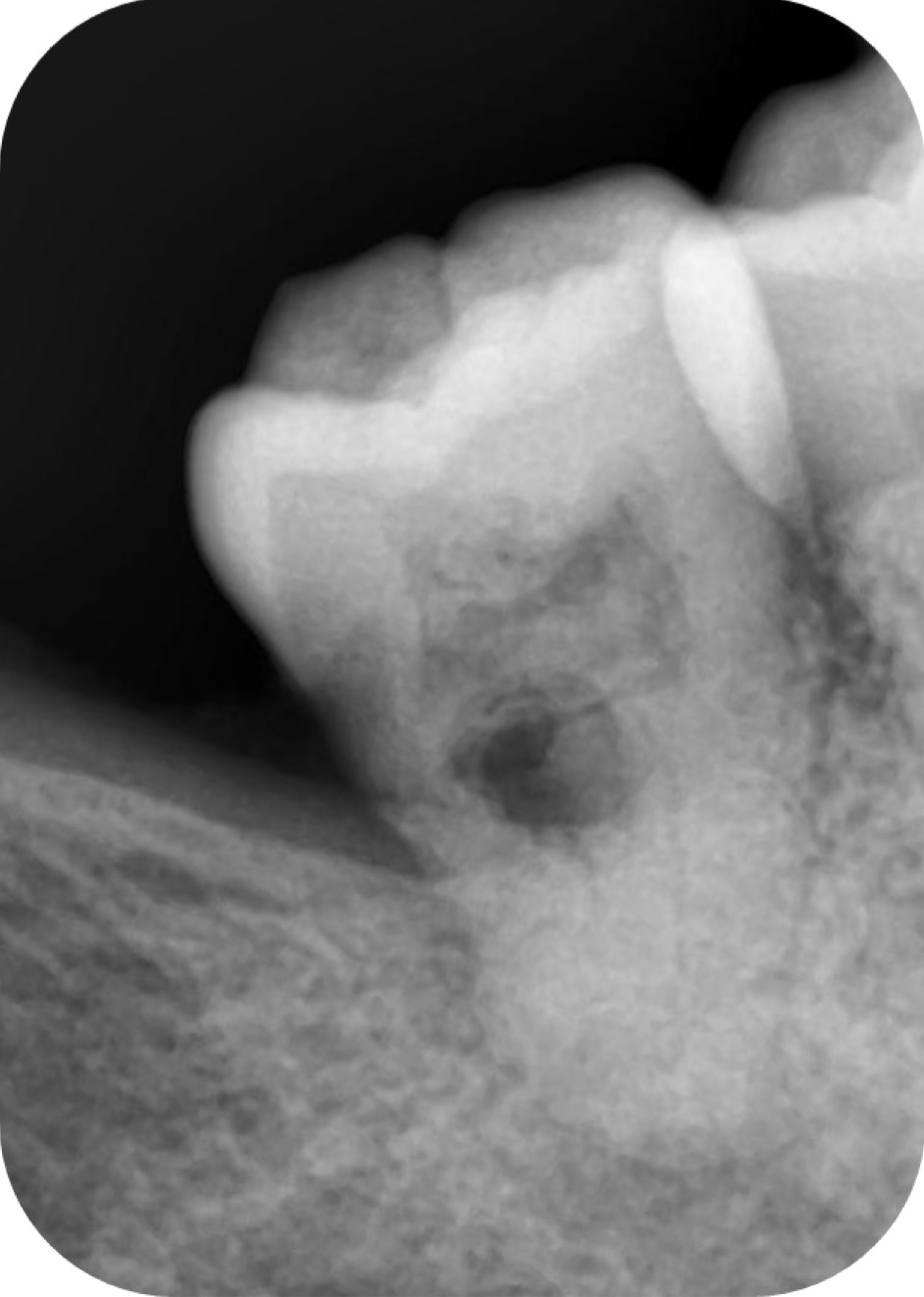
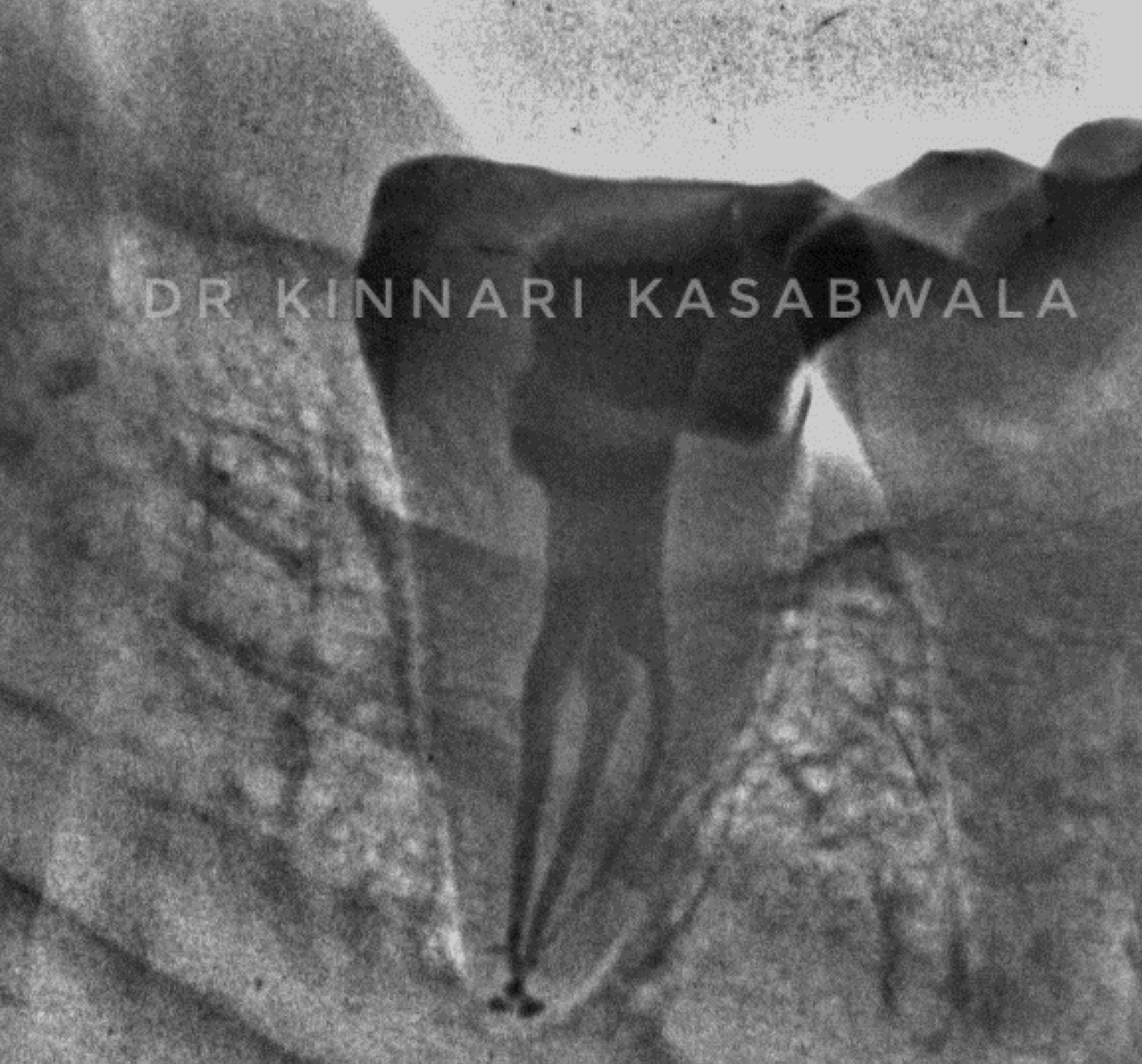
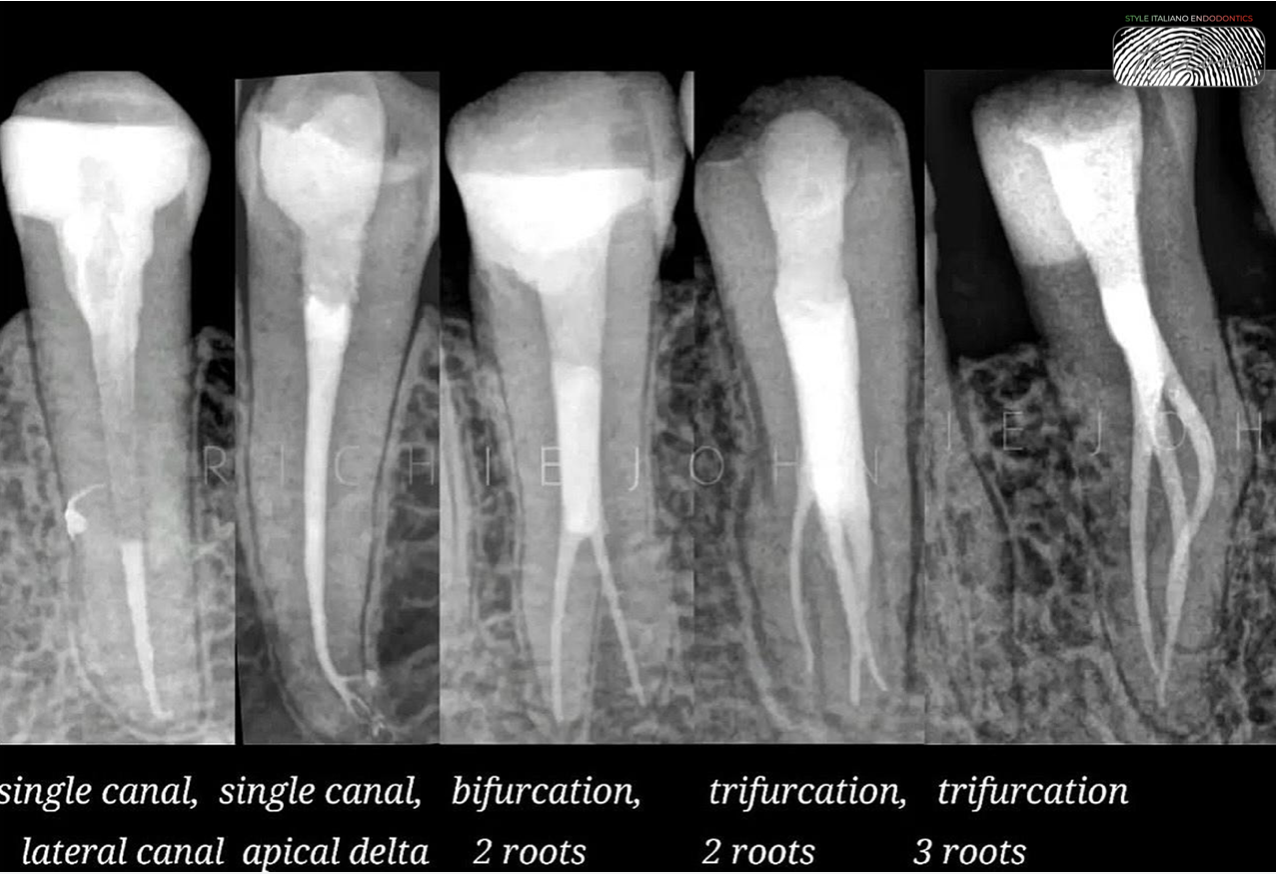
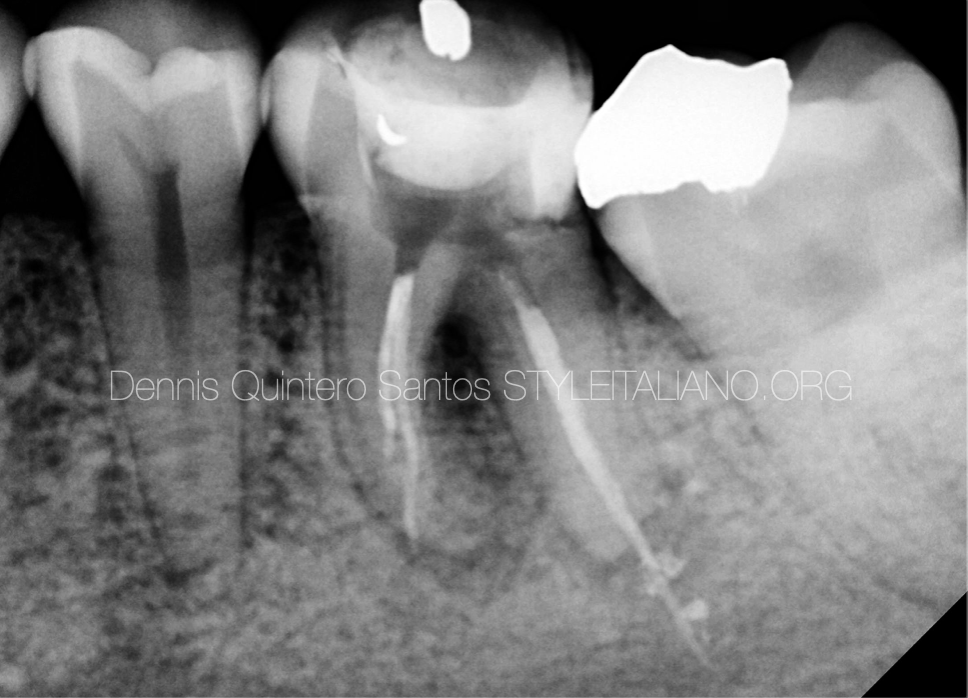
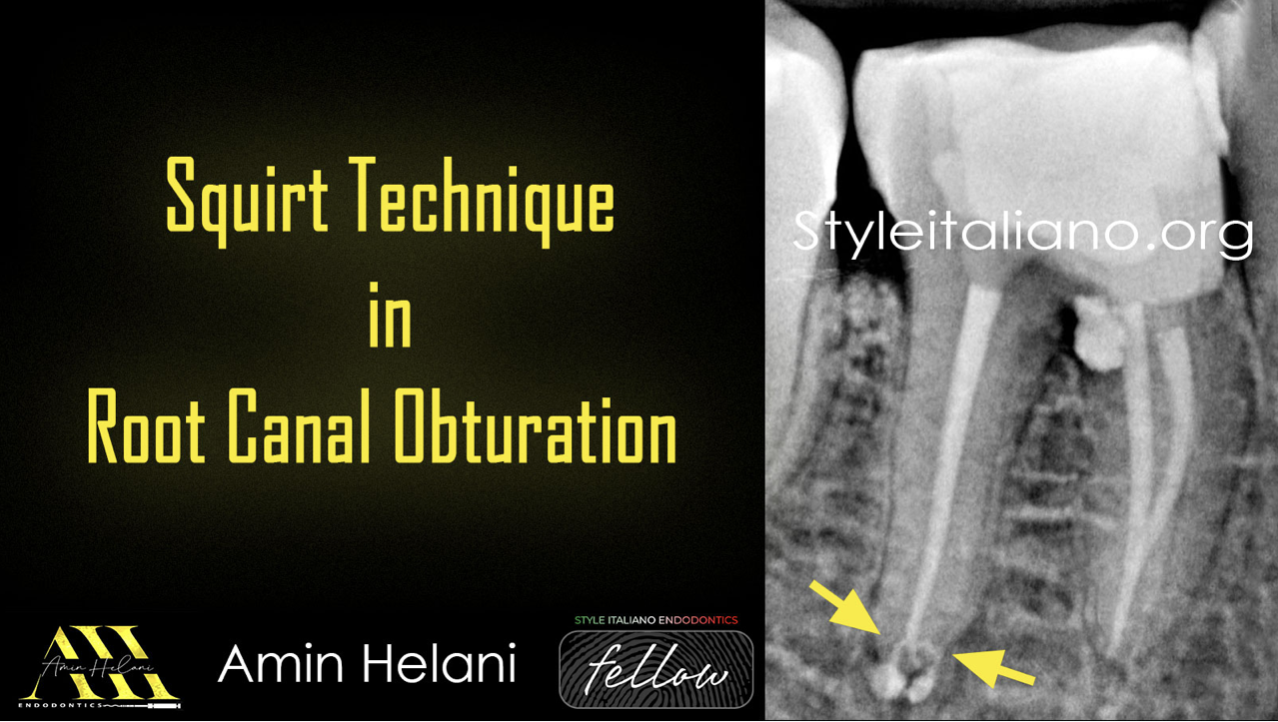
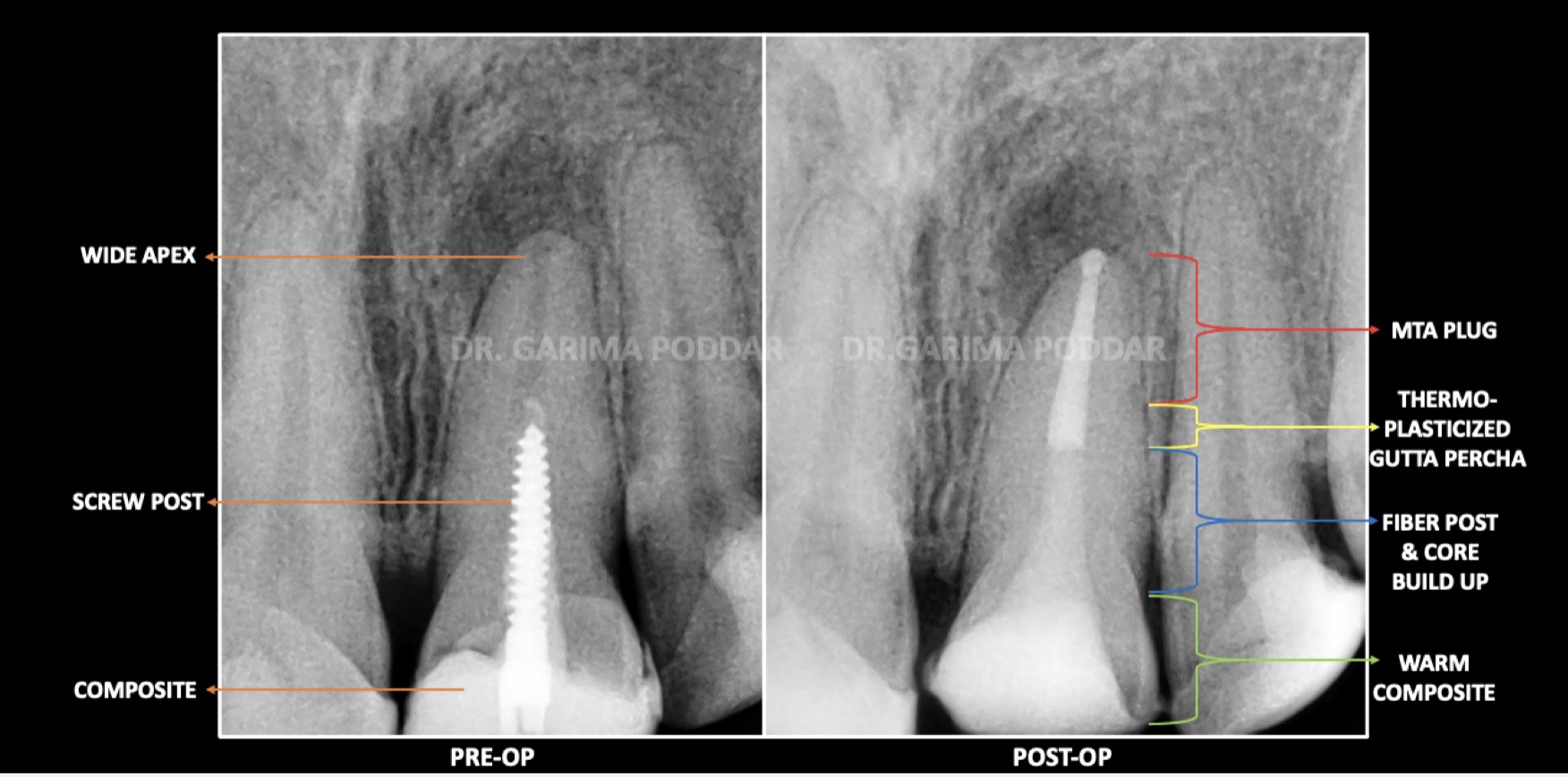
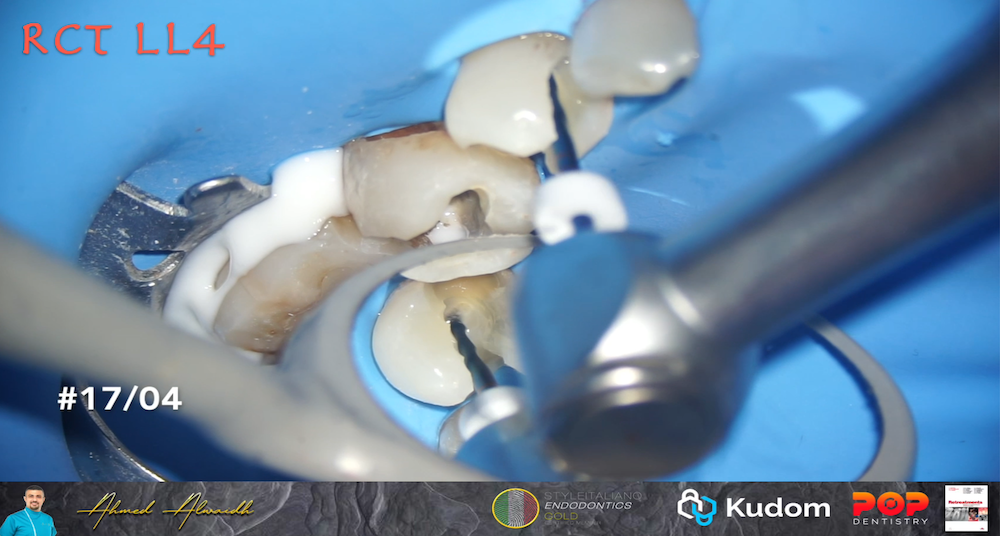
In Endodontics, while managing curved canals , an exception to dealing with the intricate canal system could be when using advanced technology like rotary instruments or nickel-titanium files.
These tools can help simplify the process by efficiently cleaning and shaping the canals, making it easier to navigate through complex canal anatomy.
By utilizing such modern techniques, Endodontist can overcome the challenges posed by intricate canal systems more effectively.