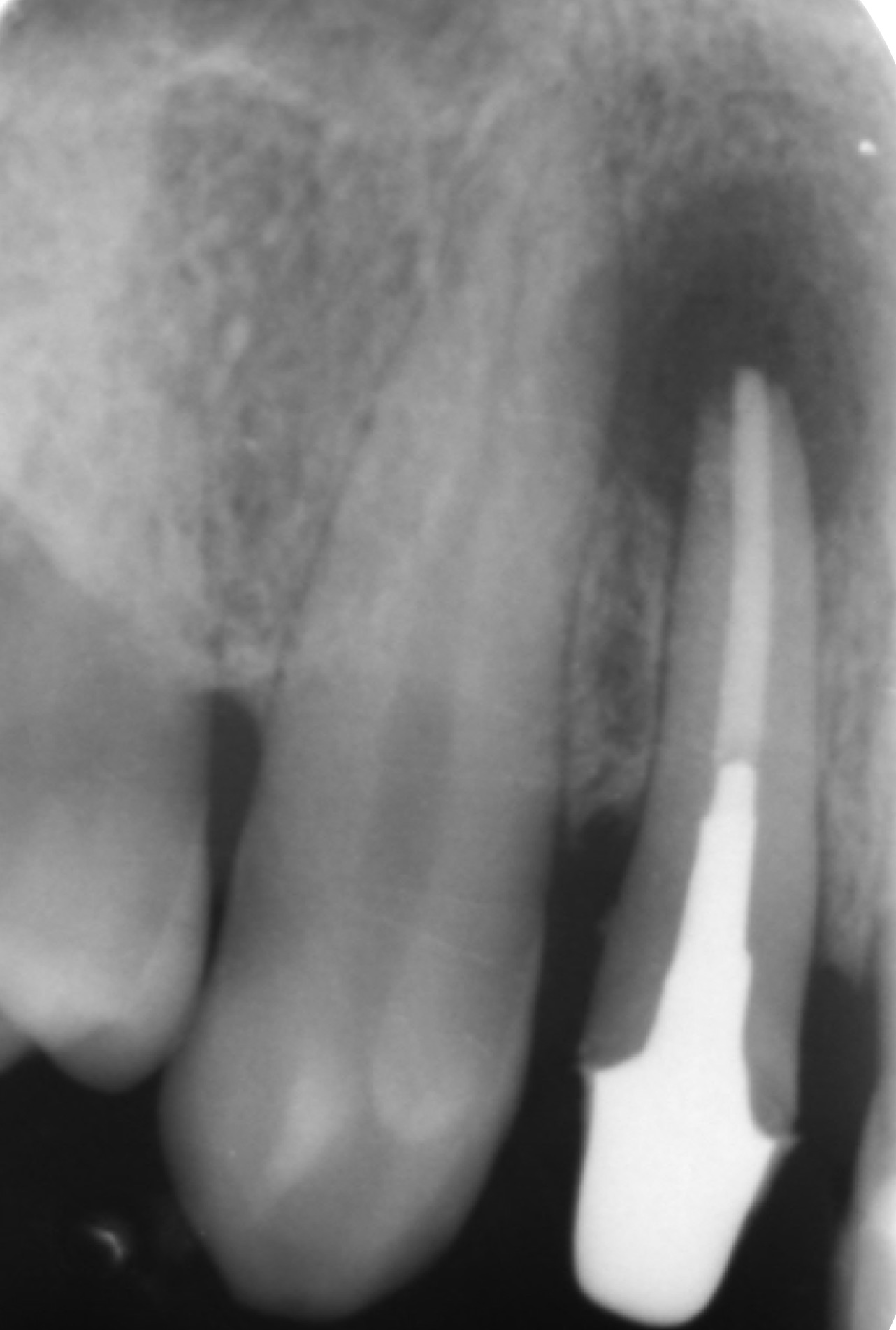
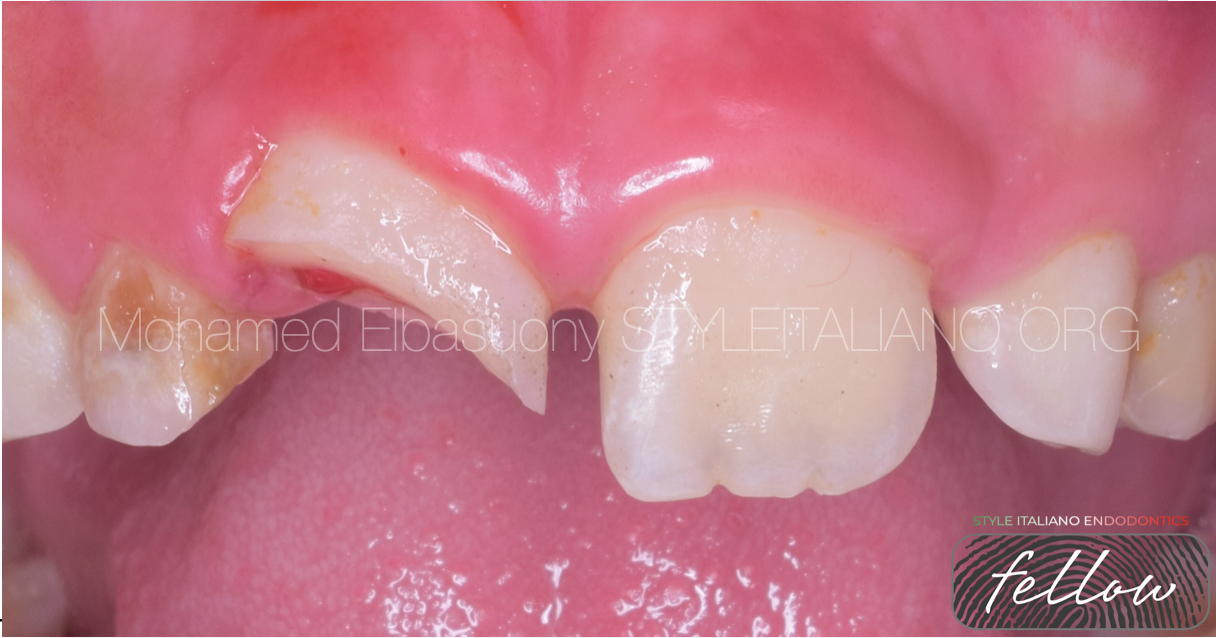 Management of complicated crown fracture of newly erupted maxillary central incisor. Conservative approach with 3 years follow up
Management of complicated crown fracture of newly erupted maxillary central incisor. Conservative approach with 3 years follow up
Coronal fractures of the anterior teeth are a common form of dental trauma that mainly affects children and adolescents. One of the options for managing coronal tooth fractures when the tooth fragment is available is the reattachment of the dental fragment.
This article reports on coronal tooth fracture case that was successfully treated using tooth fragment reattachment.
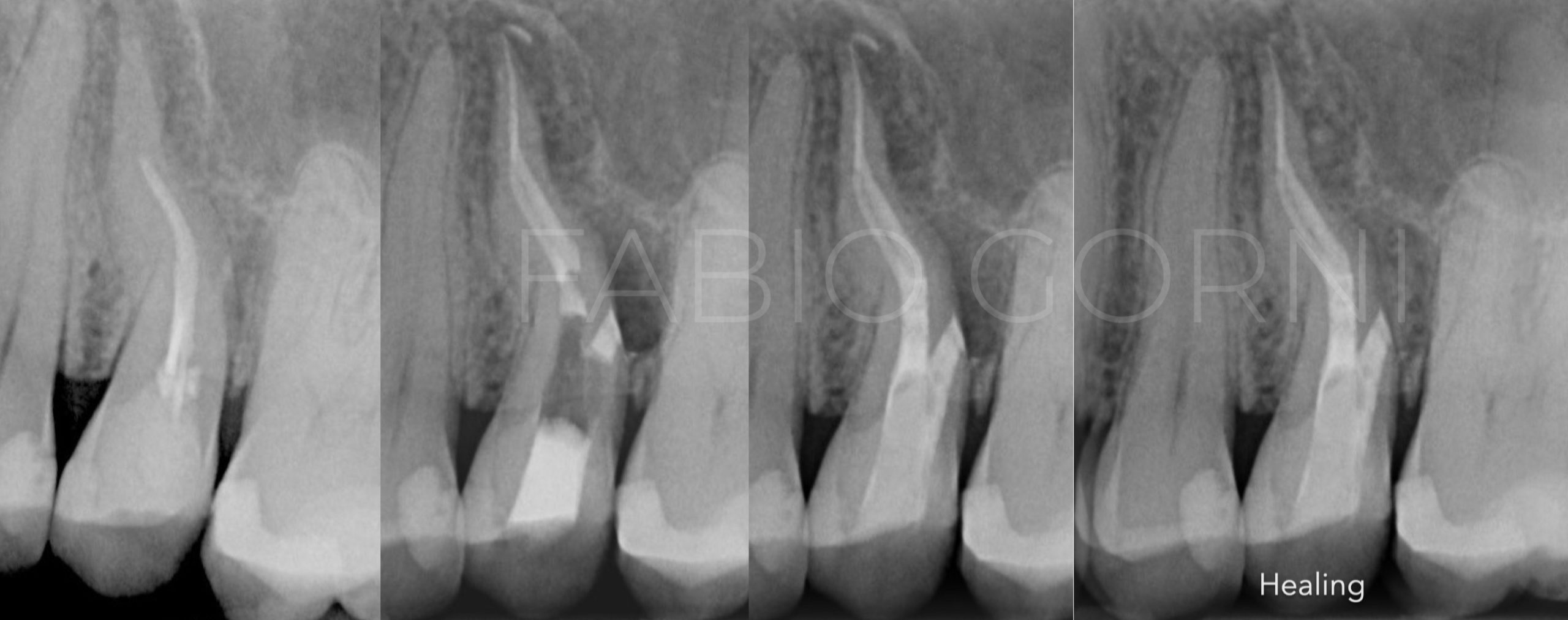 Retreatment of a second upper premolar
Retreatment of a second upper premolar
The patient came to my office with a big swelling and acute pain , after the pre-op X-ray the situation was clear , apical periodontitis plus a lateral lesion . […]
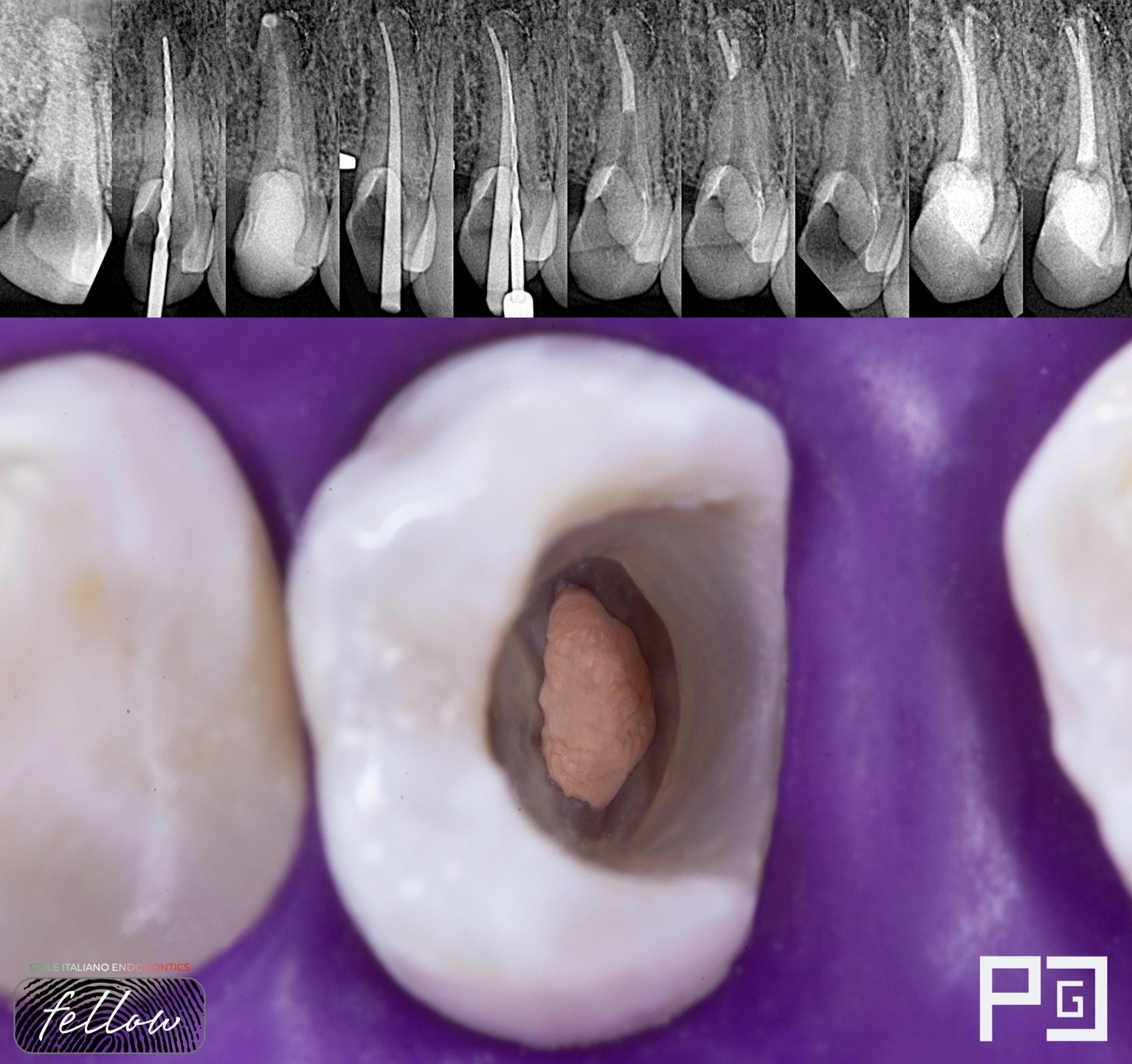 Management of anatomy in a first tricky premolar (Deep Split)
Management of anatomy in a first tricky premolar (Deep Split)
The clinician must be aware of the possible anatomical variations of these teeth and their relationship to adjacent anatomical structures when planning and performing endodontic procedures.
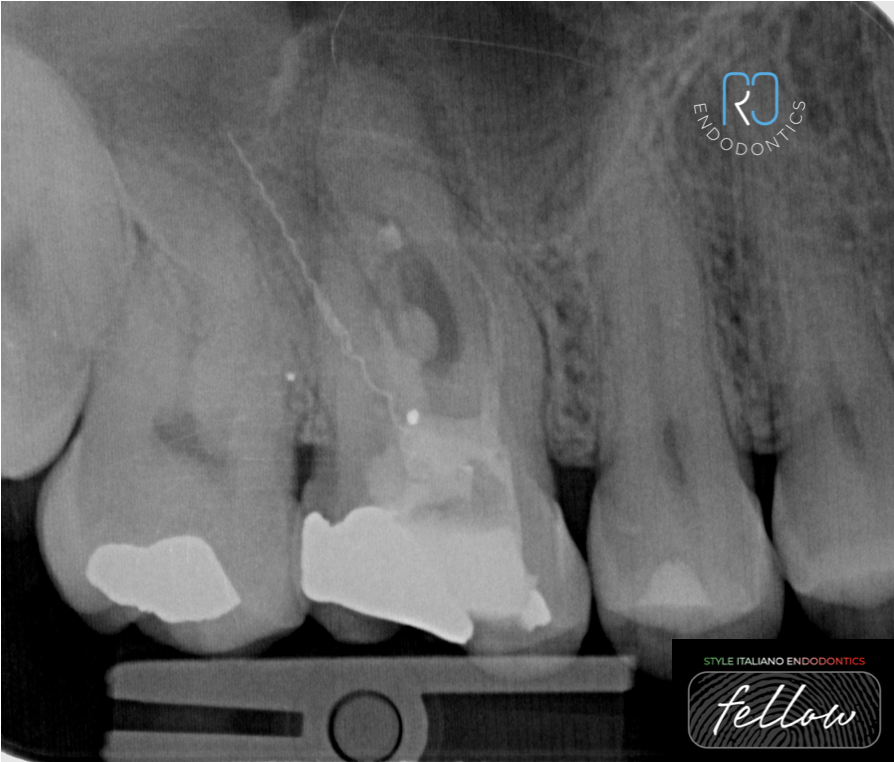 One canal, two broken files
One canal, two broken files
The position and anatomy of upper molars can make root canal treatment challenging, and instrument separation is common. In the presented case, tooth 1.6 had an abscess, and an attempt […]
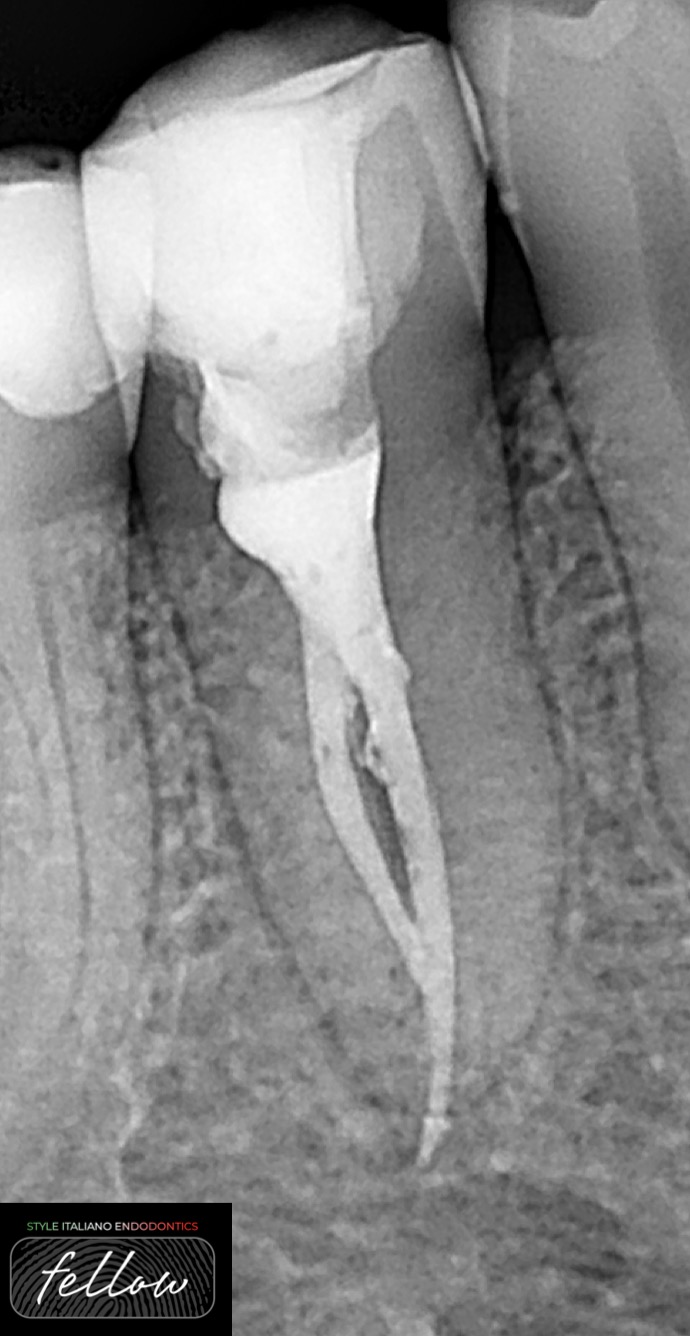 Retreatment case with two types of perforations
Retreatment case with two types of perforations
Root perforations were the second greatest cause of failure accounting for 9.62% of all unsuccessful cases. Seltzer et al. also attributed 3.52% of all endodontic failures to perforation. This perforation […]