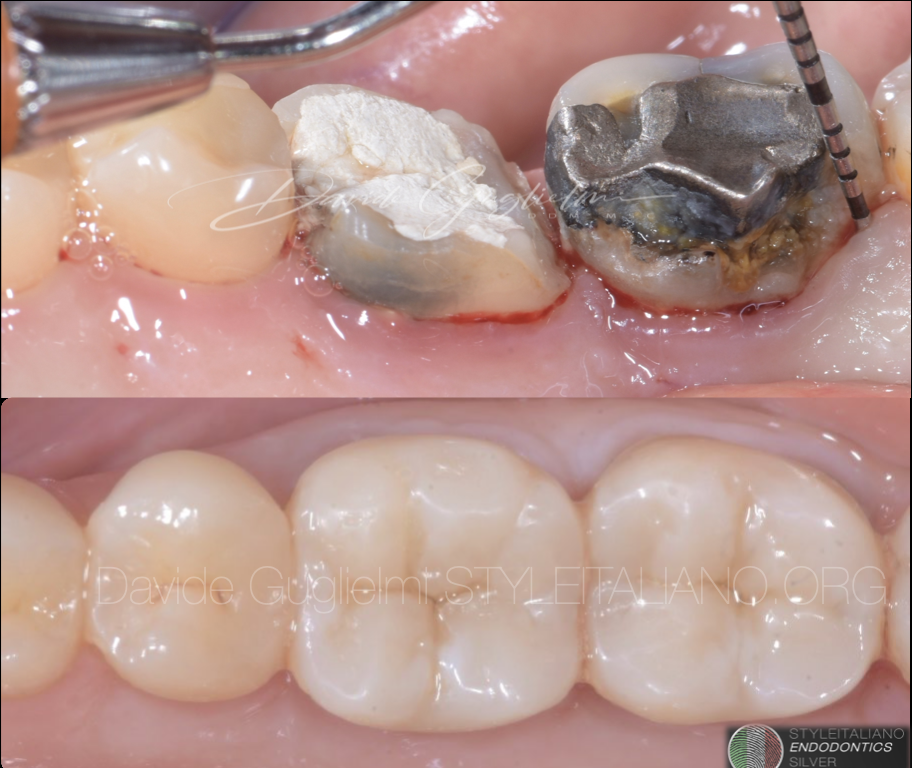
The patient, 72, had these crowns a few years earlier and had no desire to remove them. Tooth 4.5 had already been treated, but it was the only one that […]
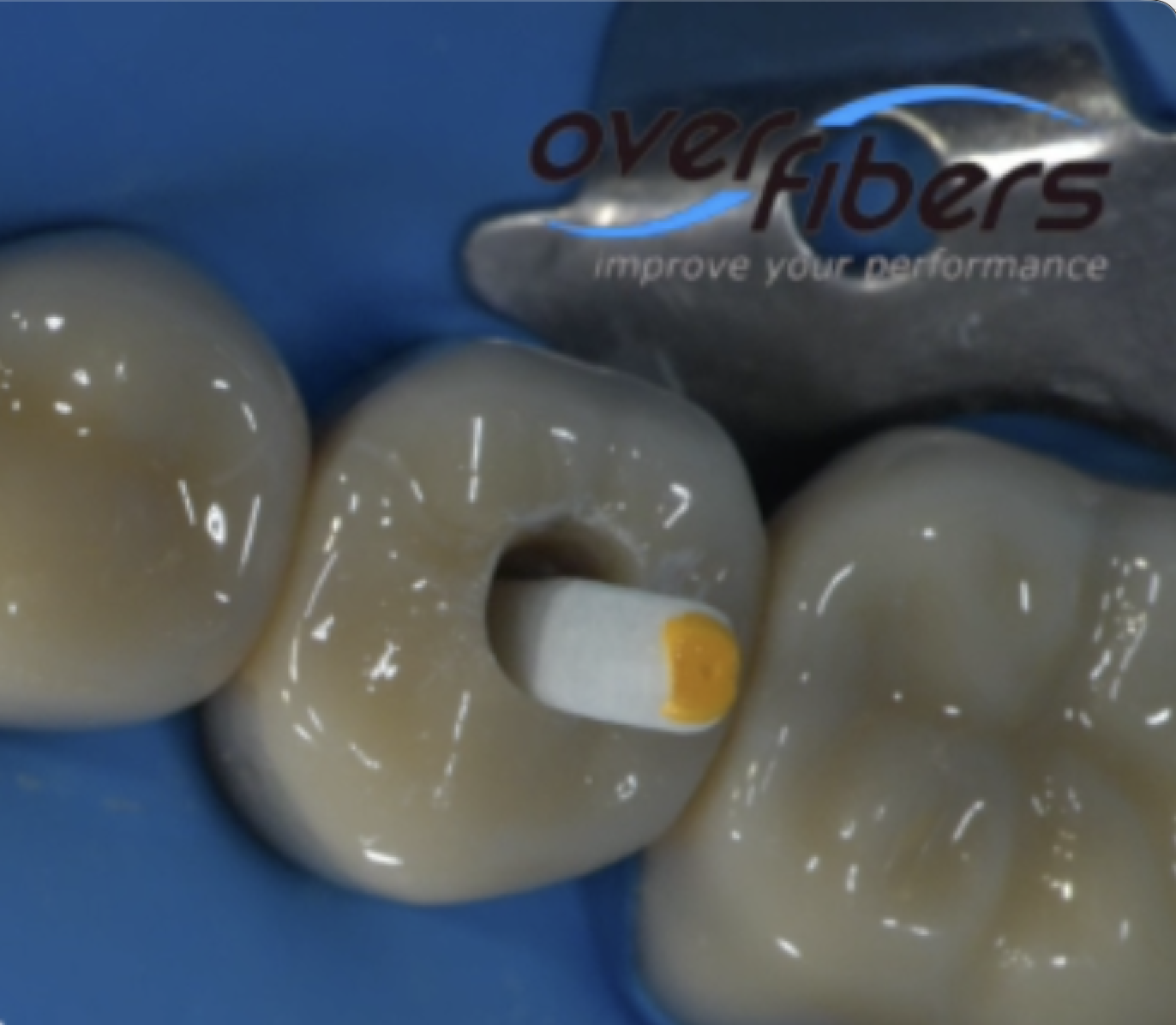 Retreatment through a crown
Retreatment through a crown
The patient, 72, had these crowns a few years earlier and had no desire to remove them. Tooth 4.5 had already been treated, but it was the only one that […]
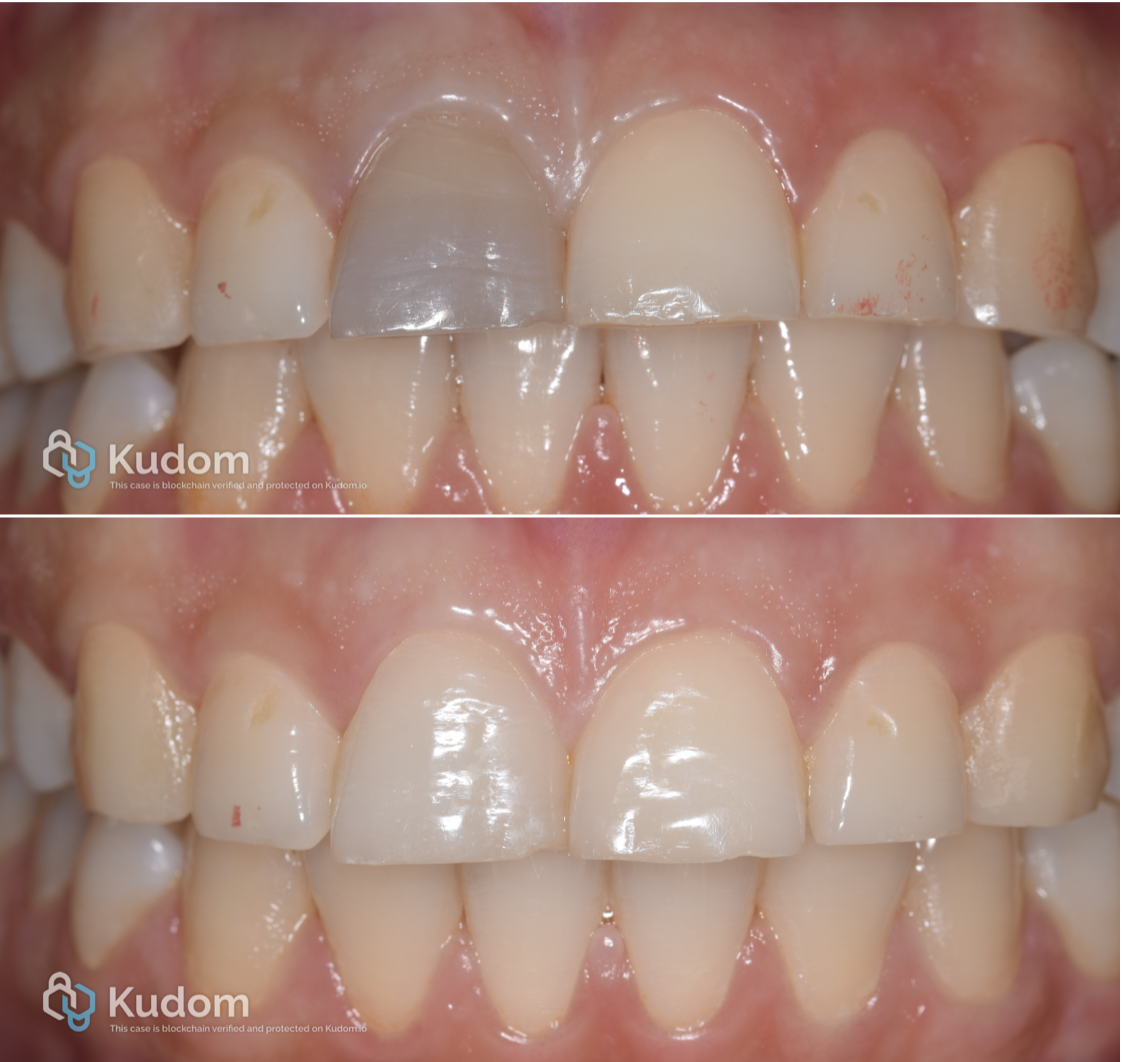 Internal Bleaching as a Conservative Alternative to Veneers in Root Canal-Treated Tooth
Internal Bleaching as a Conservative Alternative to Veneers in Root Canal-Treated Tooth
This article discusses the use of internal bleaching as a conservative and effective esthetic solution for discolored, root canal–treated teeth. It highlights the clinical protocol, indications, and advantages of internal bleaching as an alternative to veneers, preserving natural tooth structure while achieving satisfactory esthetic outcomes.
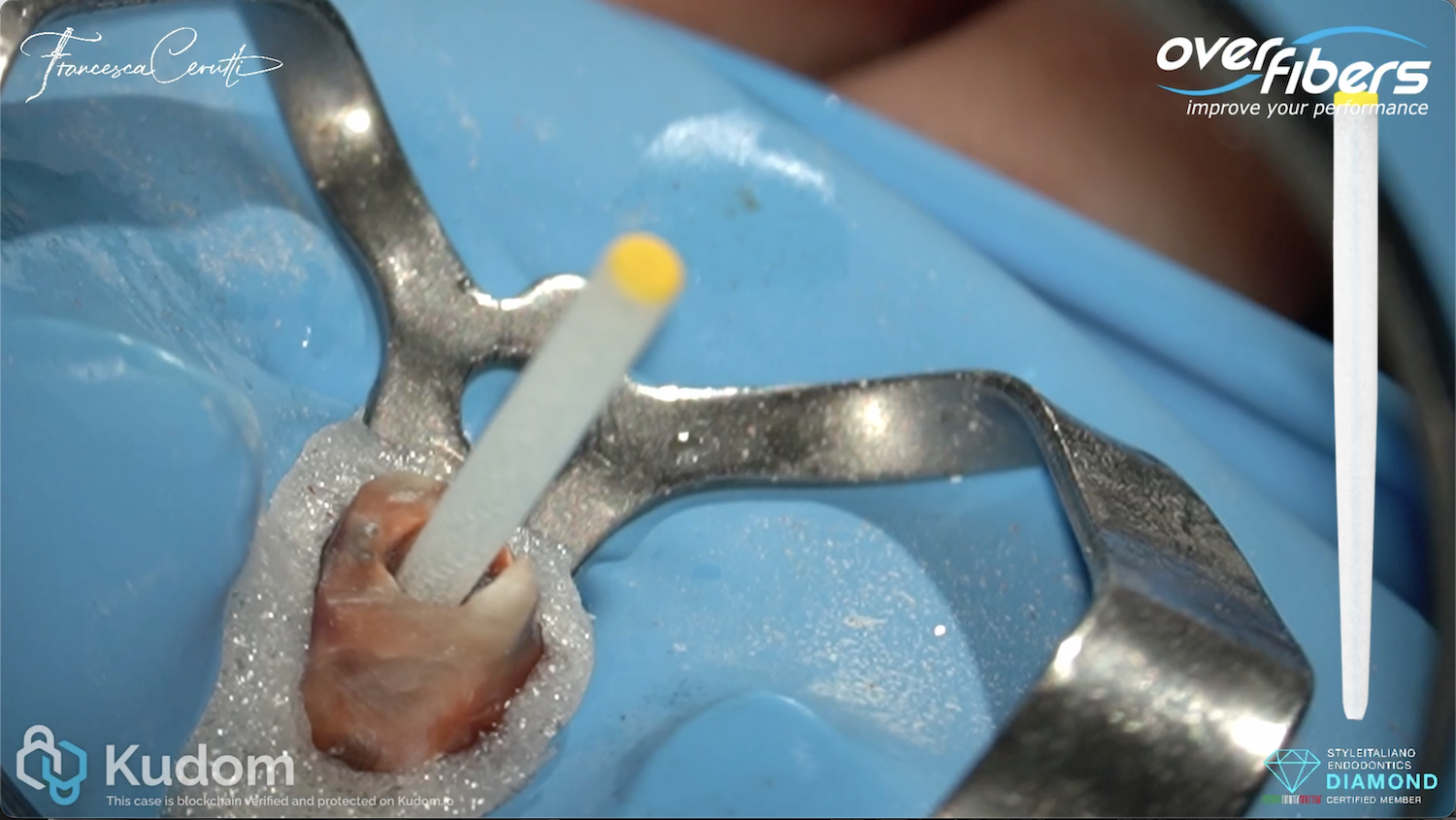 Retreatment and post-retained restoration in a central incisor
Retreatment and post-retained restoration in a central incisor
When a tooth has undergone root canal treatment and has lost a large amount of coronal structure, the restorative challenge is not only to replace missing tissue, but to recover […]
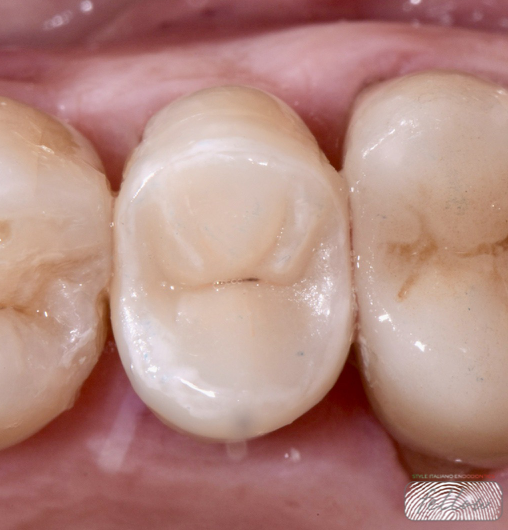
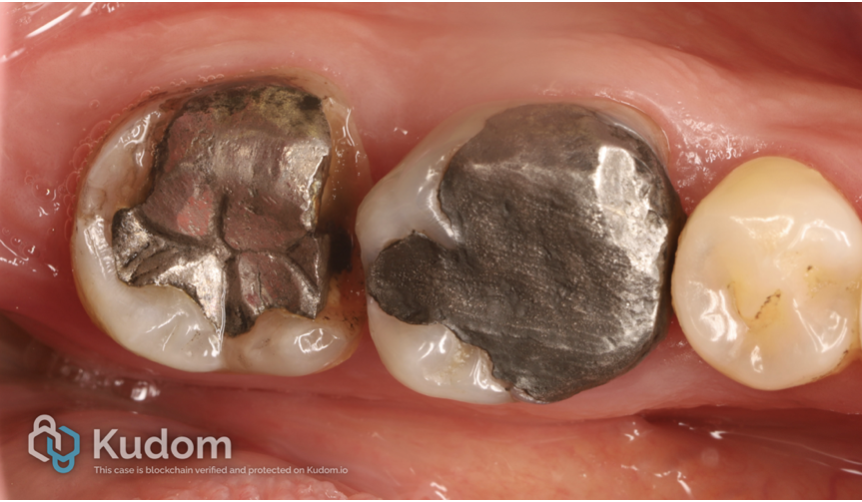 Endo-resto management of two molars with failed old large amalgam restoration
Endo-resto management of two molars with failed old large amalgam restoration
Combining precise endodontic treatment with biomimetic restorations preserves tooth structure, restores function, and enhances long-term survival.
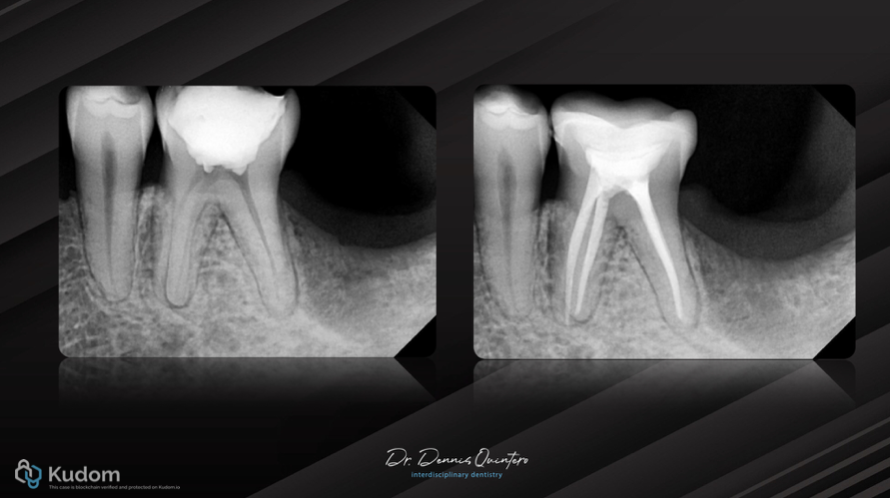
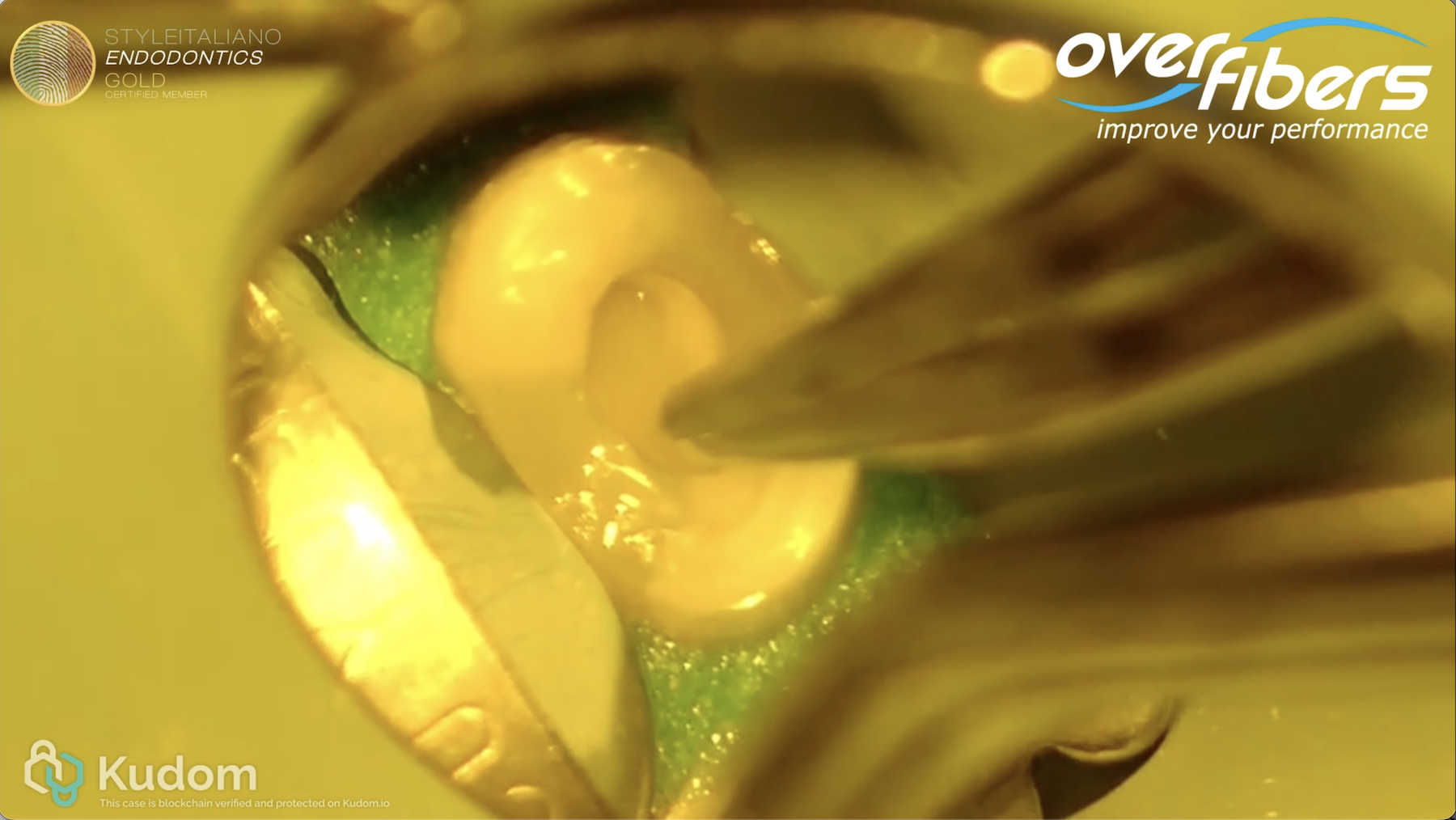 Overpost restoration of tooth 25
Overpost restoration of tooth 25
A 47-year-old female patient presented with a structurally compromised maxillary left second premolar (tooth 25) following completed endodontic treatment. Due to the significant loss of coronal tooth structure, a post-endodontic […]
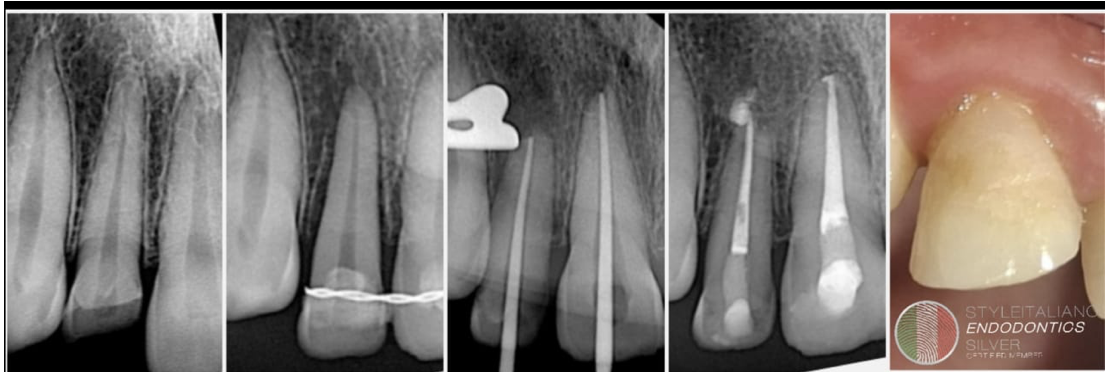
 Endodontic–restorative management of a periapical lesion involving tooth 25: diagnosis, treatment, and clinical outcome
Endodontic–restorative management of a periapical lesion involving tooth 25: diagnosis, treatment, and clinical outcome
Endodontic–restorative management of tooth 25 with periapical lesion: confirmed necrosis and 11 -months radiographic healing.
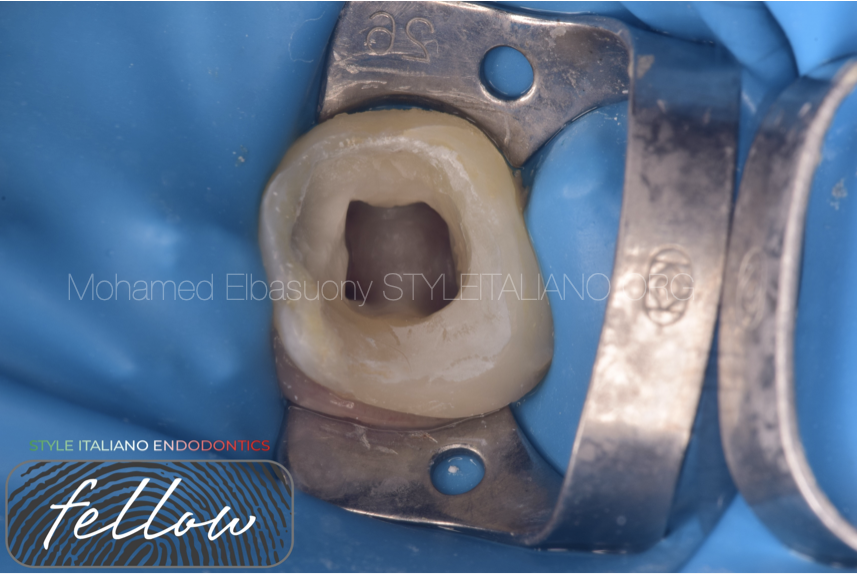
 Primary Endo treatment & final restoration
Primary Endo treatment & final restoration
The success of Endodontic treatment relies not only on the proper cleaning and disinfection of the root canal but also in the adequate restoration of the treated tooth. A well […]
 Surgical Extrusion of upper lateral incisor with oblique fracture
Surgical Extrusion of upper lateral incisor with oblique fracture
Crown-root fractures extending subgingivally pose significant restorative challenges and often threaten tooth preservation. Surgical extrusion is a conservative technique that repositions the remaining tooth structure coronally, facilitating optimal restorative margins while maintaining periodontal health. This case report presents the management of an upper lateral incisor with an oblique fracture treated successfully by surgical extrusion. The procedure involved atraumatic repositioning of the tooth, careful stabilization, and subsequent restoration. Follow-up demonstrated favorable periodontal healing, functional stability, and satisfactory esthetics. This case underscores the clinical value of surgical extrusion as a predictable, tooth-preserving treatment option in selected cases of complicated crown-root fractures.)
 Radix Entomolaris: Case Report with Clinical Implication
Radix Entomolaris: Case Report with Clinical Implication
Usually, first mandibular molars have one mesial and distal root but in some cases there are anatomical variations. Presence of an additional lingual root distally in mandibular molars is called radix entomolaris (RE). If present, an awareness and understanding of this unusual root and its root canal morphology can contribute to the successful outcome of root canal treatment. The article describes the endodontic management of mandibular molar with RE.
 Deep Margin Elevation and Clinical Crown Lengthening: Biological considerations and clinical procedures
Deep Margin Elevation and Clinical Crown Lengthening: Biological considerations and clinical procedures
The restoration of a severely compromised tooth represents a challenge for the clinician, not only due to a significant loss of structure of the element but also due to the invasion of the supracrestal tissue attachment, with consequent compromization of periodontal health.
The technique of deep margin elevation can be applied when the healthy margin of the tooth needing restoration is localized within the sulcular epithelium or at the level of the junctional epithelium.
On the other side, the presence of lesions of the dental element involving the space for the supracrestal connective attachment and/or the bone crest makes the surgical intervention necessary. The following article aims to describe the indications and surgical procedures for clinical crown lengthening from a biological, periodontal and biomechanical point of view.
Therefore, the operational steps of the clinical crown lengthening surgical procedure (bone-resective surgery) and the sub- sequent endodontic/restorative clinical phases will be illustrated.
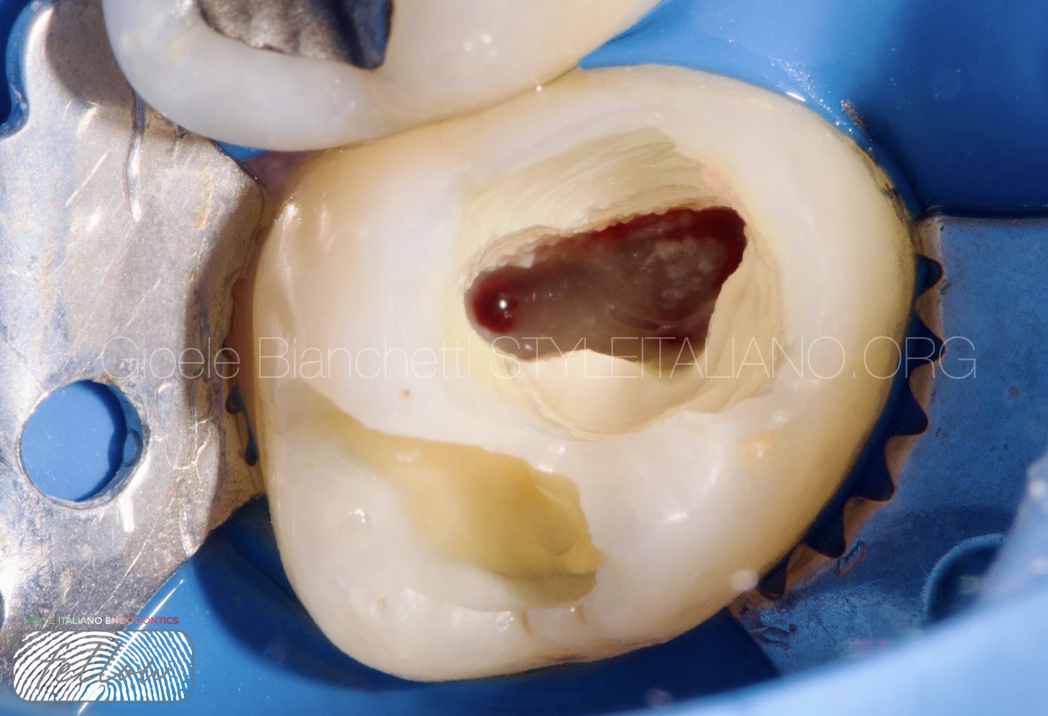 Single session endo resto treatment of an upper second molar
Single session endo resto treatment of an upper second molar
A smooth workflow in endodontics and restorative starts from the application of a strict protocol