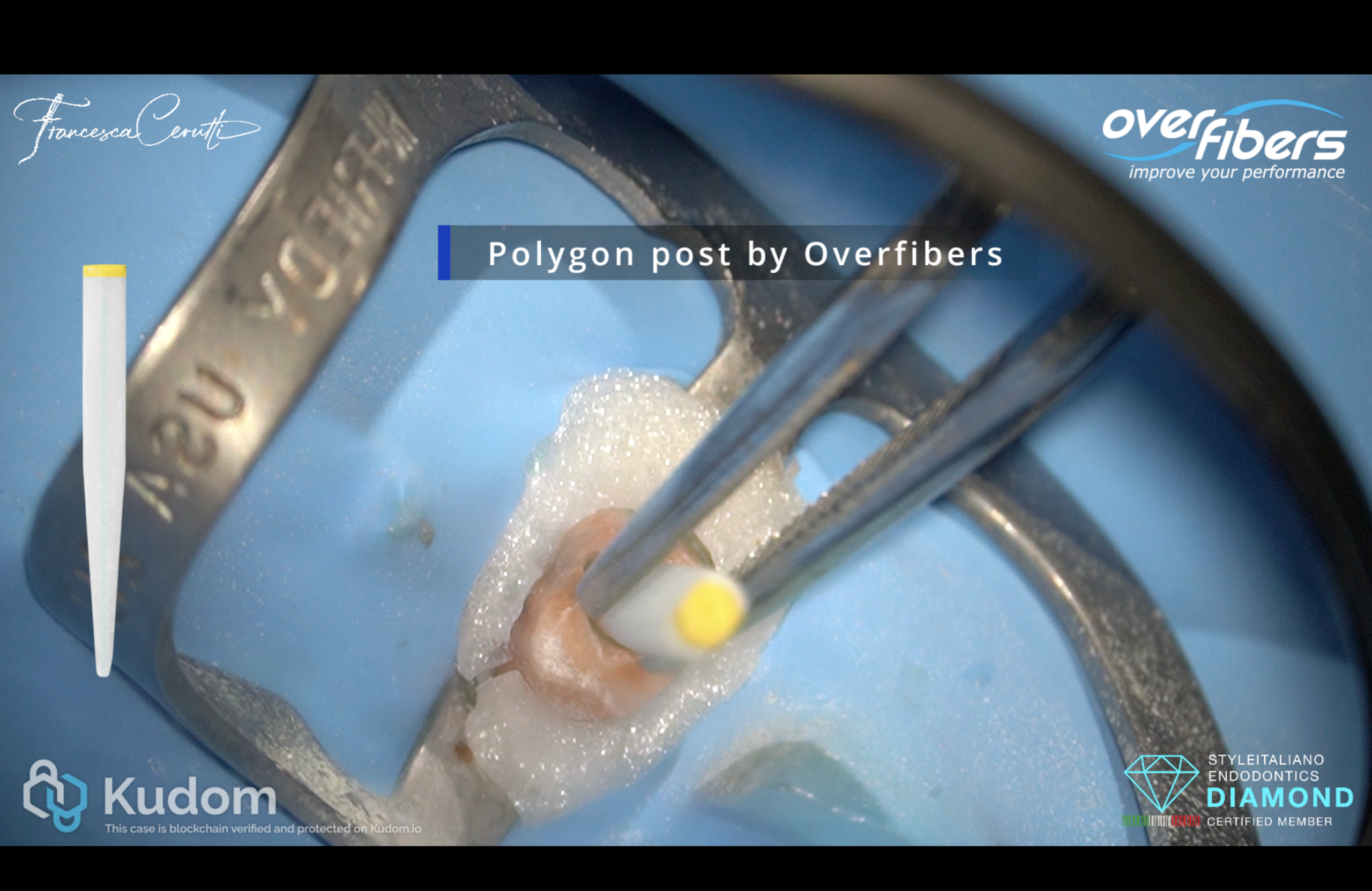
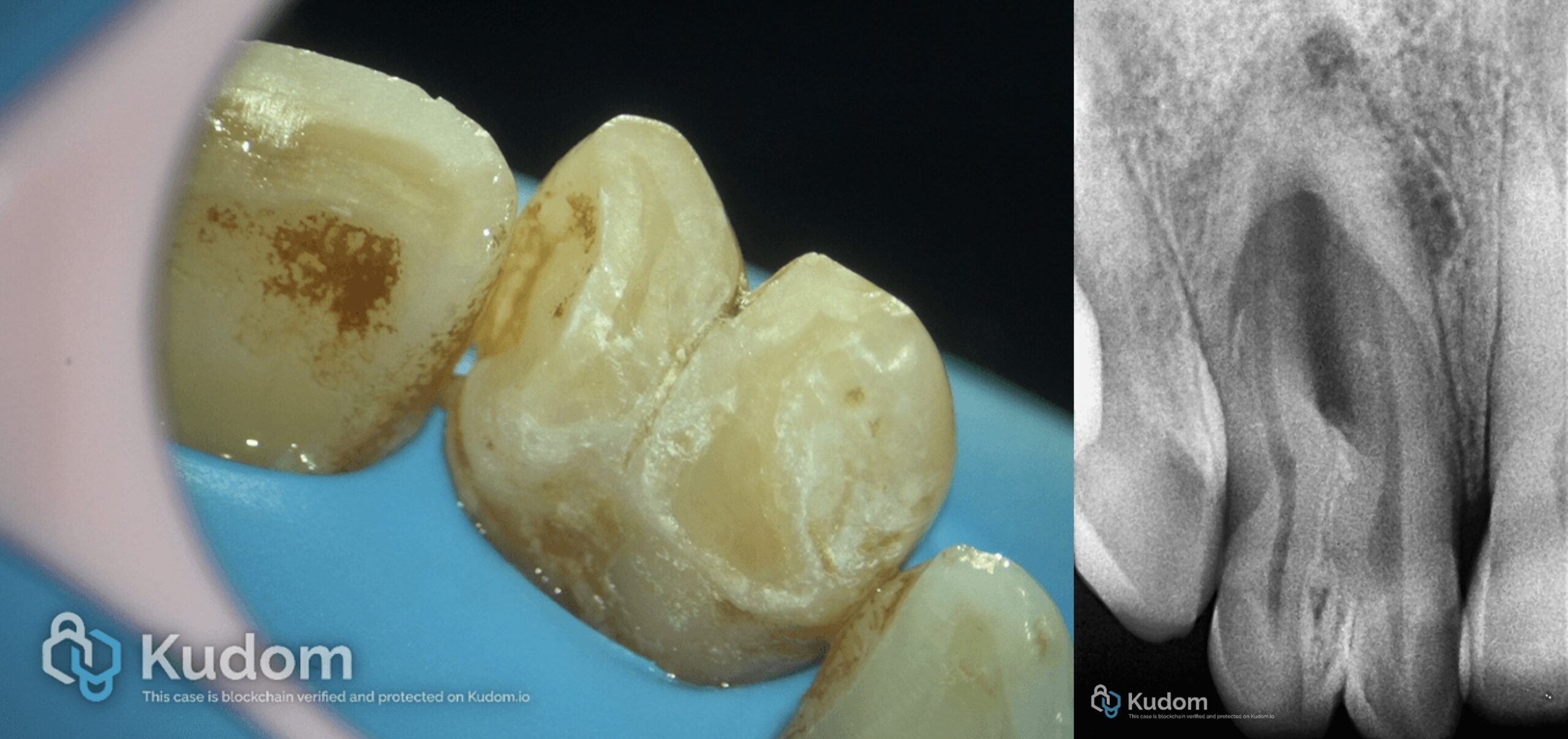
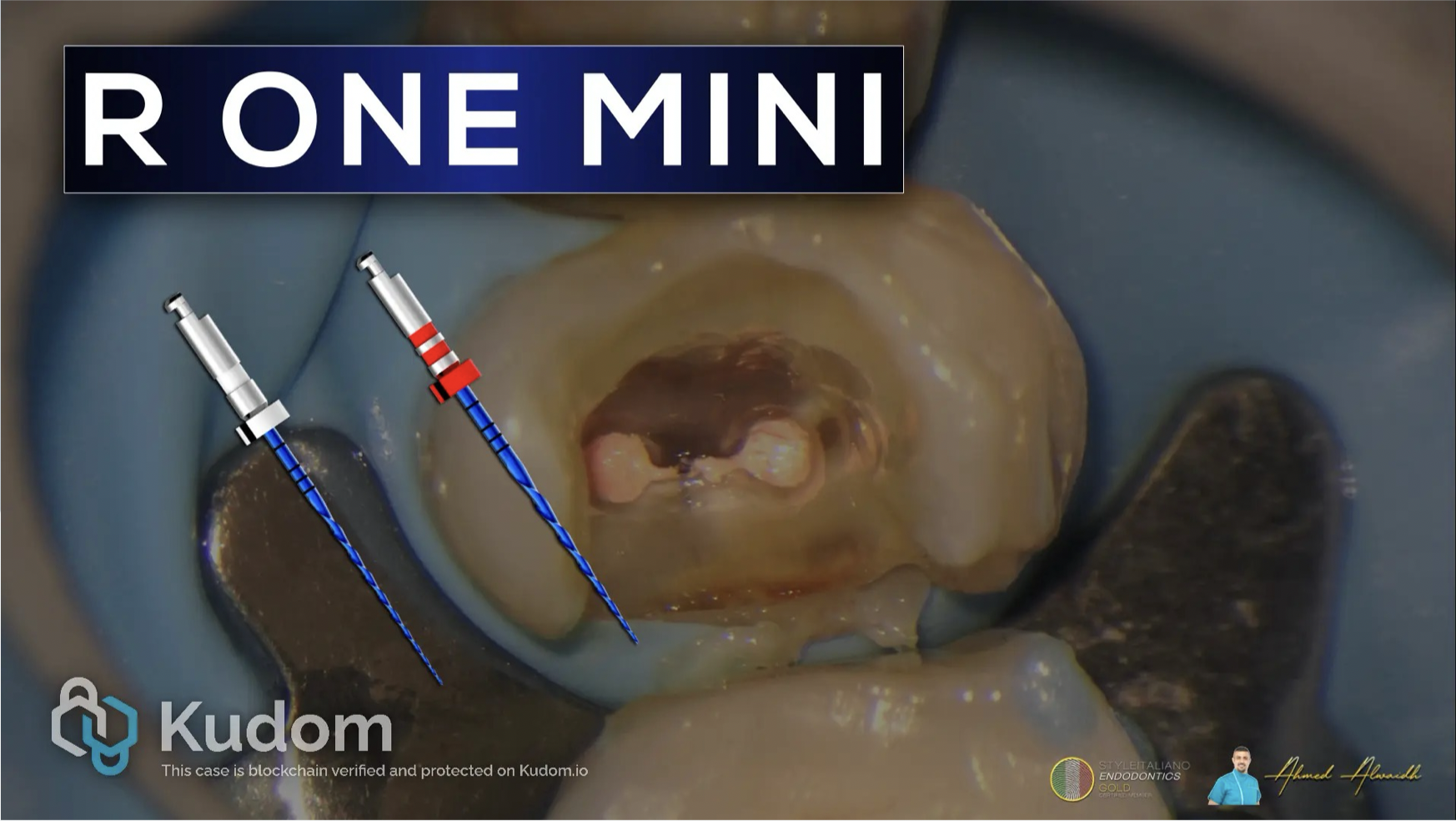
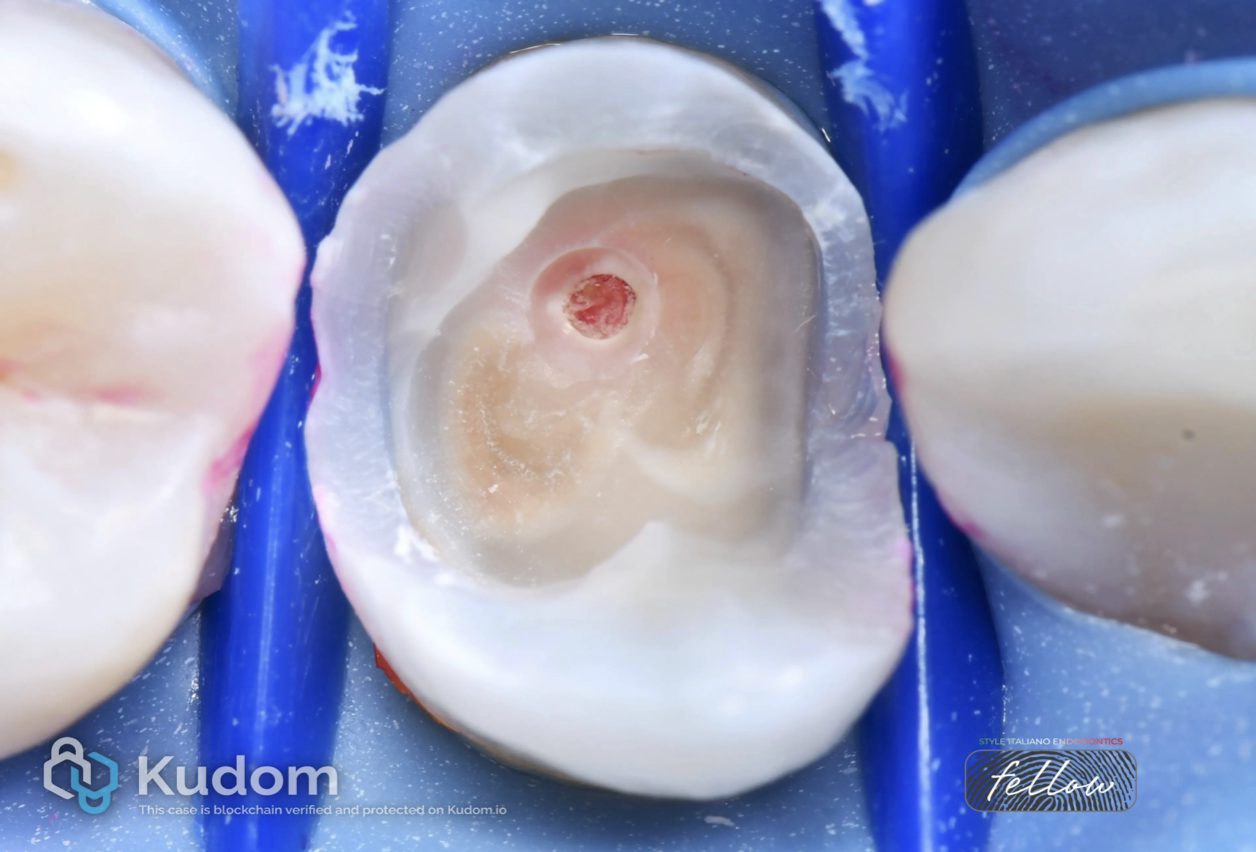
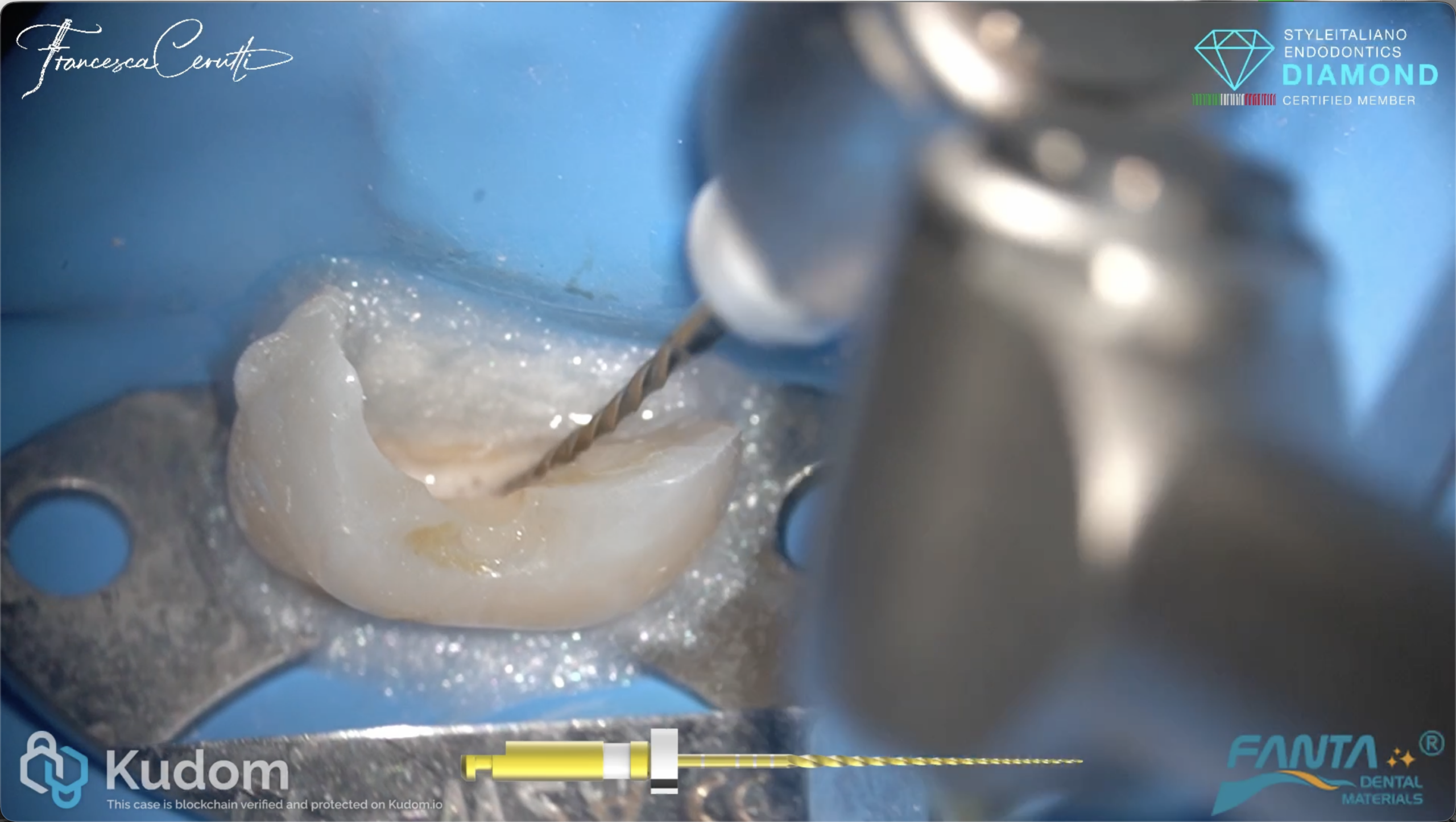
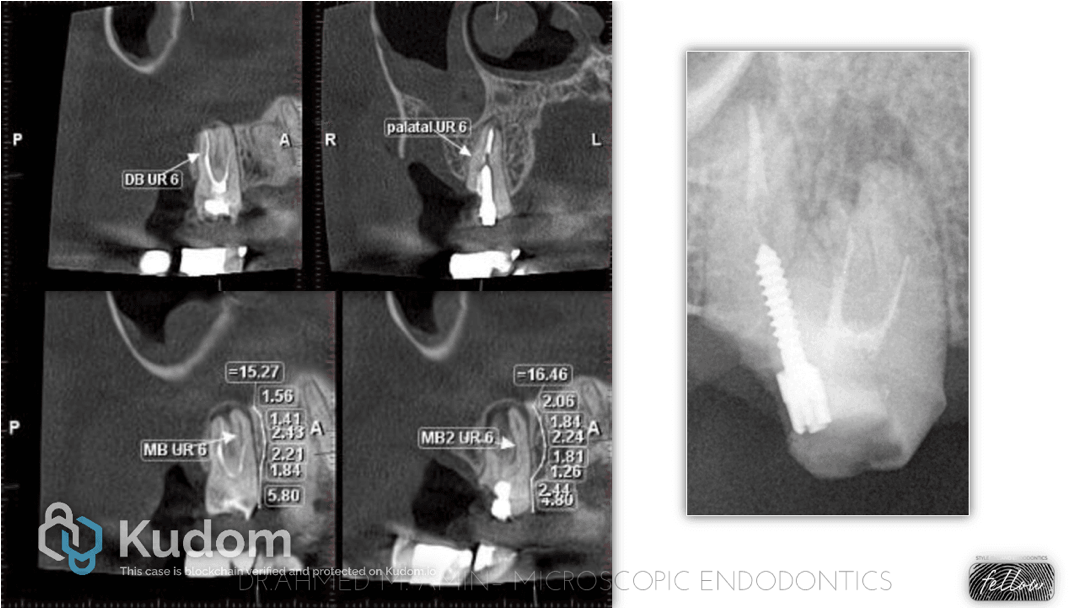
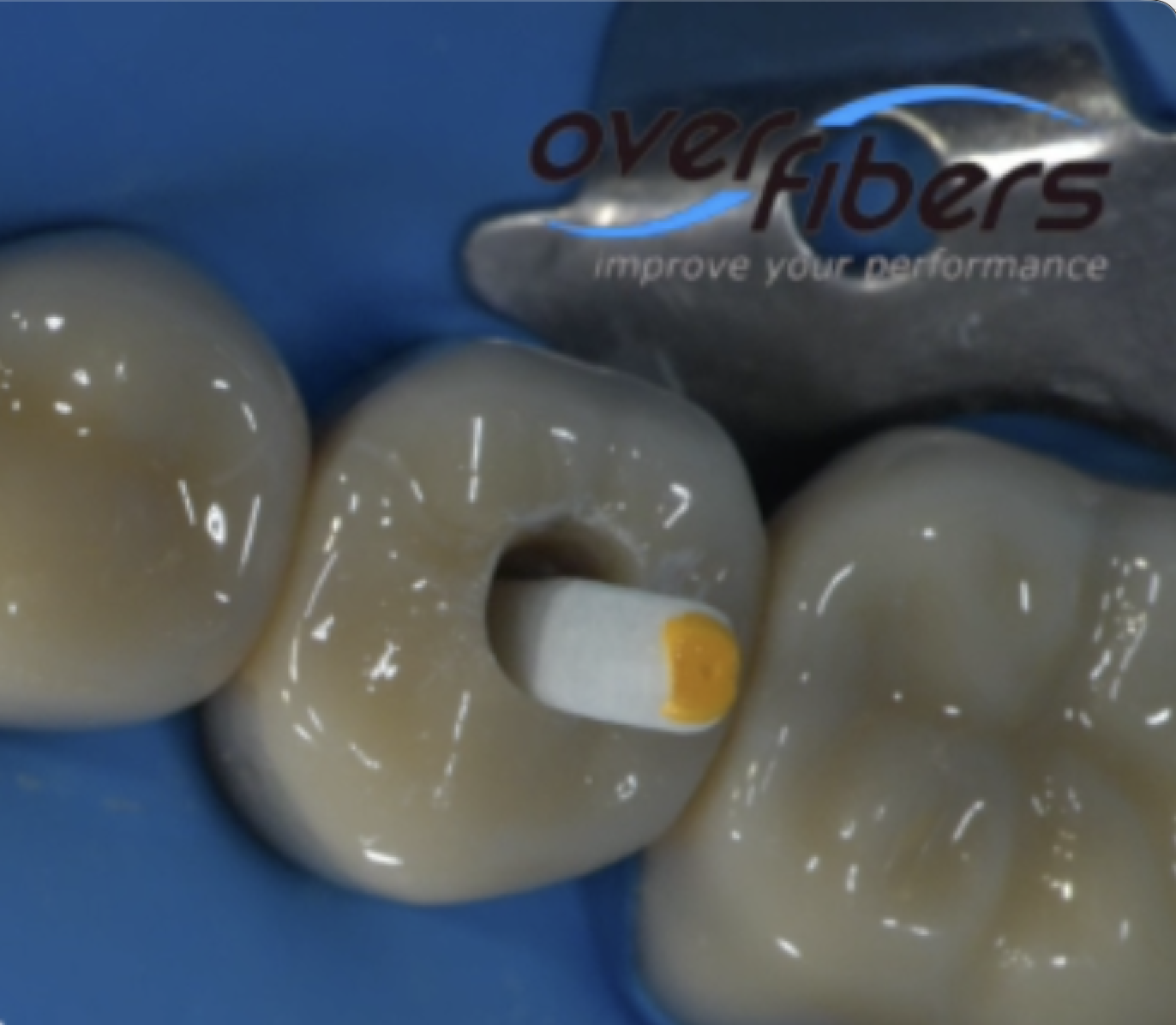
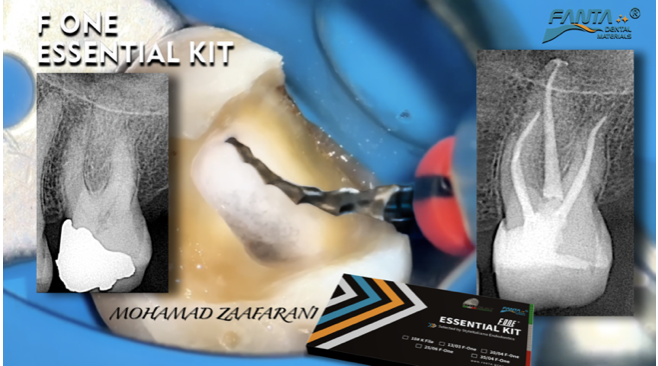
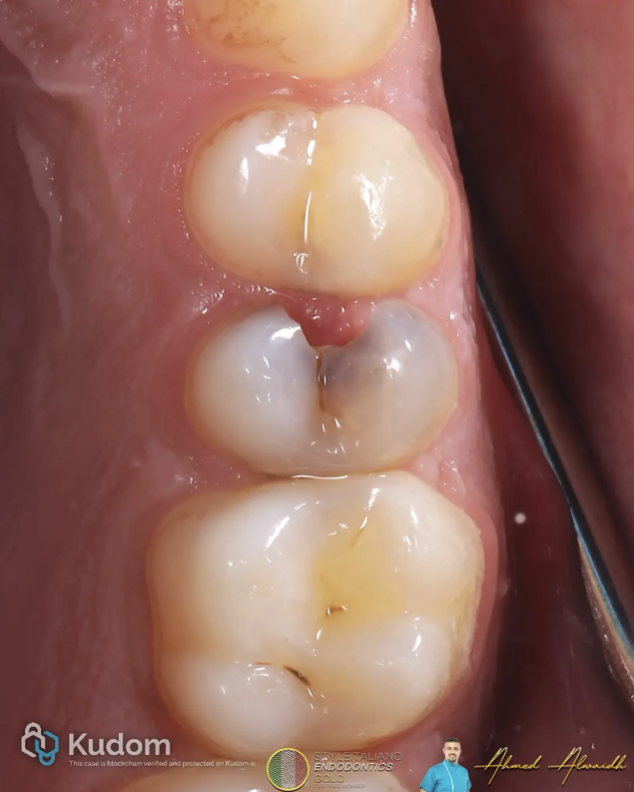
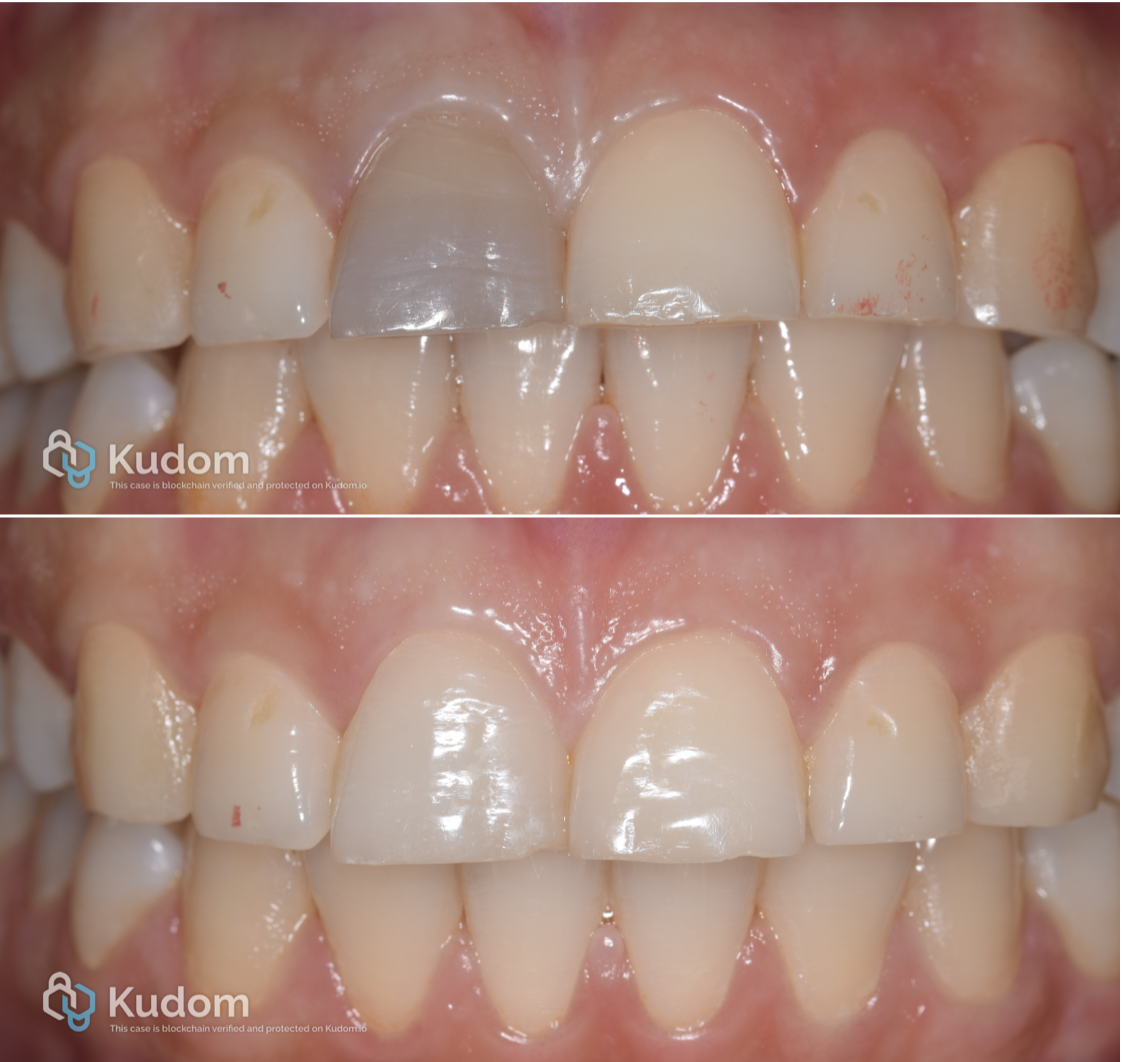
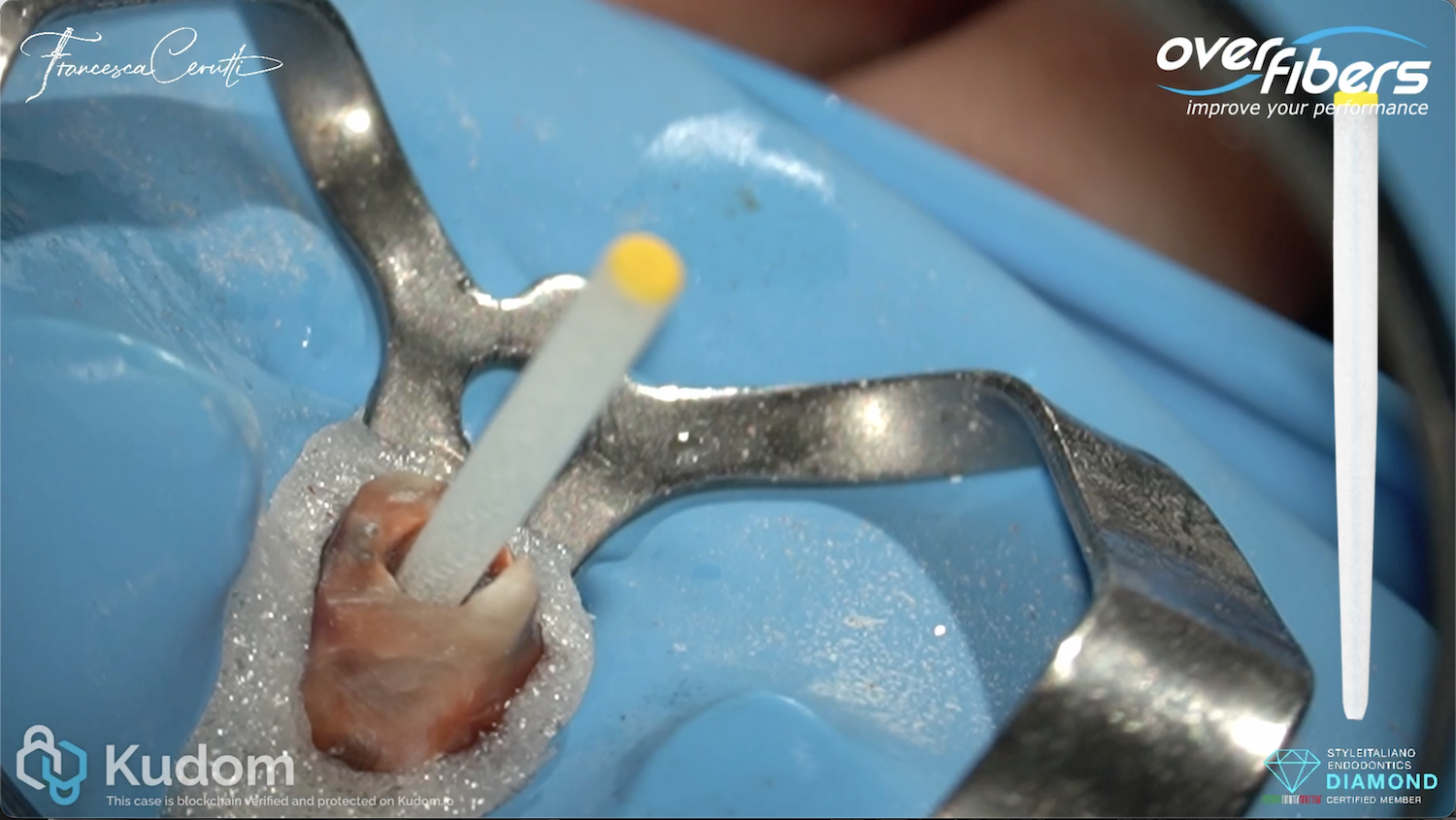
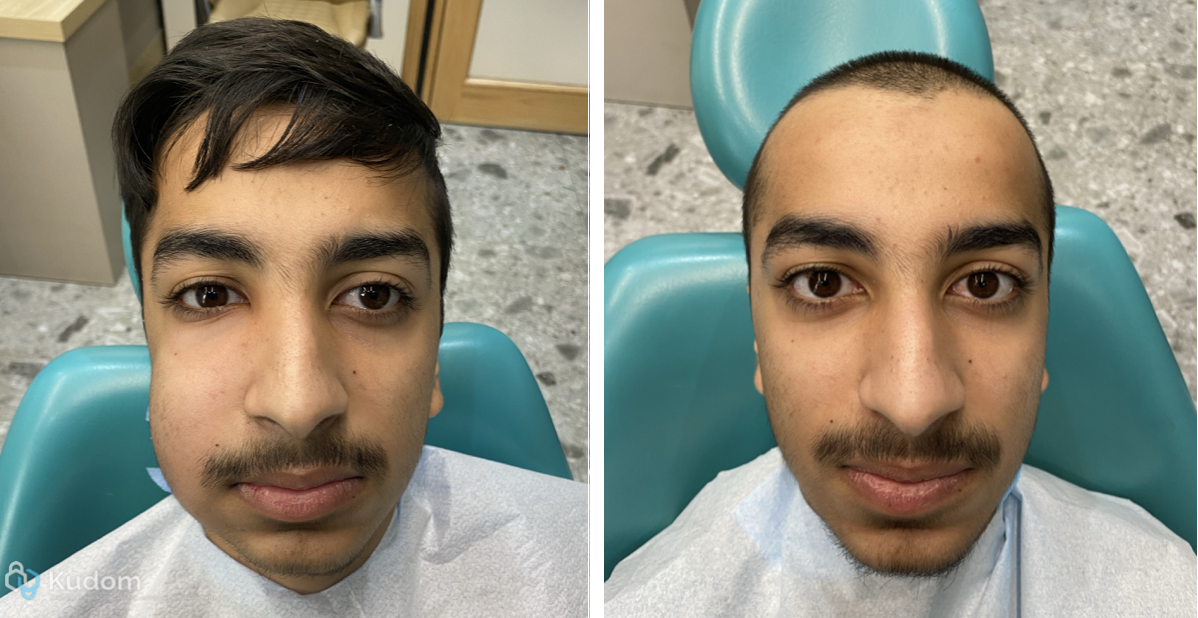
In this case I had to retreat two badly decayed teeth. We put provisional crowns first, in order to preserve the aesthetics of the patient between treatments, then I scheduled two appointments for endo + post endo + adaptation of the provisional crown. After that, the patient had the final crowns.