Root canal retreatment seems to be one of the biggest challenges in the Endodontic therapy, in the retreatment episodes we will review different scenarios with different cases. In Endodontics we […]
 Retreatment Series: Episode 2
Retreatment Series: Episode 2
Root canal retreatment seems to be one of the biggest challenges in the Endodontic therapy, in the retreatment episodes we will review different scenarios with different cases. In Endodontics we […]
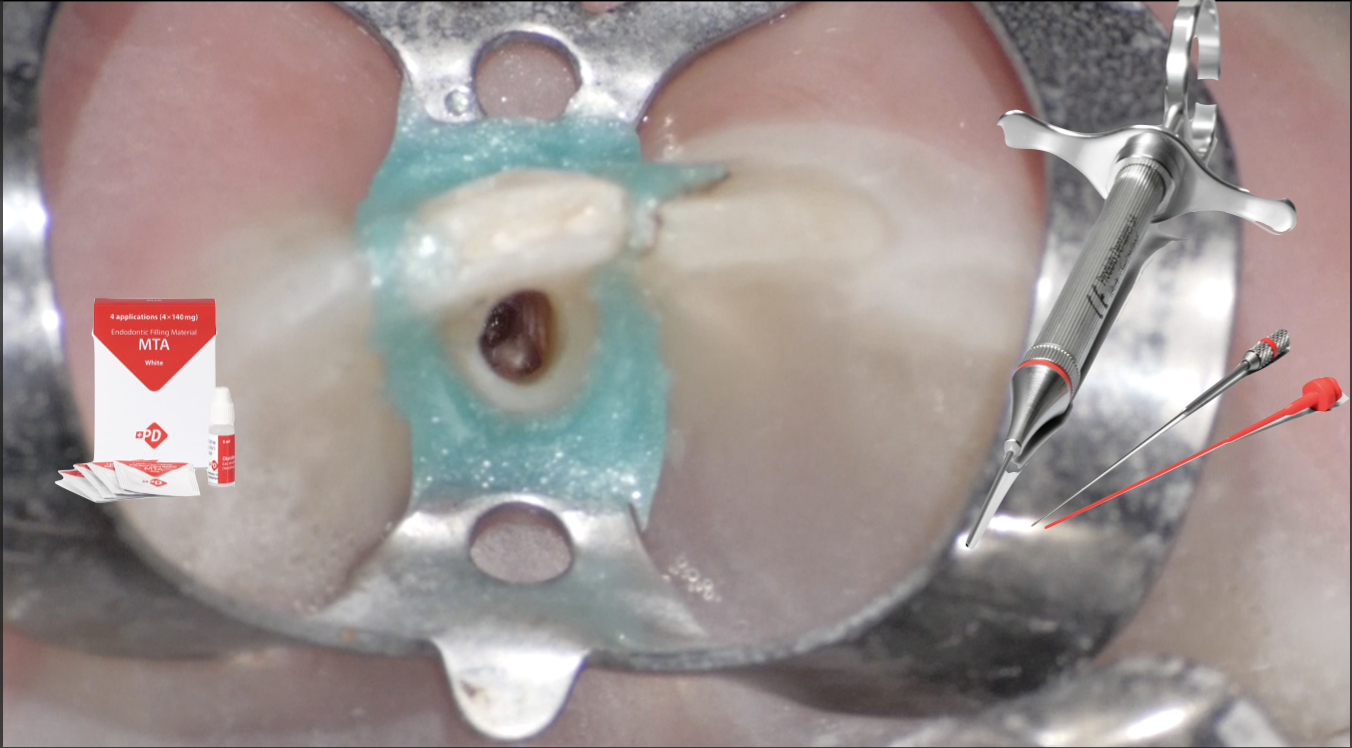 The management of a buccal perforation in a lower incisor
The management of a buccal perforation in a lower incisor
Root perforations are characterized by a communication between the root canal system and the external tooth surface. They are caused by a pathological process or an operative procedural accident. When iatrogenic, they can occur during […]
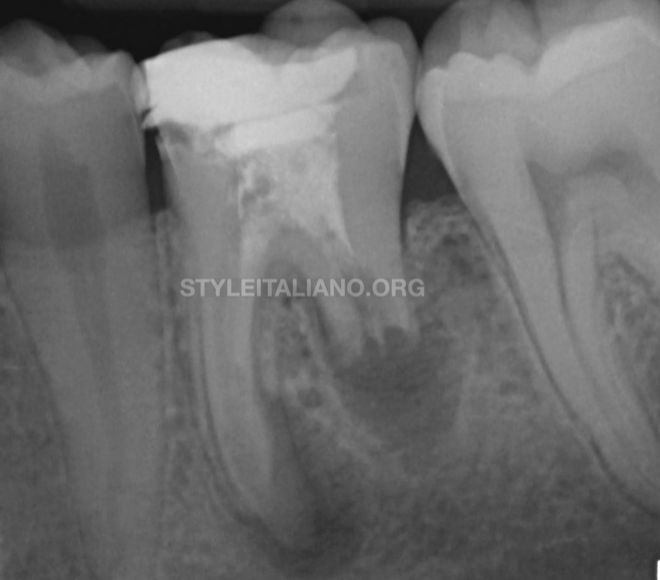 The management of two mandibular molars with apical inflammatory root resorption
The management of two mandibular molars with apical inflammatory root resorption
Apical pathology can appear as a straightforward diagnosis, however the tools available for assessment come across different limitations. Histology has highlighted various aspects that can not be yet coherently linked […]
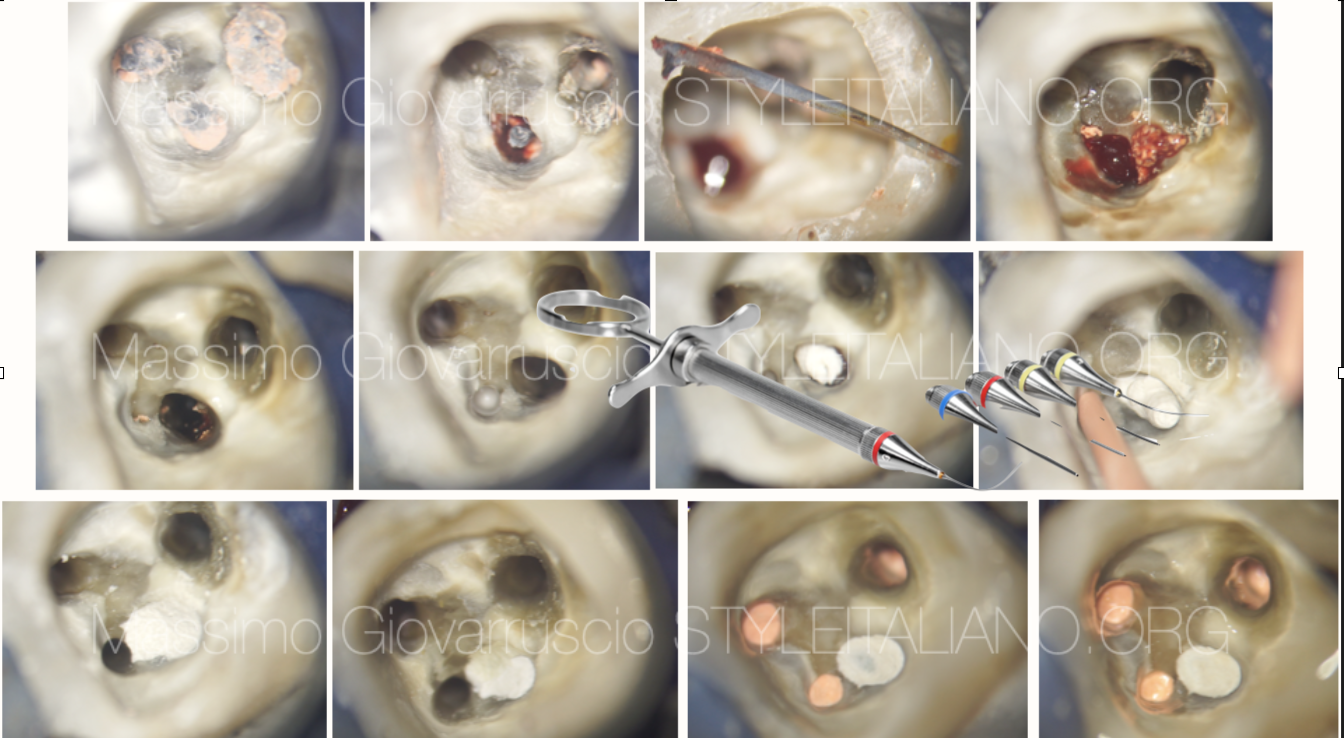 Lower second molar: carrier based obturation...through the furcation
Lower second molar: carrier based obturation...through the furcation
Perforations are defined as artificial communications between the root canal space and the surrounding tissues. Endodontic perforations represent an interruption of the continuum between the endodontic space and the periradicular […]
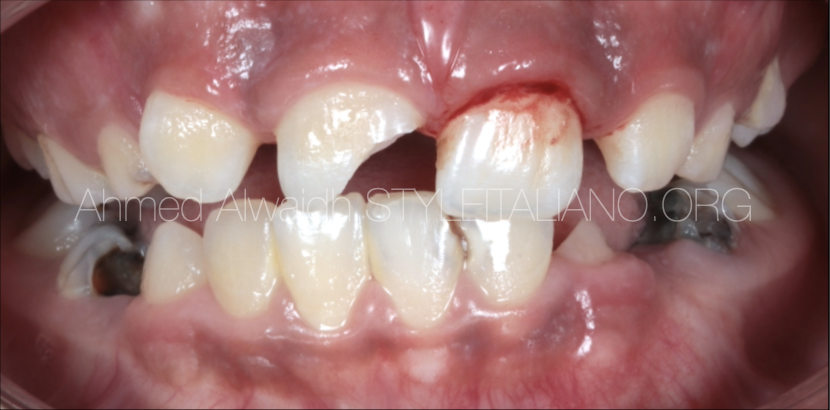 Vital Pulp Therapy: Part 1: Direct Pulp Capping for A Traumatic Exposure of Permanent Maxillary Right Central Incisor
Vital Pulp Therapy: Part 1: Direct Pulp Capping for A Traumatic Exposure of Permanent Maxillary Right Central Incisor
Pulp inflammation or exposure may occur as a result of many reasons like carries, trauma, or over-zealous preparation. However, if left untreated, this may lead to pulpits, pulp necrosis, and […]
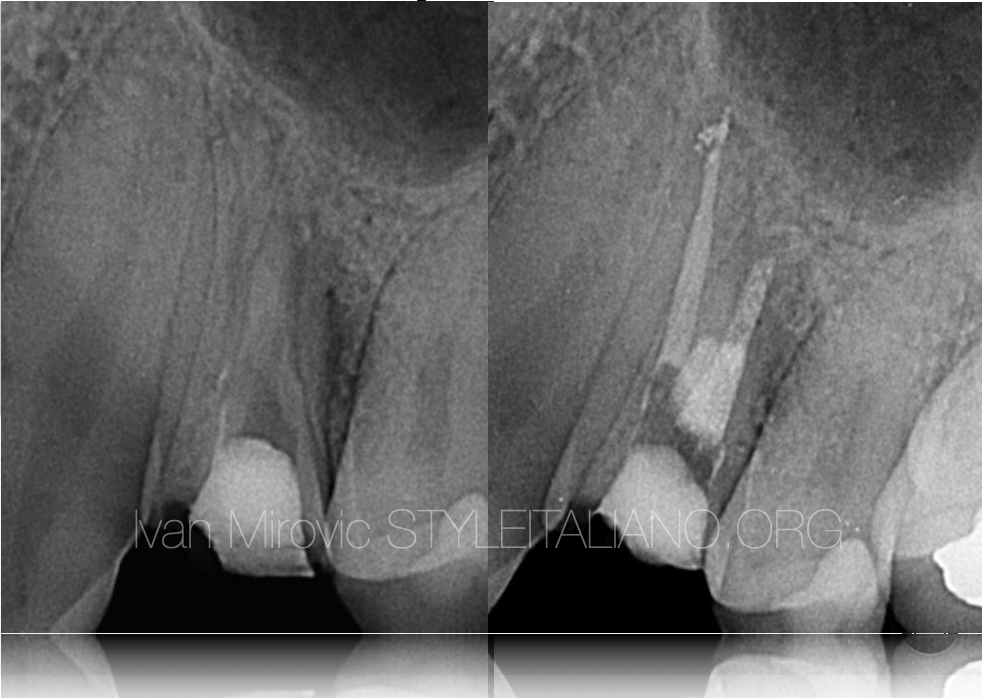 Saving hopeless tooth: case report
Saving hopeless tooth: case report
With introduction of mineral trioxide aggregate and other bioactive materials in endodontics possibilities of saving compromised teeth have improved significantly.
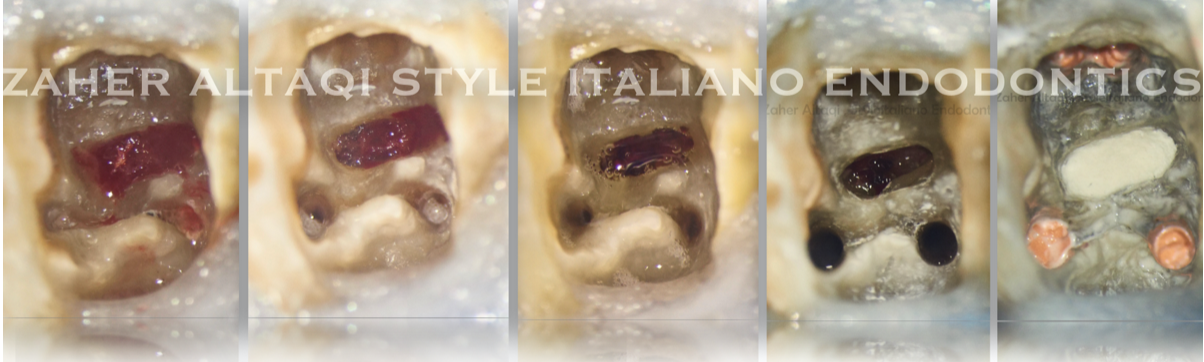 Perforation repair: step by step
Perforation repair: step by step
A tooth perforation is a pathologic or iatrogenic communication between the root canal space and the periodontal apparatus. To clinically determine if an endodontically perforated tooth should be extracted or […]
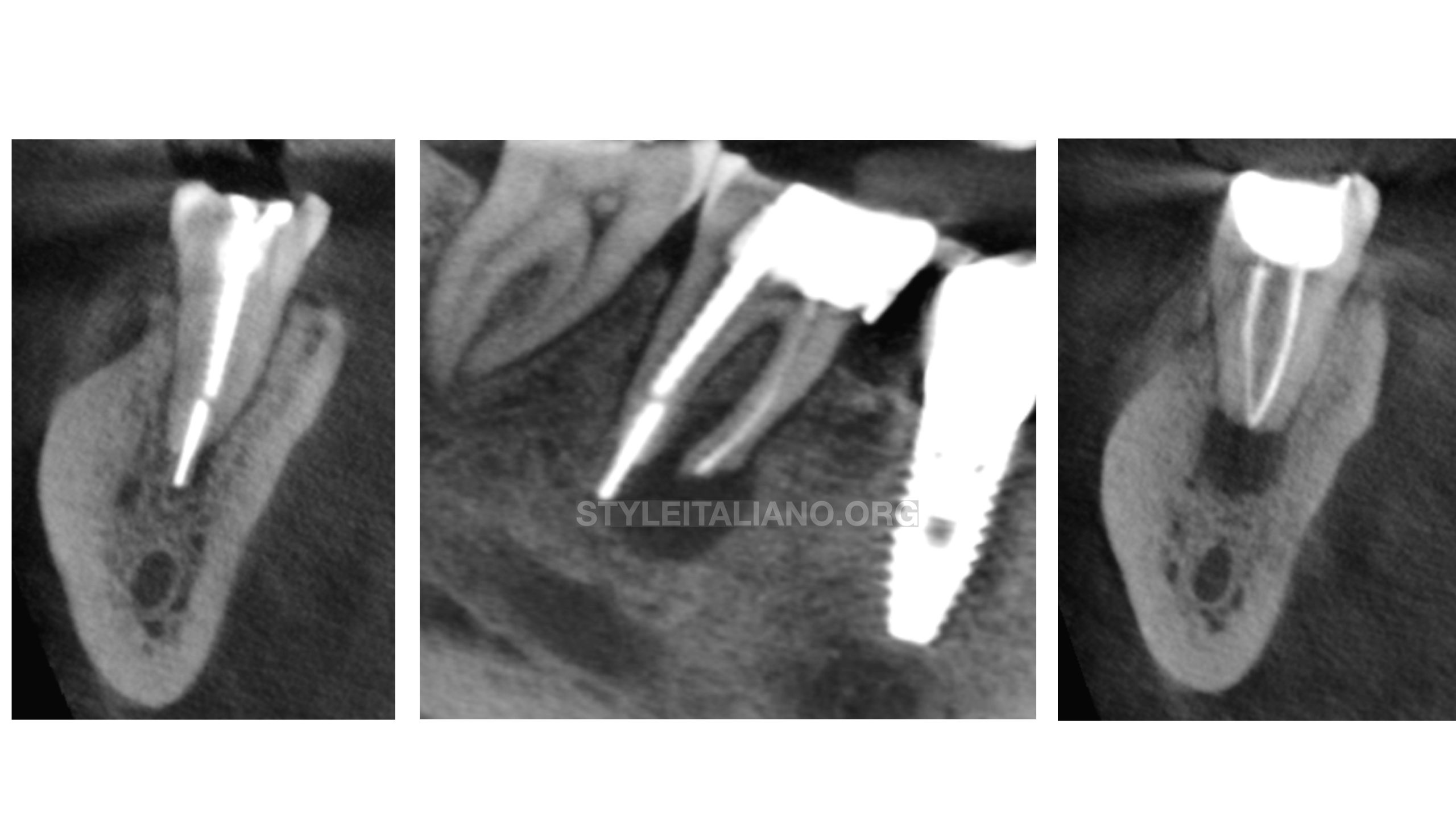 Triple MTA apical plug in second lower molar with overextended guttapercha
Triple MTA apical plug in second lower molar with overextended guttapercha
Mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) was developed in the 1990s as a root-end filling material and has also been recognized as promising when used to form an apical barrier because of […]
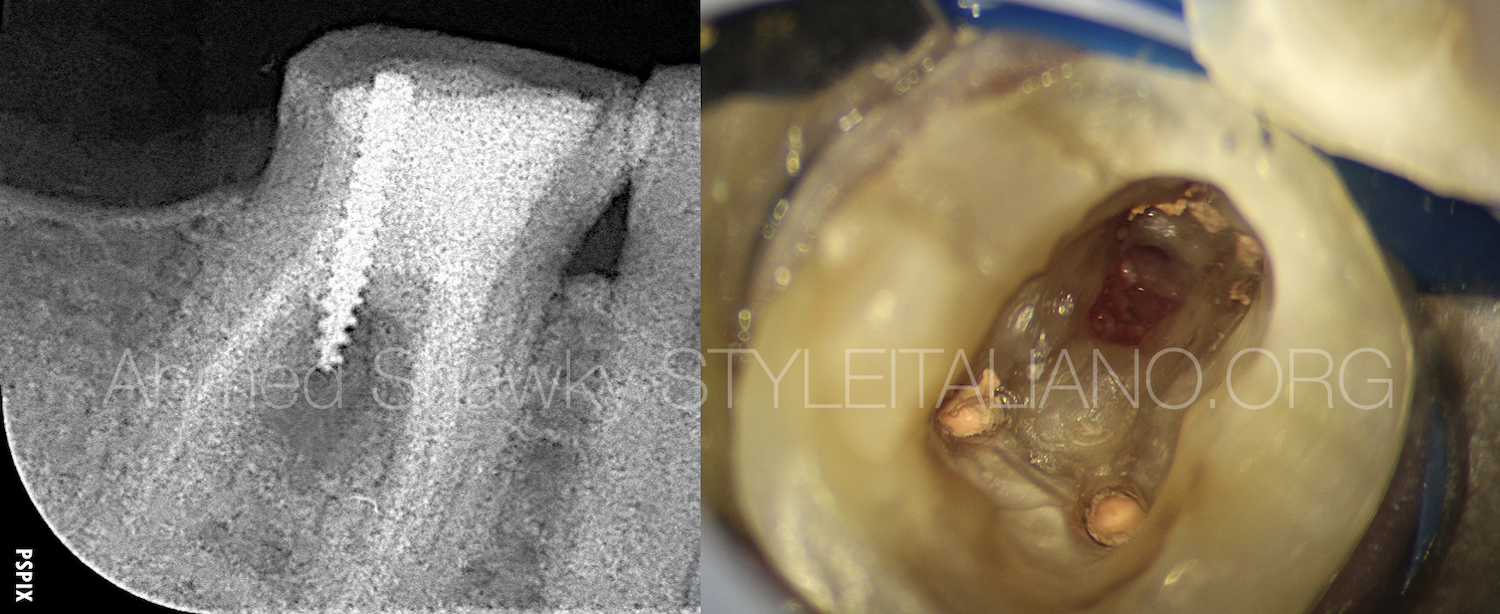 A goal in the hole
A goal in the hole
The main goal of endodontic treatment is the treatment and/or prevention of peri-radicular periodontitis aiming for a long term disease-free survival. The presence of any form of communication between the […]
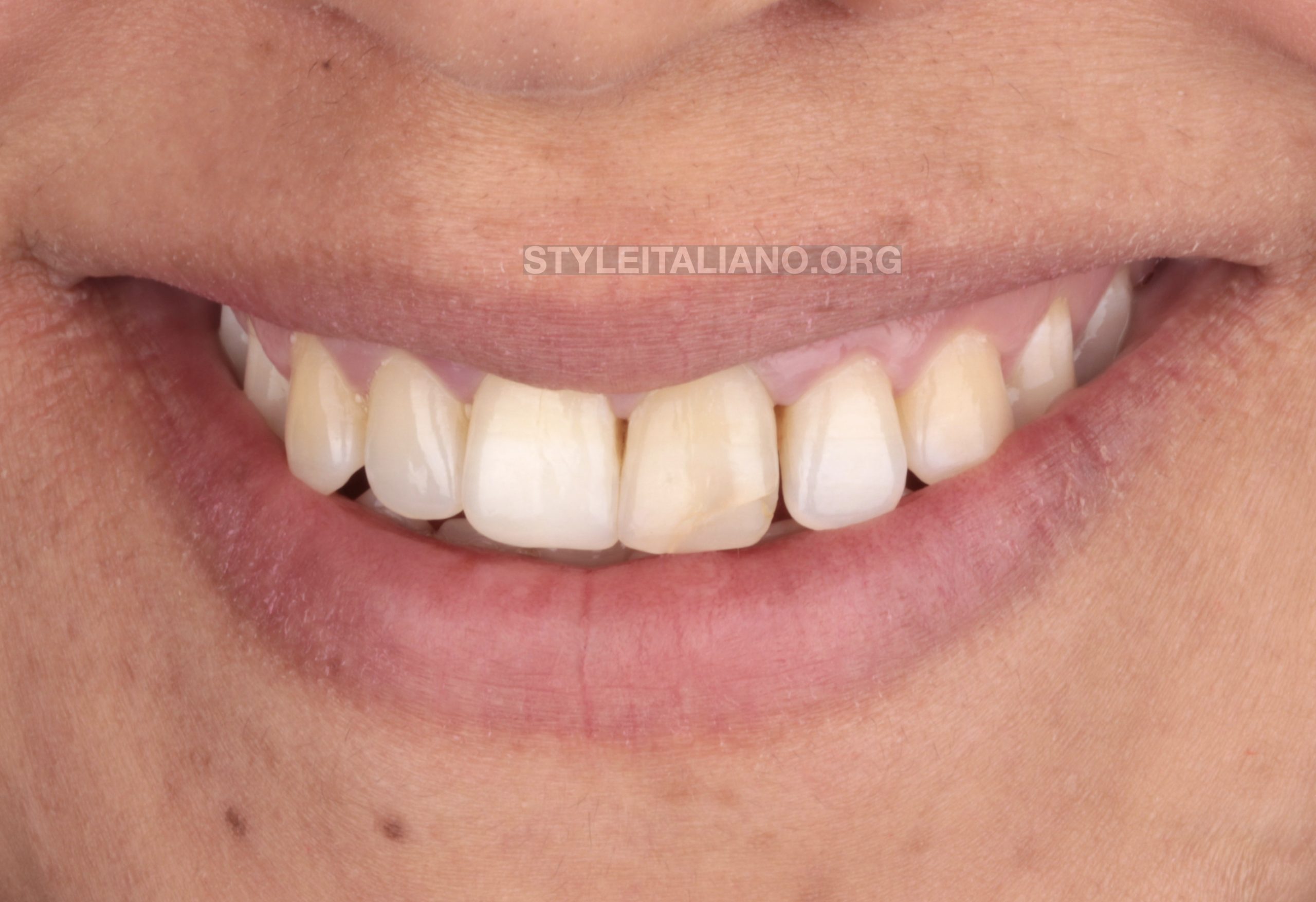
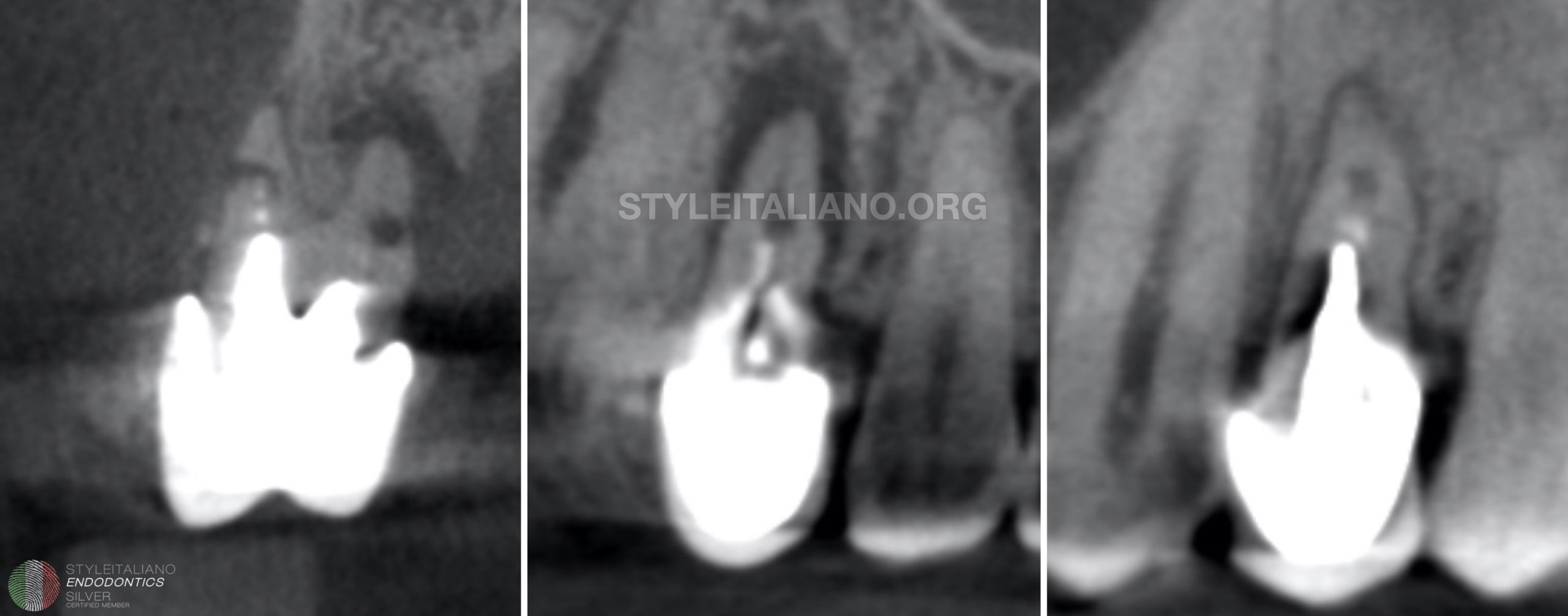 Necrodontics - saving hopeless teeth
Necrodontics - saving hopeless teeth
Both non-surgical and surgical retreatment procedures are performed when the primary treatment fails and we are trying to preserve the tooth. Usually the next attempt after the primary treatment is […]
 Three Years Follow-up of Large Lesion Treated With MTA Apical Plug
Three Years Follow-up of Large Lesion Treated With MTA Apical Plug
The goal of Endodontic treatment is to cure or prevent apical periodontitis (Ørstavik & Pitt Ford 2008). Endodontic treatment does not end when the root canal being filled, but when […]
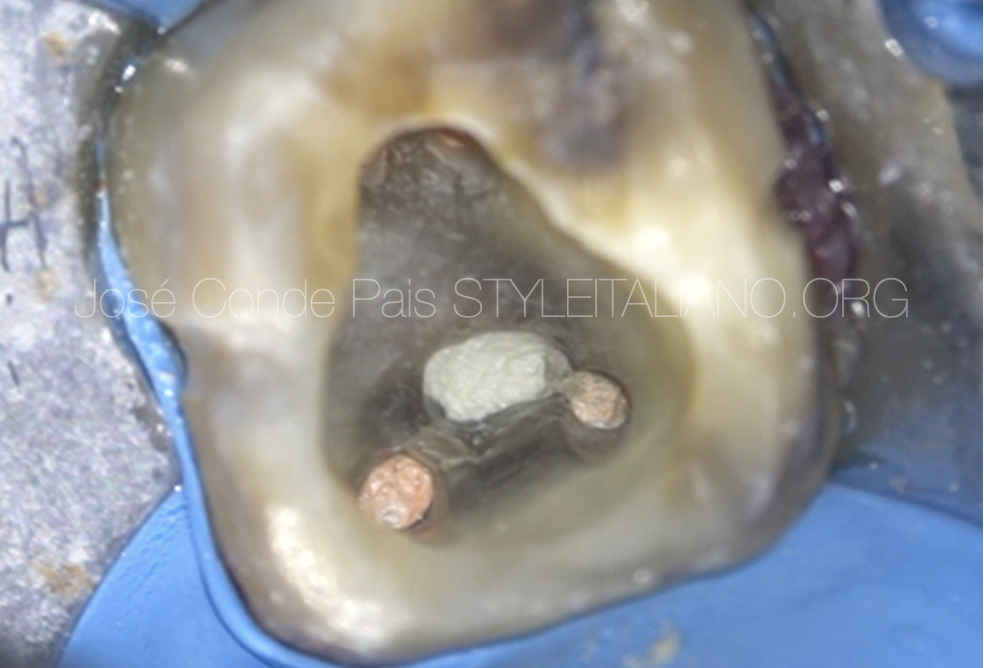 Management of Iatrogenic Furcal Perforation in tooth with obliterated root canal
Management of Iatrogenic Furcal Perforation in tooth with obliterated root canal
Perforation is a pathologic or iatrogenic communication between root canal system and the supporting tissues of teeth or the oral cavity. Root perforations are common complications of endodontic treatment or […]