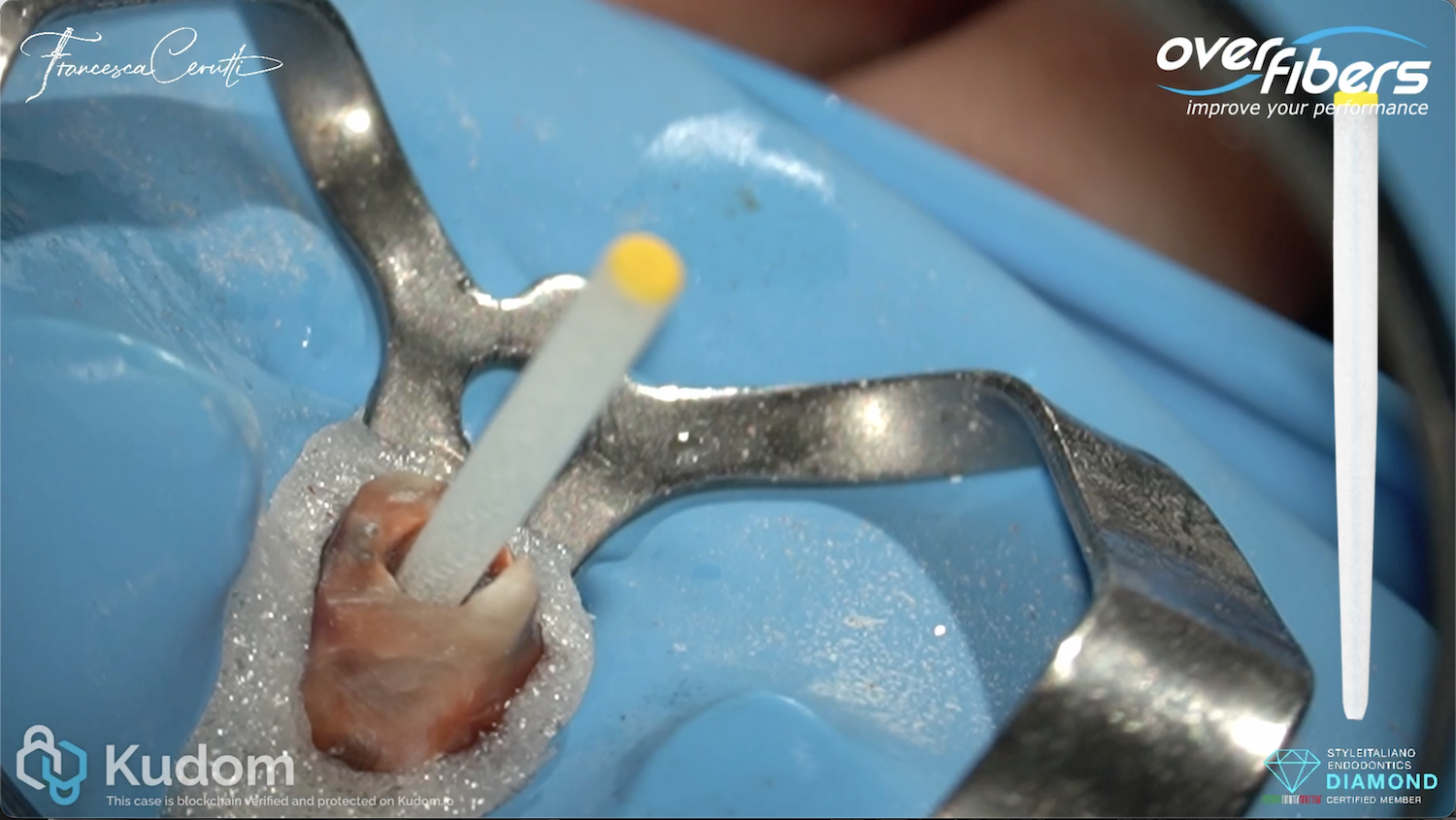
R One Mini reciprocating file system by Fanta is an excellent file system to be used in different scenarios like narrow and calcified canals. It is an easy system (two files), safe, and minimal invasive approach due to variable taper.
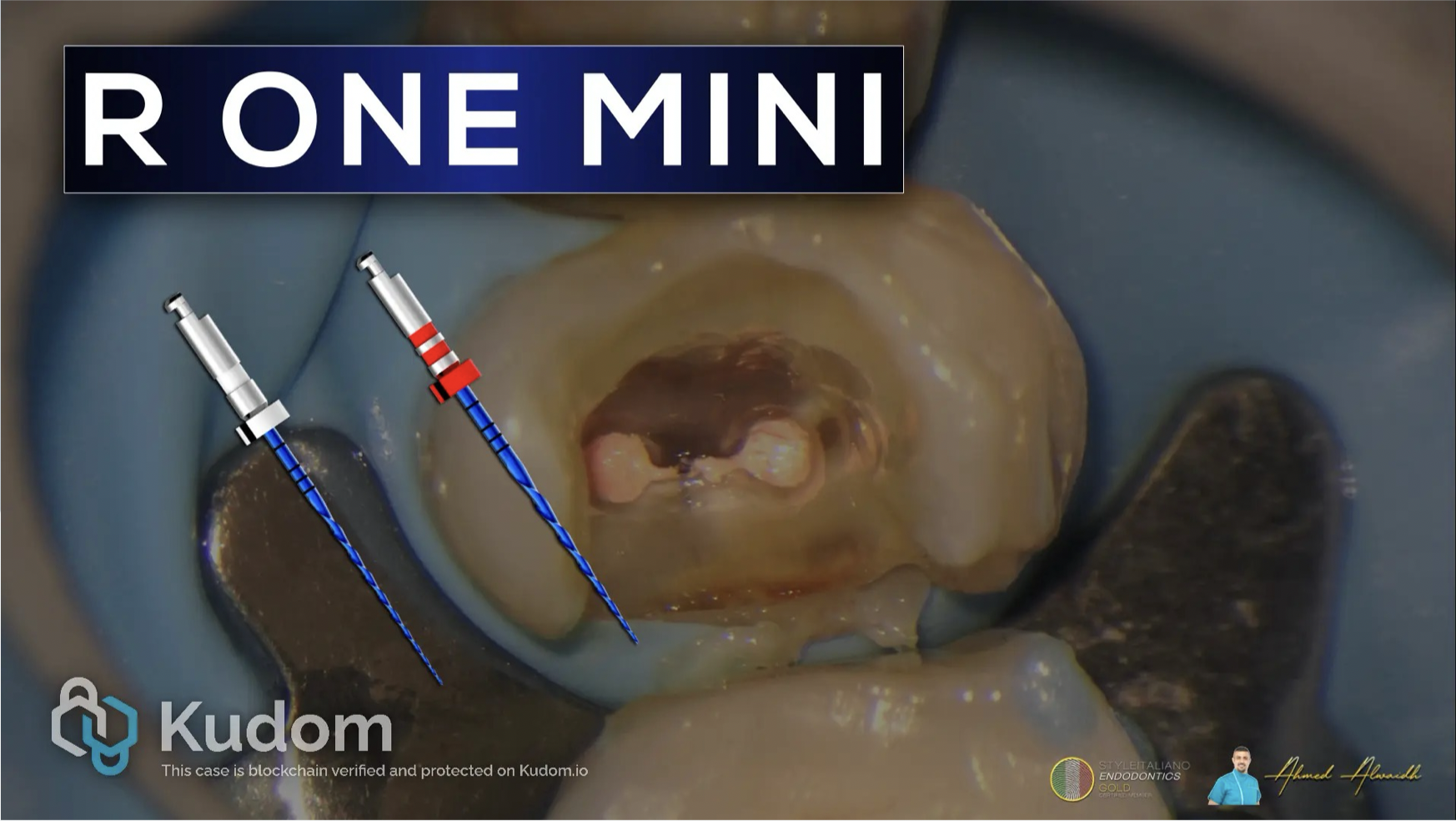 R One Mini in a narrow and calcified upper first premolar
R One Mini in a narrow and calcified upper first premolar
R One Mini reciprocating file system by Fanta is an excellent file system to be used in different scenarios like narrow and calcified canals. It is an easy system (two files), safe, and minimal invasive approach due to variable taper.
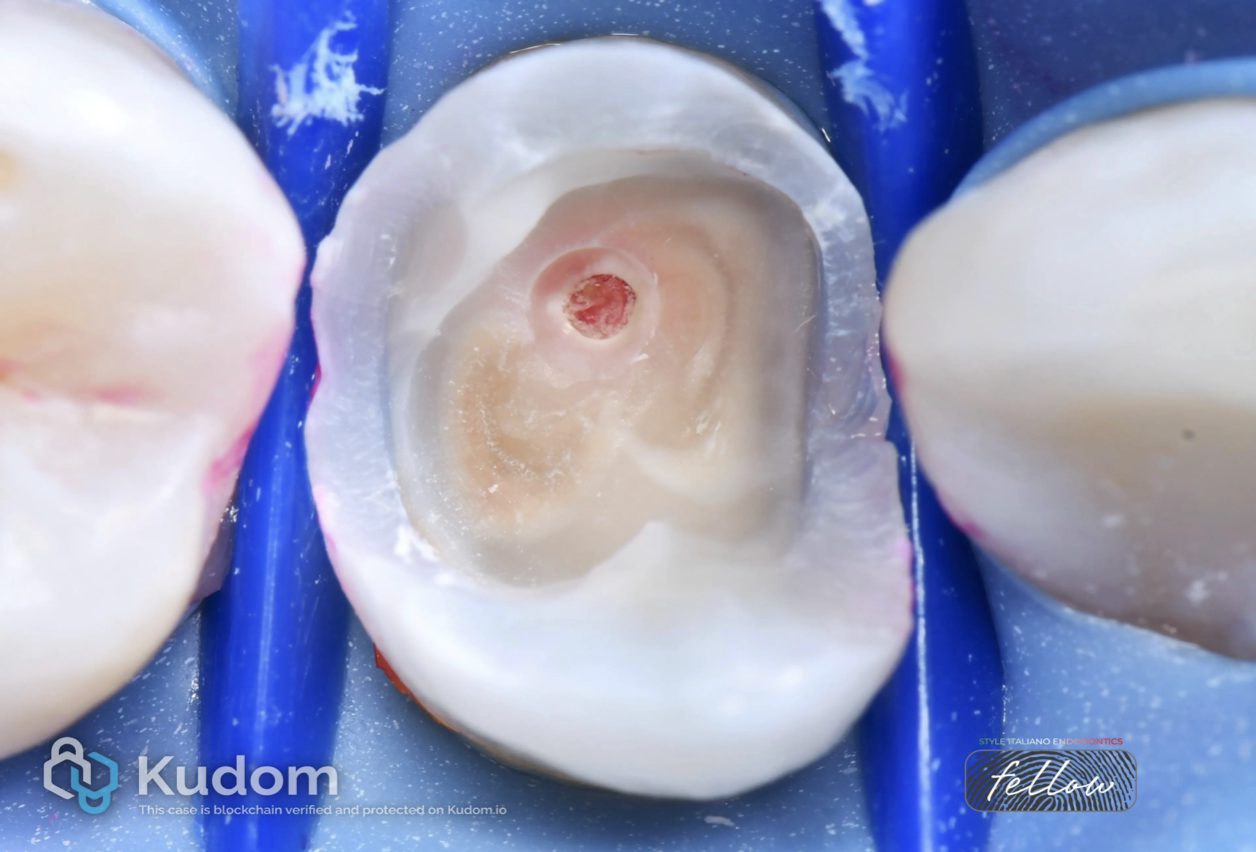 Touching the pulp
Touching the pulp
In the modern conservative dentistry, minimal invasive dental protocols are so important to preserve the pulp tissue vitality as long as we can to keep tooth strength, reduce treatment complexity, and to support long term oral health.
The pulp is a highly vascularized and innervated tissue that plays an essential role in dentin formation, nutrition, immune defense, and sensory function.
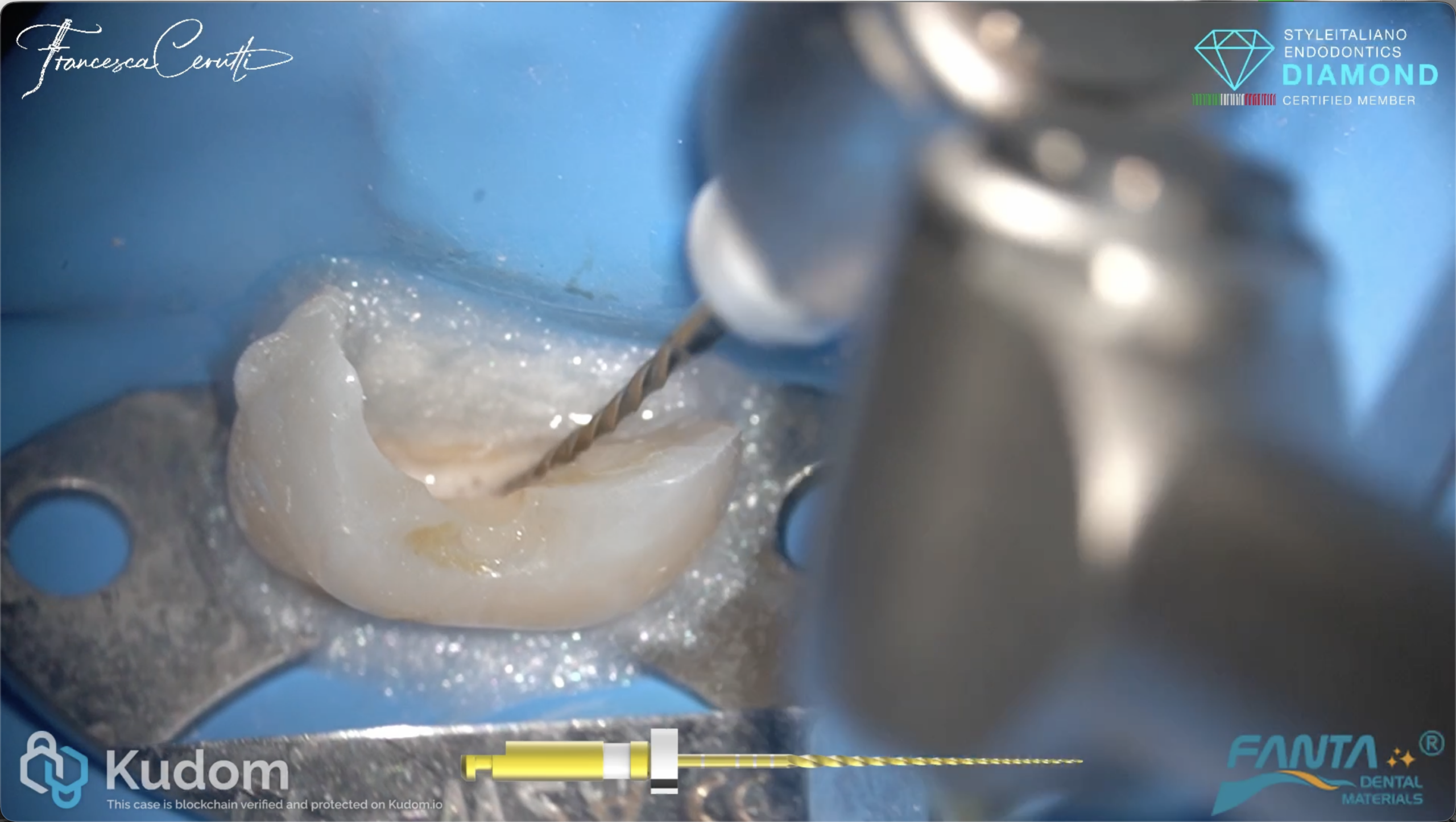 Rising files in the treatment of an upper premolar
Rising files in the treatment of an upper premolar
In daily dental practice, we frequently witness the late failure of restorative procedures that were originally intended to preserve pulp vitality. Over time, the dental pulp may undergo irreversible inflammation […]
 Retreatment of badly decayed tooth with multiple mishaps
Retreatment of badly decayed tooth with multiple mishaps
In the world of endodontics, the line between a routine procedure and a clinical "detour" can be incredibly thin. Whether it’s a stubborn calcified canal or an unexpected instrument fracture, mishaps are less a sign of incompetence and more a reflection of the biological and anatomical complexities we face daily.
 Retreatment through a crown
Retreatment through a crown
The patient, 72, had these crowns a few years earlier and had no desire to remove them. Tooth 4.5 had already been treated, but it was the only one that […]
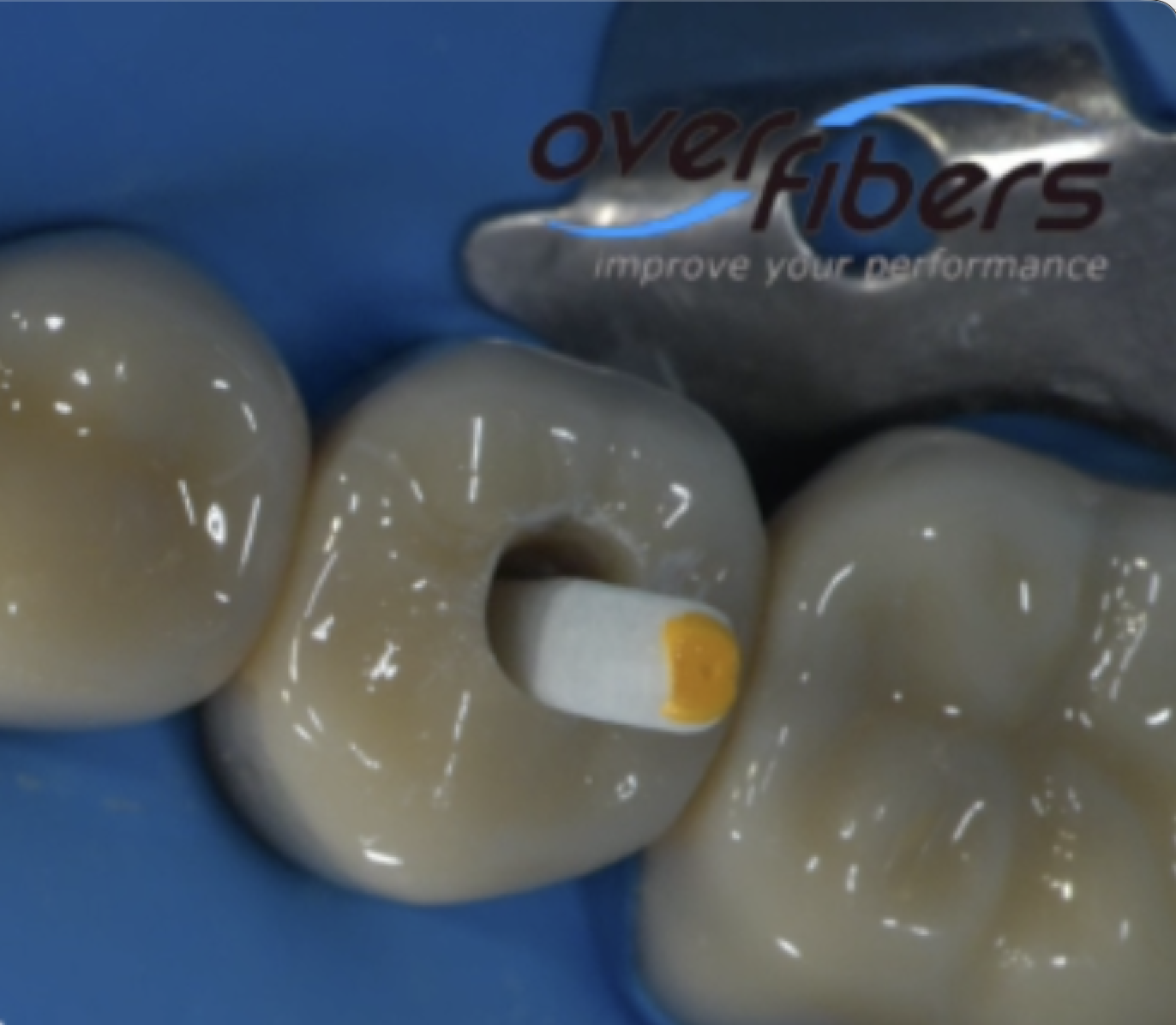
 Maxillary Molar and F One Essential Kit
Maxillary Molar and F One Essential Kit
Narrow canals
Shaping challenges
Conservative preparation
Multi planner curvature
Calcification
F One
Fanta
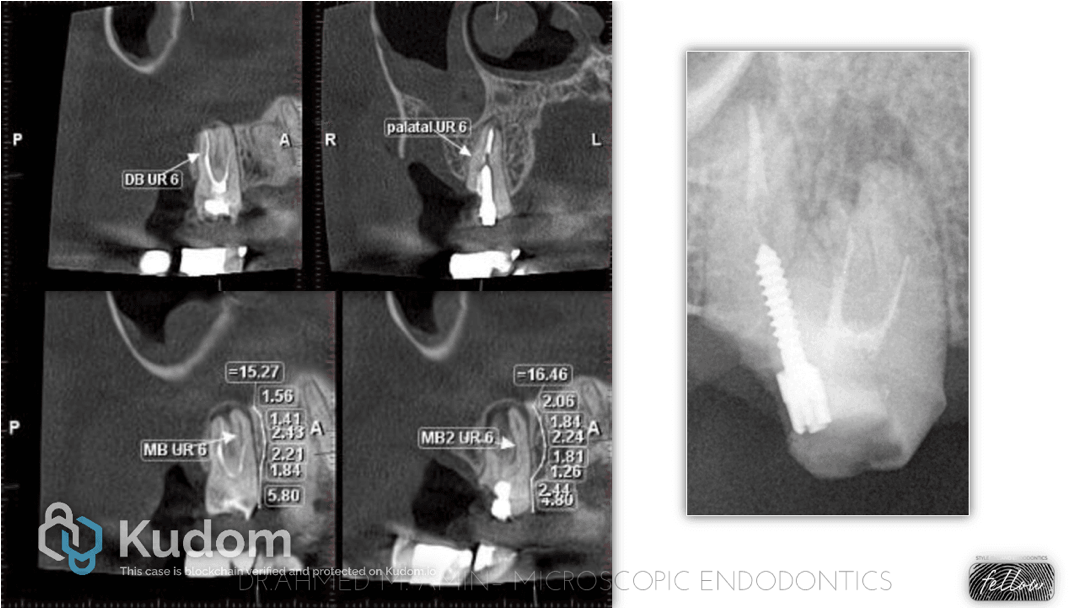
 S obturation with hydraulic BC cement for UR5 with deep apical split
S obturation with hydraulic BC cement for UR5 with deep apical split
Root canal system is a very complex three-dimensional system. Although there are general rules about the anatomy, number of root/s or canal/s for each tooth, but we should expect everything. For that reason, we should have goon understanding, good reading of radiographs, good tools, and experience to deal with different scenarios
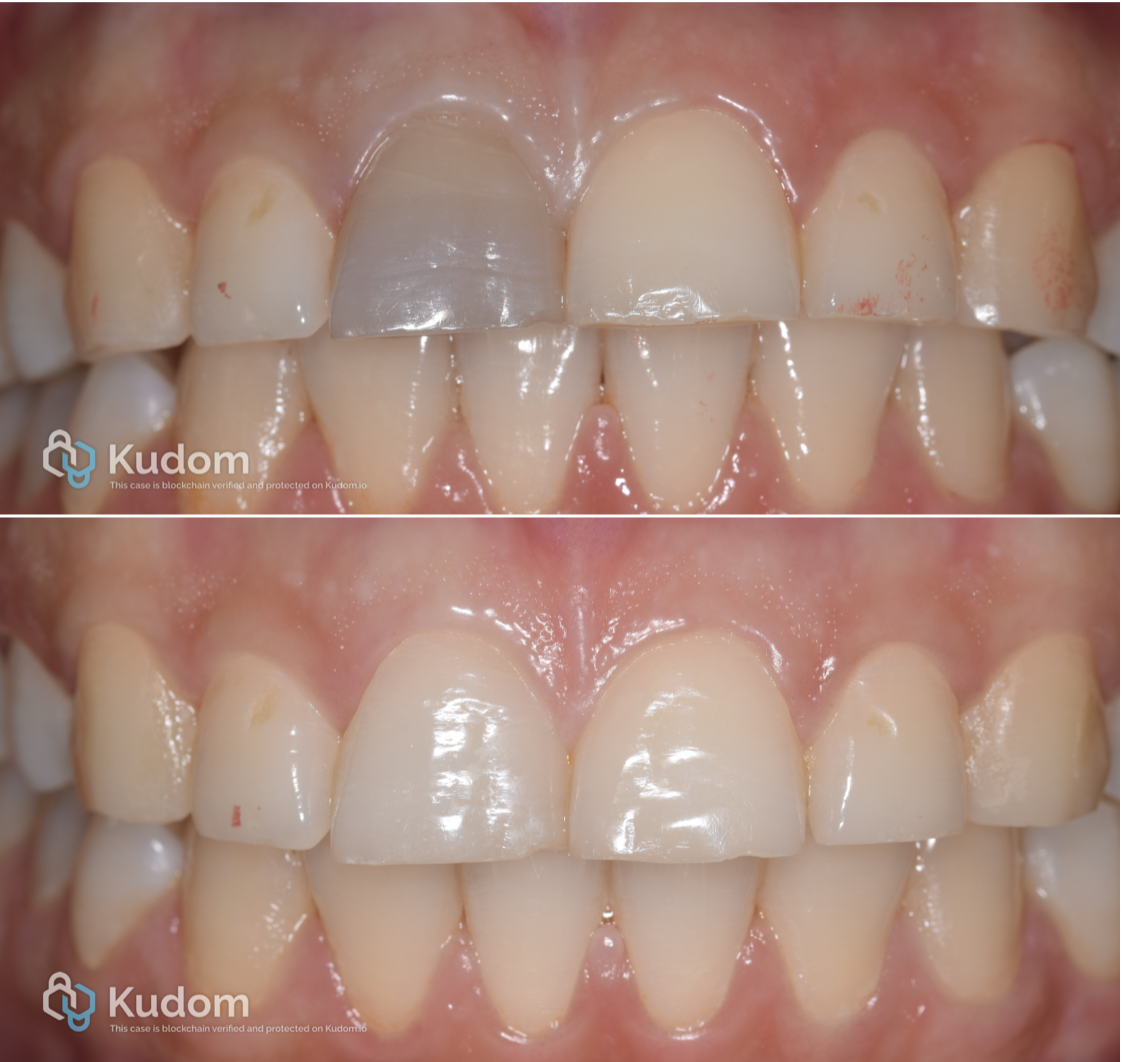 Internal Bleaching as a Conservative Alternative to Veneers in Root Canal-Treated Tooth
Internal Bleaching as a Conservative Alternative to Veneers in Root Canal-Treated Tooth
This article discusses the use of internal bleaching as a conservative and effective esthetic solution for discolored, root canal–treated teeth. It highlights the clinical protocol, indications, and advantages of internal bleaching as an alternative to veneers, preserving natural tooth structure while achieving satisfactory esthetic outcomes.
 Retreatment and post-retained restoration in a central incisor
Retreatment and post-retained restoration in a central incisor
When a tooth has undergone root canal treatment and has lost a large amount of coronal structure, the restorative challenge is not only to replace missing tissue, but to recover […]
 Complication of bad endodontic treatment
Complication of bad endodontic treatment
Endodontic treatment aims to eliminate infection from the root canal system and prevent reinfection of periapical tissues. Inadequate endodontic procedures, such as insufficient canal debridement, improper working length determination, or poor obturation, may result in persistent intracanal infection. This can lead to periapical inflammation and the development of swelling, commonly presenting as a dentoalveolar abscess. Such complications not only cause patient discomfort but may also compromise the prognosis of the affected tooth. This case report highlights a clinical presentation of facial swelling resulting from failed endodontic treatment and discusses its management
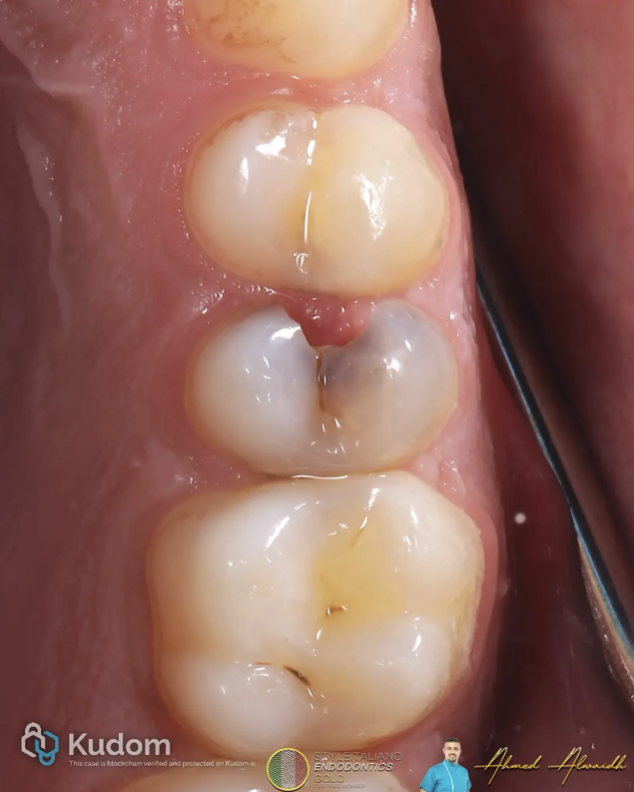
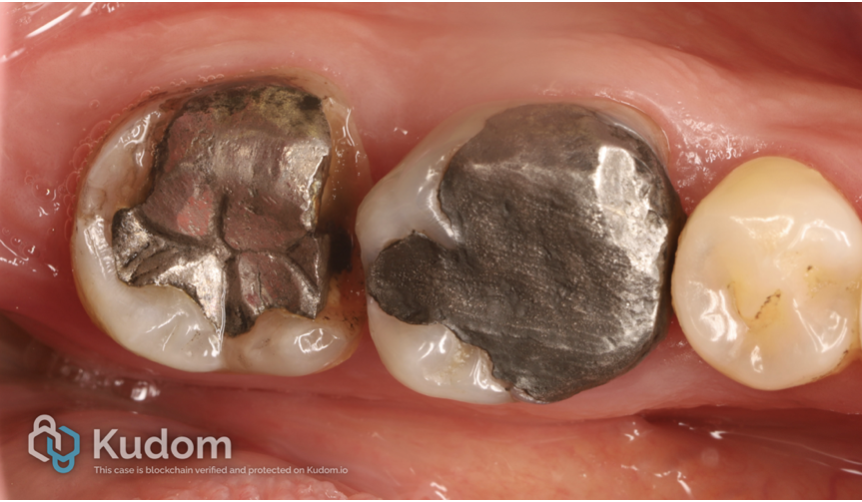 Endo-resto management of two molars with failed old large amalgam restoration
Endo-resto management of two molars with failed old large amalgam restoration
Combining precise endodontic treatment with biomimetic restorations preserves tooth structure, restores function, and enhances long-term survival.
 Overpost restoration of tooth 25
Overpost restoration of tooth 25
A 47-year-old female patient presented with a structurally compromised maxillary left second premolar (tooth 25) following completed endodontic treatment. Due to the significant loss of coronal tooth structure, a post-endodontic […]