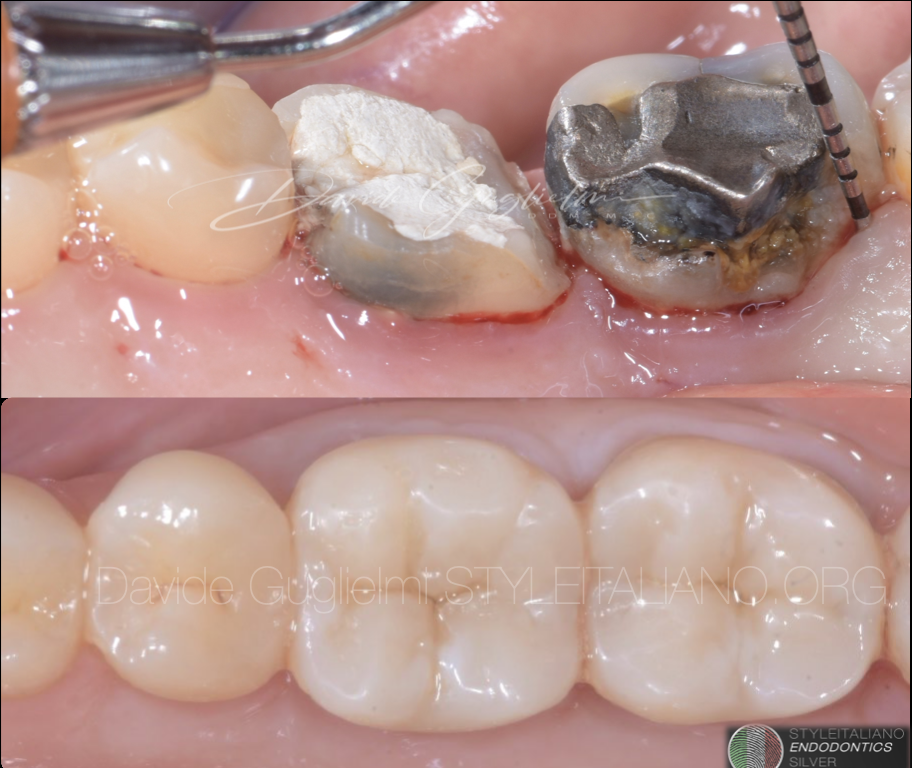
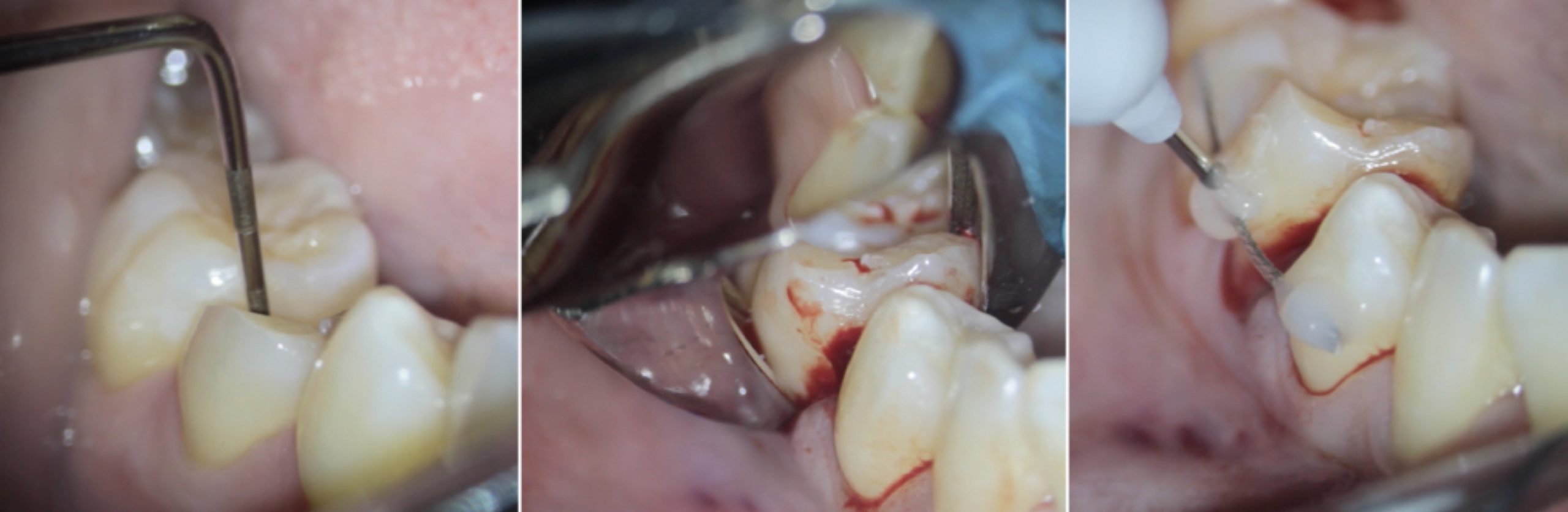
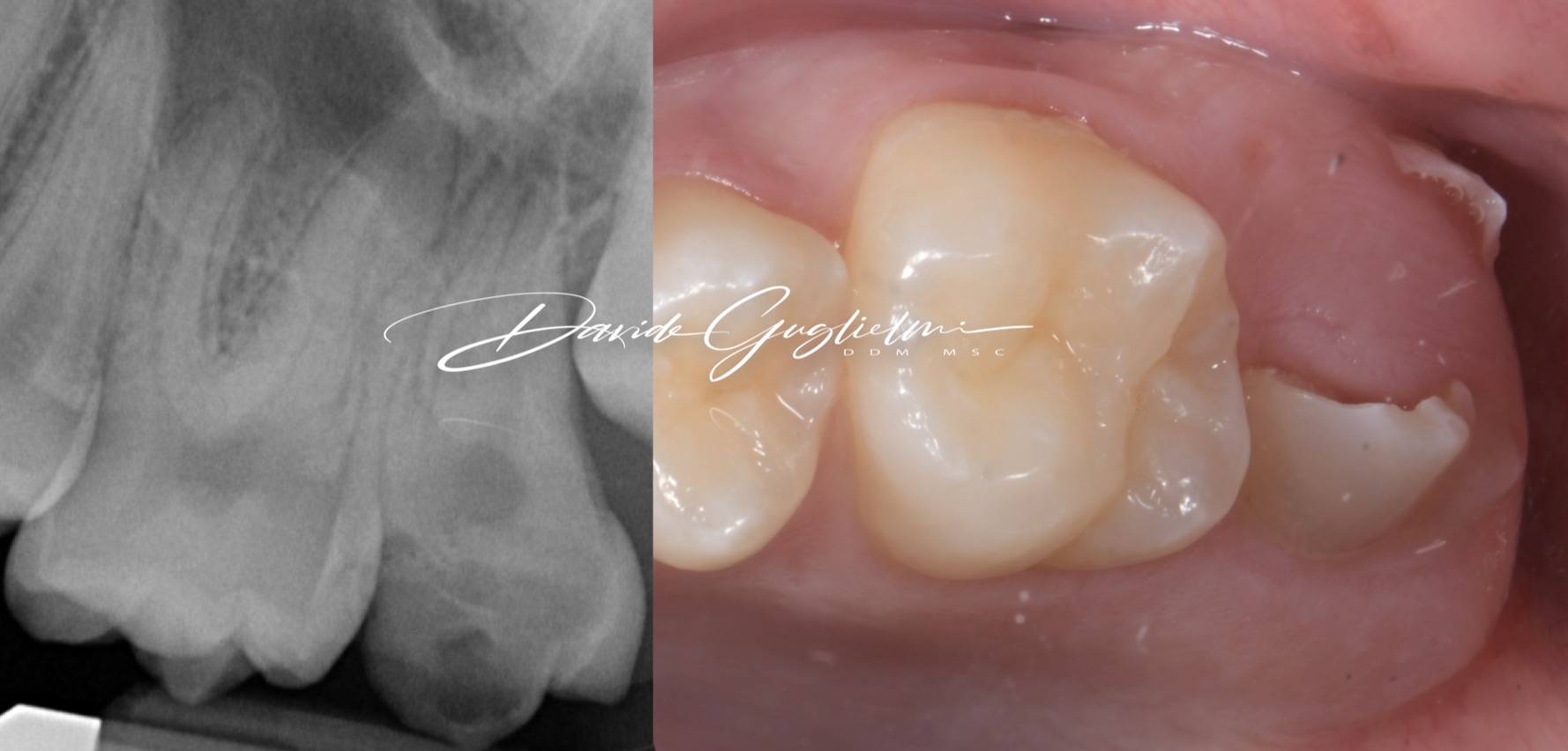
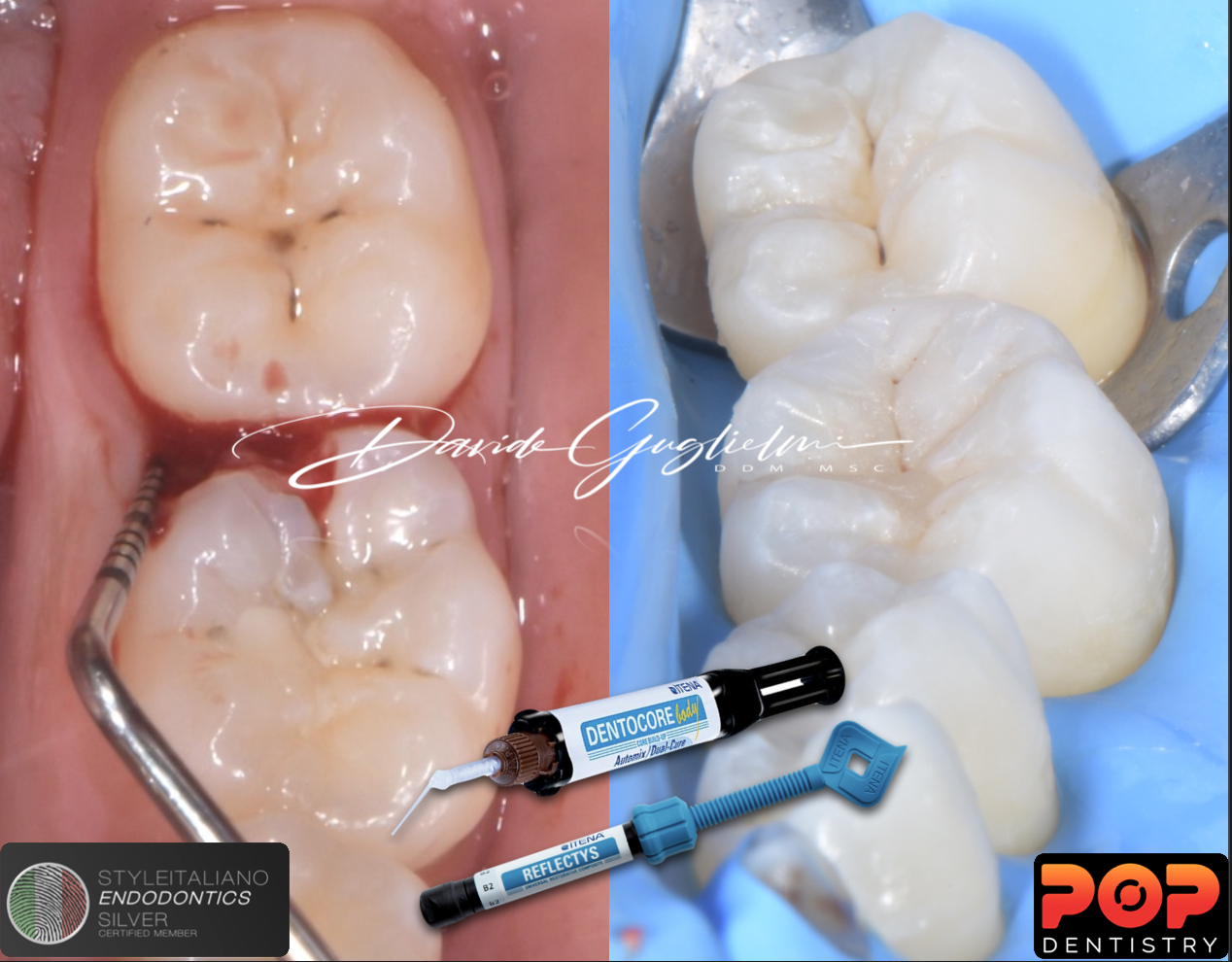
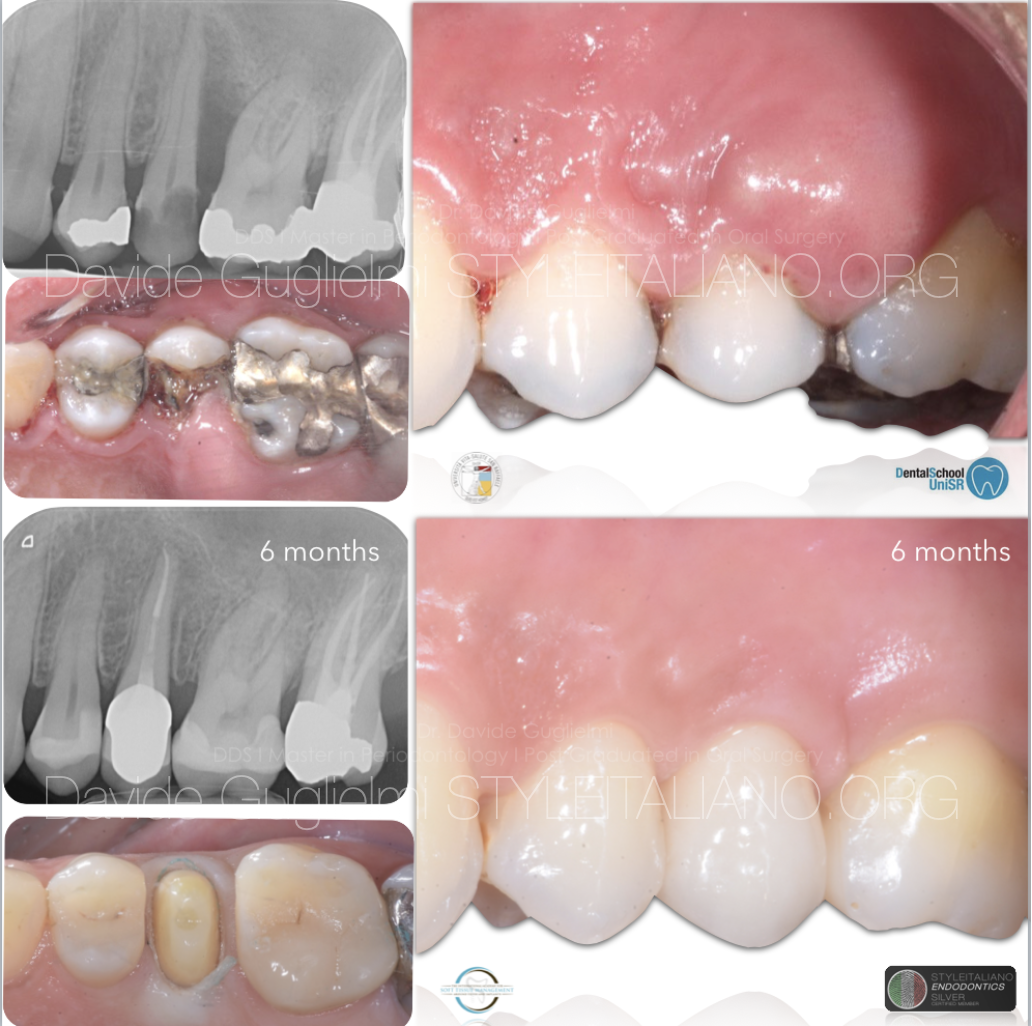
The restoration of a severely compromised tooth represents a challenge for the clinician, not only due to a significant loss of structure of the element but also due to the invasion of the supracrestal tissue attachment, with consequent compromization of periodontal health.
The technique of deep margin elevation can be applied when the healthy margin of the tooth needing restoration is localized within the sulcular epithelium or at the level of the junctional epithelium.
On the other side, the presence of lesions of the dental element involving the space for the supracrestal connective attachment and/or the bone crest makes the surgical intervention necessary. The following article aims to describe the indications and surgical procedures for clinical crown lengthening from a biological, periodontal and biomechanical point of view.
Therefore, the operational steps of the clinical crown lengthening surgical procedure (bone-resective surgery) and the sub- sequent endodontic/restorative clinical phases will be illustrated.