Ledge detection and bypass with Explora after broken file removal
18/12/2021
Marc Kaloustian
Warning: Undefined variable $post in /home/styleendo/htdocs/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
Warning: Attempt to read property "ID" on null in /home/styleendo/htdocs/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
The success of Endodontic retreatment is multifactorial and will depend on the degree of root canal morphology alteration. Irreversible iatrogenic errors such as large perforations or canal transportation will decrease drastically the good prognosis of the treatment.
In cases where it is possible to regain the original anatomy and shape, clean and fill the entire system, the survival and the success rate of the retreatment are mostly favorable.
Among many other criteria, the possibility to remove an instrument and to bypass the beginning of a false canal, commonly called a ledge can be advantageous in the long term prognosis of the root canal treatment.
In fact, the non instrumented area of the canal can potentially contain necrotic tissues and bacteria often assembled in biofilm. These bacteria and their toxins have the opportunity to diffuse on the long term into the peri-apical tissues through the main canal or the accessory and lateral canals and cause symptomatic or asymptomatic apical periodontitis.
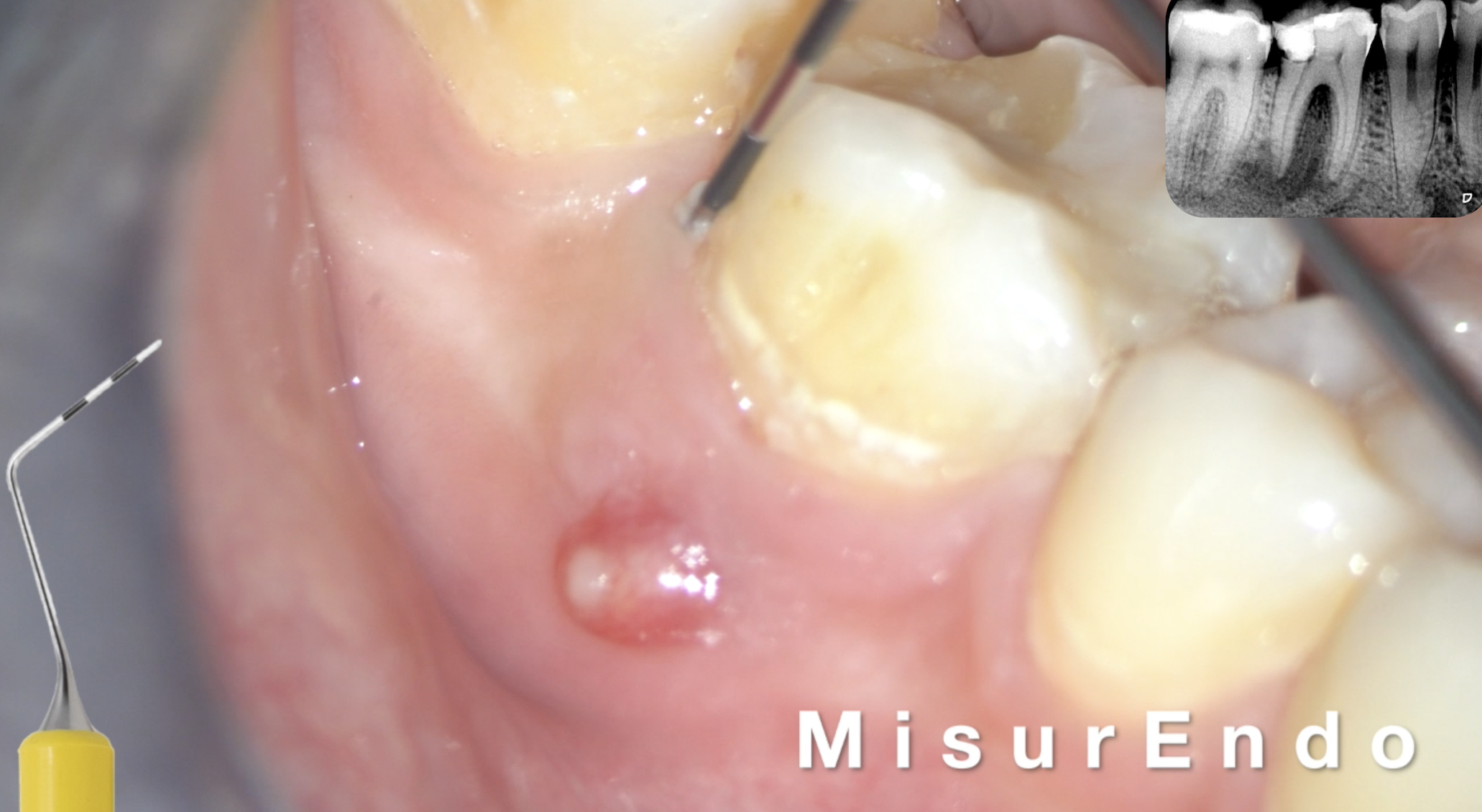
This case report will describe a detailed retreatment technique of an upper right second molar with a broken file in the mesio buccal canal and a ledge in the midroot

Fig. 1
The patient’s chief complaint was a spontaneous pain aggravated by pressure on mastication, on the second upper right molar. Lateral and vertical percussion were positive on that tooth and negative on both the upper first and second premolar.
Upon radiographic examination, the distal and palatal canals presented short fillings with numerous voids and a broken file was detected in the mesial root.
The diagnosis of an apical symptomatic periodontitis was established. The decision of a non surgical retreatment was taken.
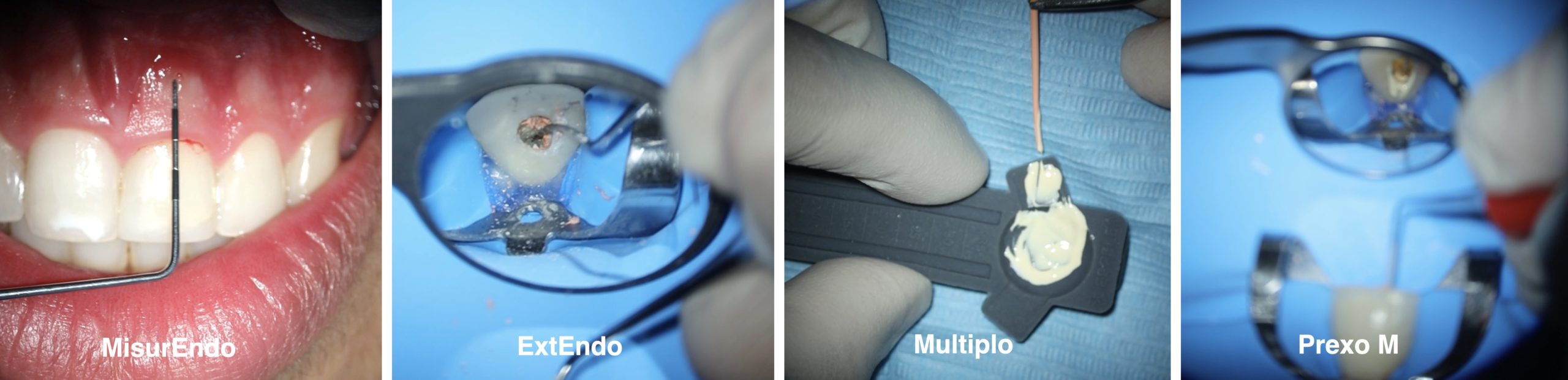
After access cavity refinement using ultrasonic tips, Explora (Deppeler, La pièce 6, Swizerland) was used to explore the canals.
3 canals were detected and the hardness of the filling material was assessed with explorer. The use of any solvent was discarded, since the old material was rather soft
The filling material was removed from the palatal and the disco-buccal with XP-Endo Shaper without the use of any solvent
A direct access was established to the broken file in the mesio-buccal canal with a heat treated NiTi file in reciprocation, R-Motion 25 and the file was retrieved with an ultrasonic tip ET25
After the removal of the broken file, a ledge was discovered in the mesio-buccal canal. The ledge was pointed precisely with the long Explora (Deppeler) on the buccal wall of the canal and the orifice of the canal was also detected under magnification X10
According to the position of the ledge, a number 08 preserved C pilot file was introduced in the canal with a watch winding motion till the apical patent was secured. The working length was taken using an apex locator.
The mesio-buccal canal was shaped with a single reciprocating file R-Motion 25
The disto-buccal and the palatal canals were shaped exactly with the same protocol
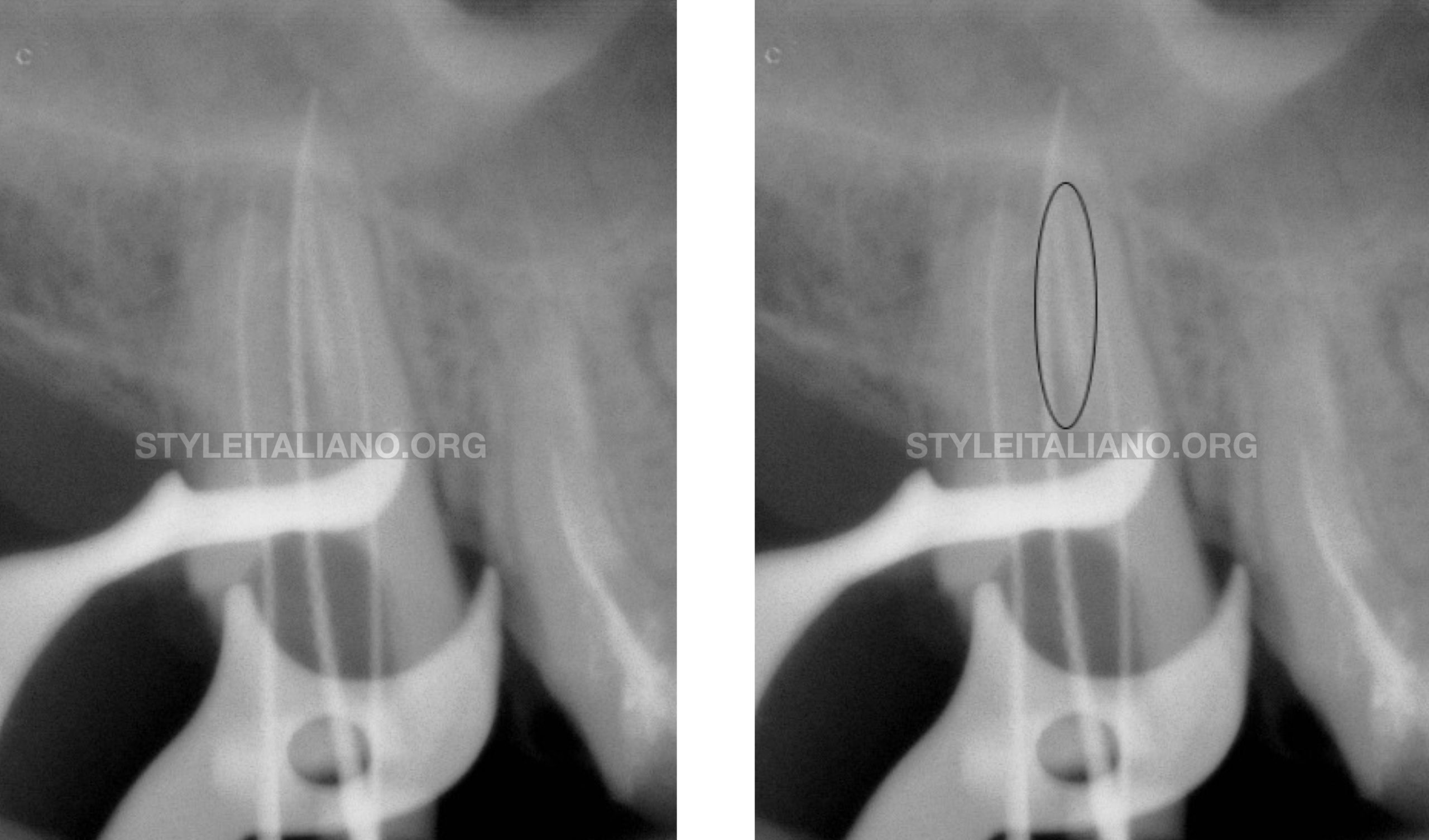
Fig. 2
A working length X-ray showed the presence of material remnants in the mesial wall of the palatal canal
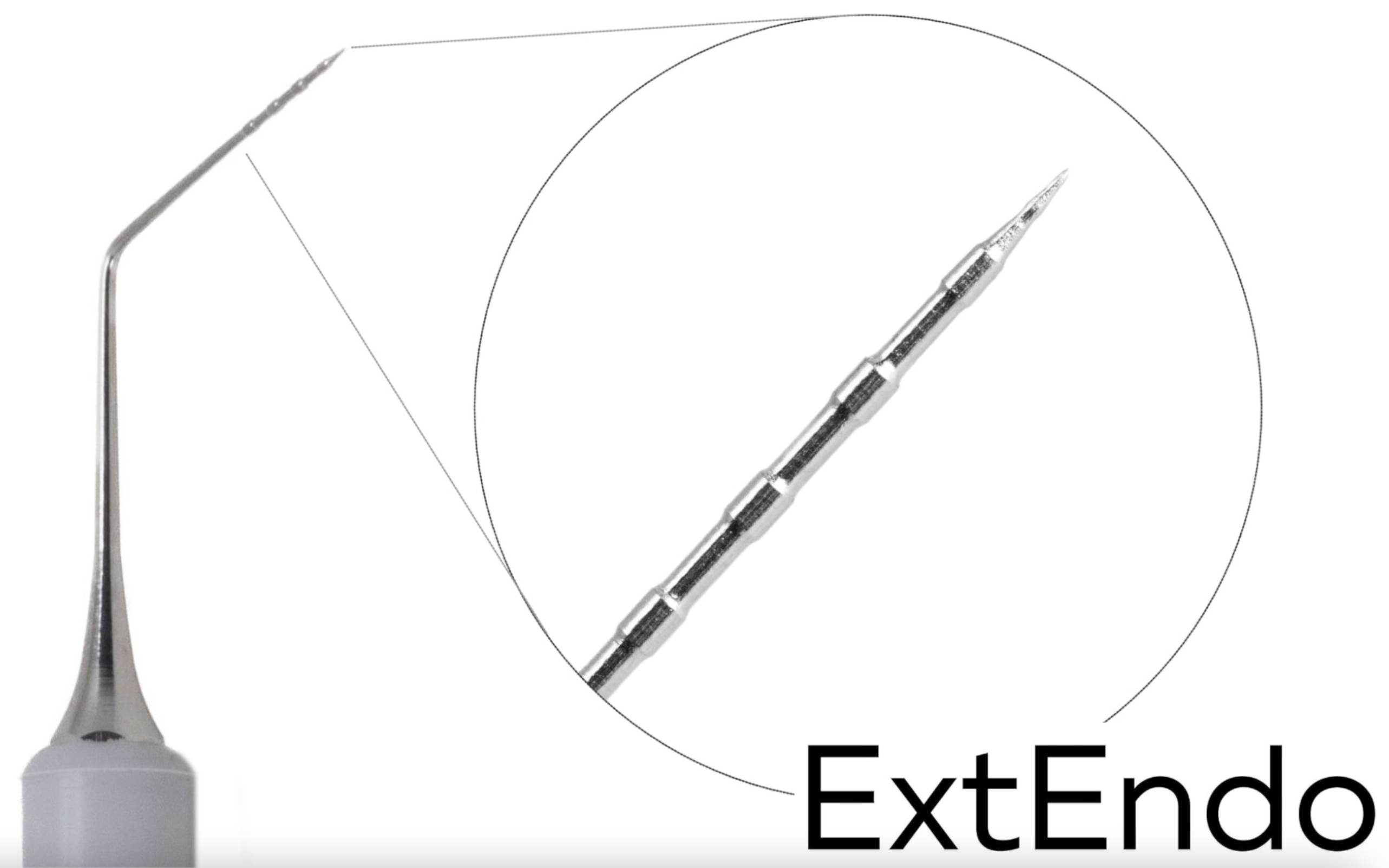
ExtEndo (Deppeler) was used to remove passively some of the remnants under magnification
Activation of the irrigation solution was performed with the XP-Endo Finisher with 1000 RPM and 1 minute in each canal
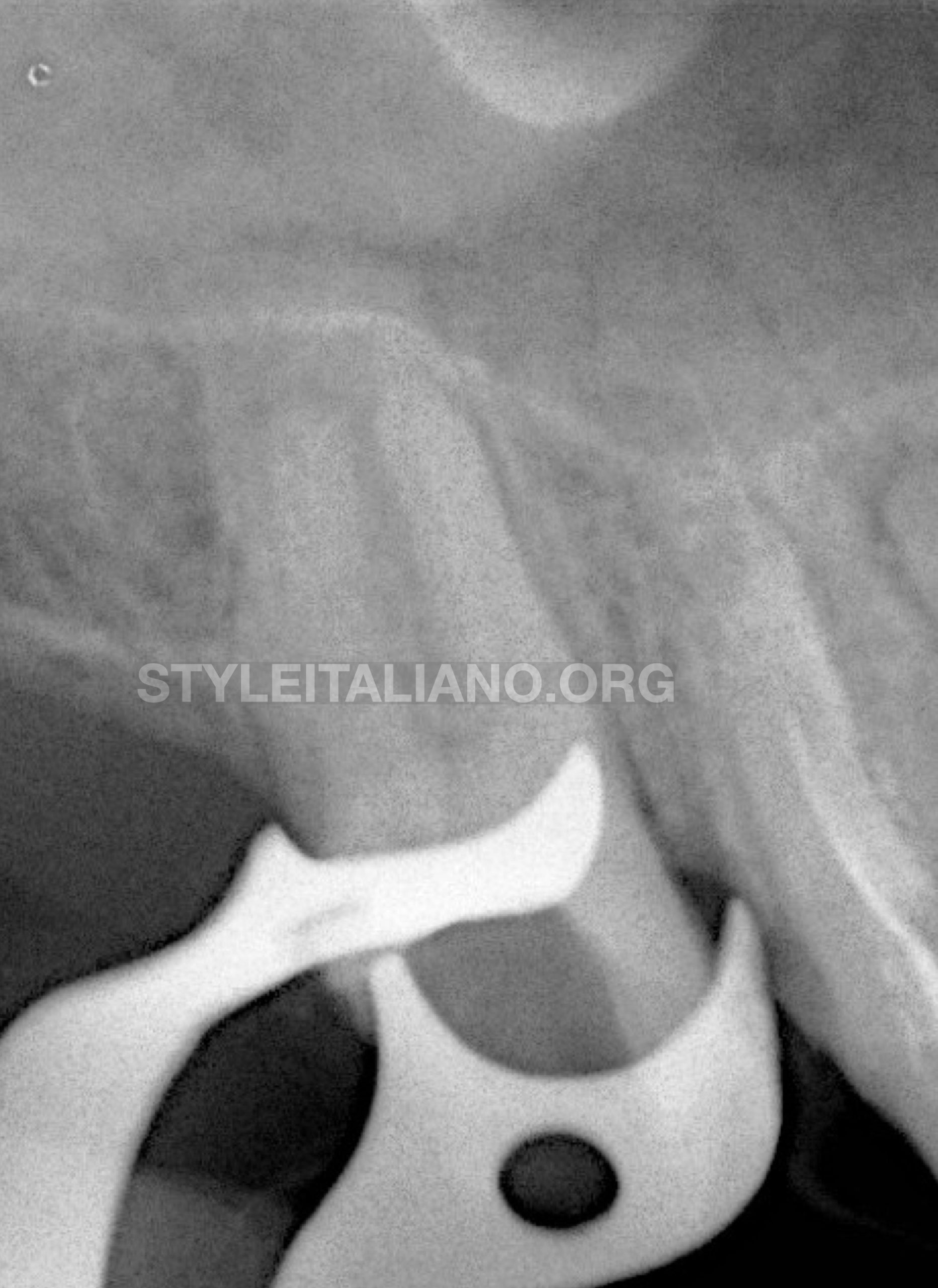
Fig. 3
An X-ray showing the removal of the broken file and the cleanness of the walls after the retreatment procedure

Fig. 4
The 3 canals were filled with warm vertical continuous technique for down pack and Prexo M (Deppeler) for manual compaction
The continuous wave technique was applied in all 3 canals
Back pack was done with the injecting technique using the back fill wireless device
Access cavity after the 3D obturation
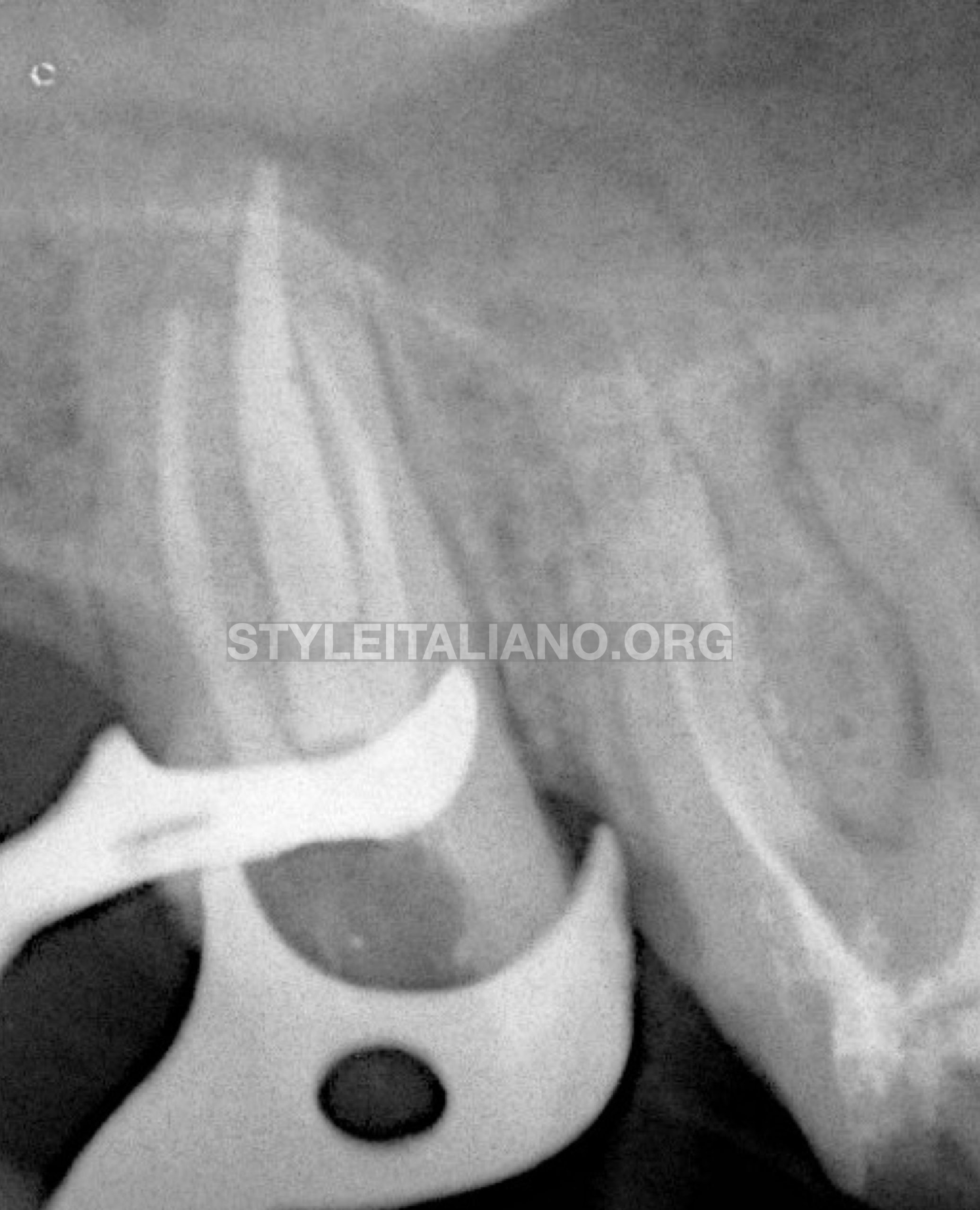
Fig. 5
Final X-ray after 3D filling of the entire Endodontic system
Conclusions
During the retreatment procedure, regaining the anatomy and cleaning the entire endodontic system is necessary for a better long term prognosis of the tooth. This will suppose the removal of the entire filling material, the retrieval of any fractured instrument and the bypass of ledges. A long and sharp explorer such as Explora will give us the possibility to detect precisely the location of the ledge, and accordingly to bypass it first with small hand files and after with NiTi files. Finally, a warm vertical continuous technique will assure the longevity of the treatment.
Bibliography
- Torabinejad M, Corr R, Handysides R, Shabahang S. Outcomes of nonsurgical retreatment and endodontic surgery: a systematic review. J Endod. 2009 Jul;35(7):930-7. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2009.04.023. PMID: 19567310.
- Kaloustian MK, Nehme W, El Hachem C, Zogheib C, Ghosn N, Mallet JP, Diemer F, Naaman A. Evaluation of two shaping systems and two sonic irrigation devices in removing root canal filling material from distal roots of mandibular molars assessed by micro CT. Int Endod J. 2019 Nov;52(11):1635-1644. doi: 10.1111/iej.13163. Epub 2019 Jun 17. PMID: 31127955.
- Jafarzadeh H, Abbott PV. Ledge formation: review of a great challenge in endodontics. J Endod. 2007 Oct;33(10):1155-62. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2007.07.015. Epub 2007 Sep 4. PMID: 17889681.
- Madarati AA, Hunter MJ, Dummer PM. Management of intracanal separated instruments. J Endod. 2013 May;39(5):569-81. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2012.12.033. Epub 2013 Mar 15. PMID: 23611371.
- Silva EJNL, Belladonna FG, Zuolo AS, Rodrigues E, Ehrhardt IC, Souza EM, De-Deus G. Effectiveness of XP-endo Finisher and XP-endo Finisher R in removing root filling remnants: a micro-CT study. Int Endod J. 2018 Jan;51(1):86-91. doi: 10.1111/iej.12788. Epub 2017 May 29. PMID: 28467618.