Complication of bad endodontic treatment
29/01/2026
Abdulwahab Al-Qaraghuli
Warning: Undefined variable $post in /var/www/vhosts/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/endodontics.styleitaliano.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
Warning: Attempt to read property "ID" on null in /var/www/vhosts/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/endodontics.styleitaliano.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
Endodontic treatment aims to eliminate infection from the root canal system and prevent reinfection of periapical tissues. Inadequate endodontic procedures, such as insufficient canal debridement, improper working length determination, or poor obturation, may result in persistent intracanal infection. This can lead to periapical inflammation and the development of swelling, commonly presenting as a dentoalveolar abscess. Such complications not only cause patient discomfort but may also compromise the prognosis of the affected tooth. This case report highlights a clinical presentation of facial swelling resulting from failed endodontic treatment and discusses its management
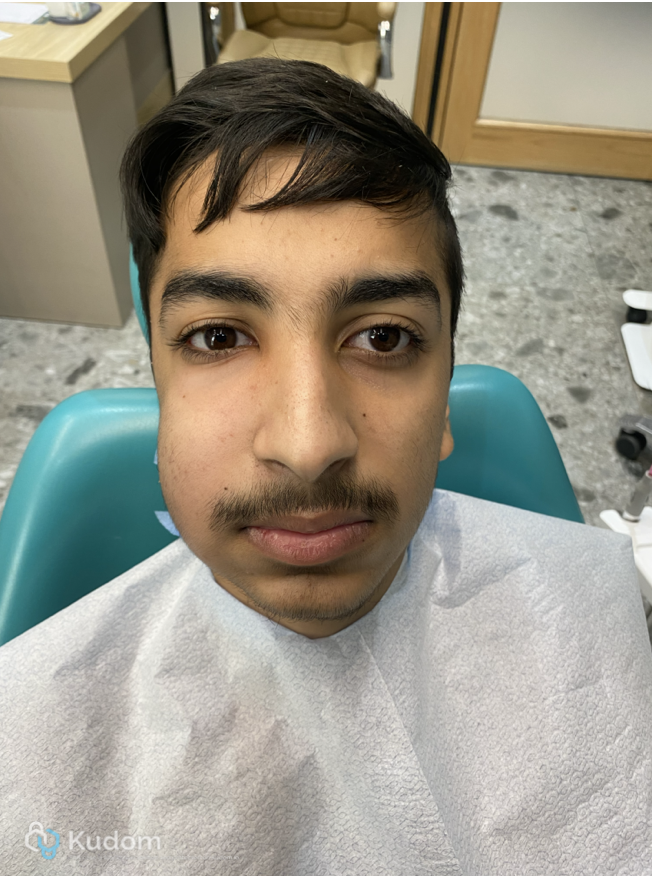
Fig. 1
Young boy presented with facial swilling in the right side of the face
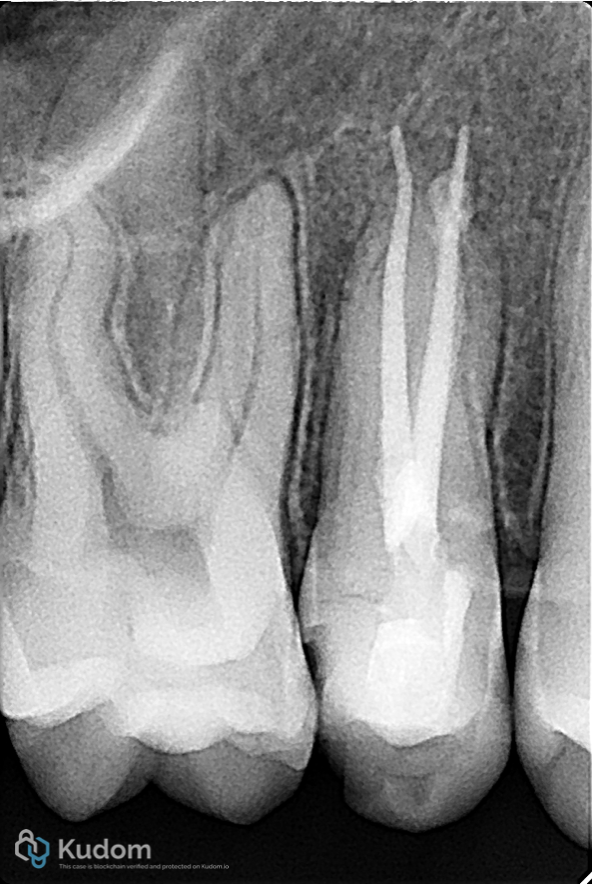
Fig. 2
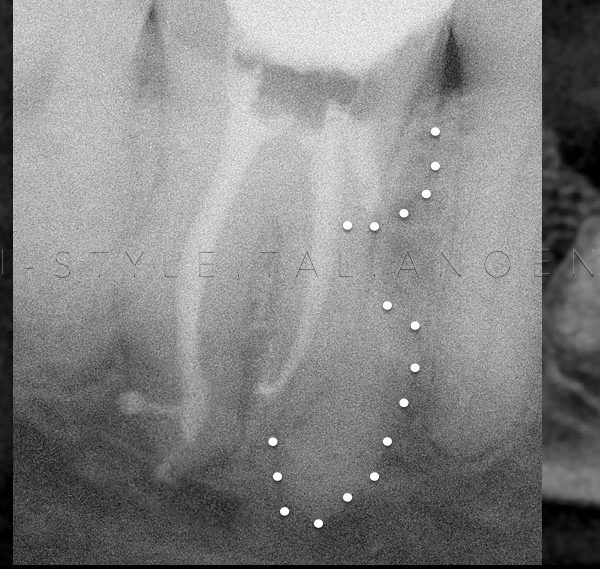
Upper 2nd Premolar had RCT before 3 week ago.
Over obturation with poor apical control in both buccal and palatal canals
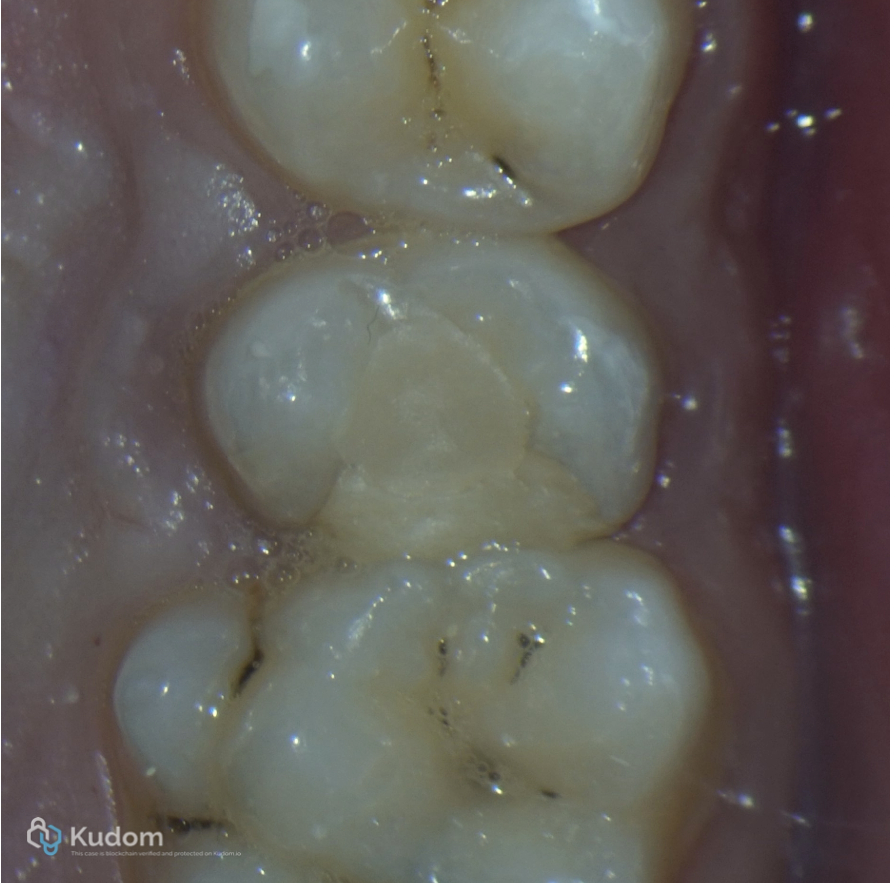
Fig. 3
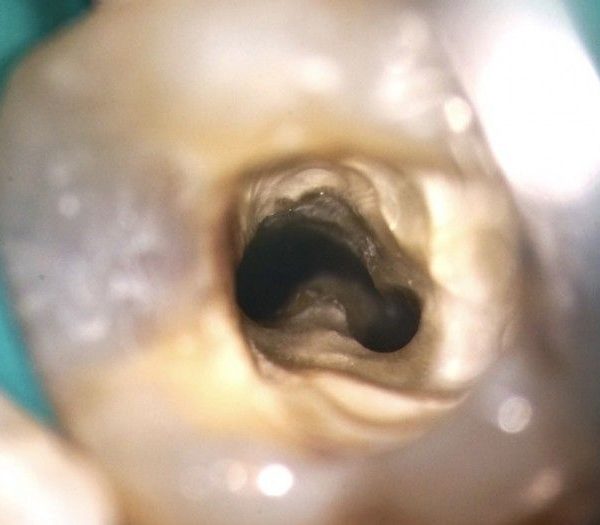
Clinical view for upper 2nd Premolar with bad restoration
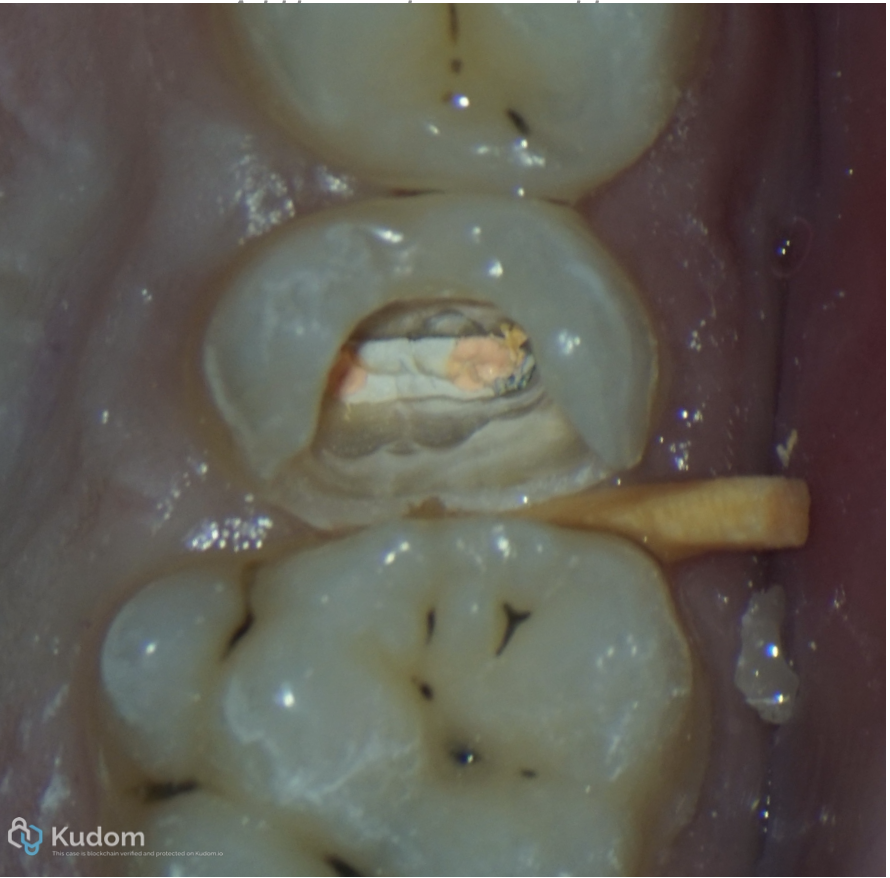
Fig. 4
Removal of the old filling material
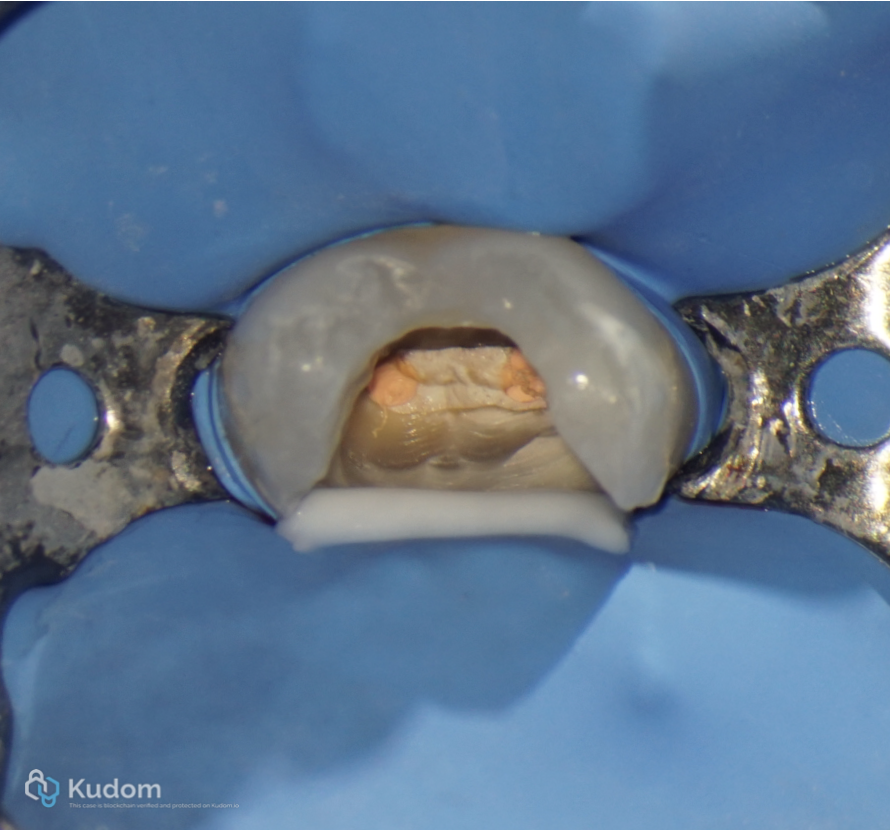
Fig. 5
Rubber dam isolation
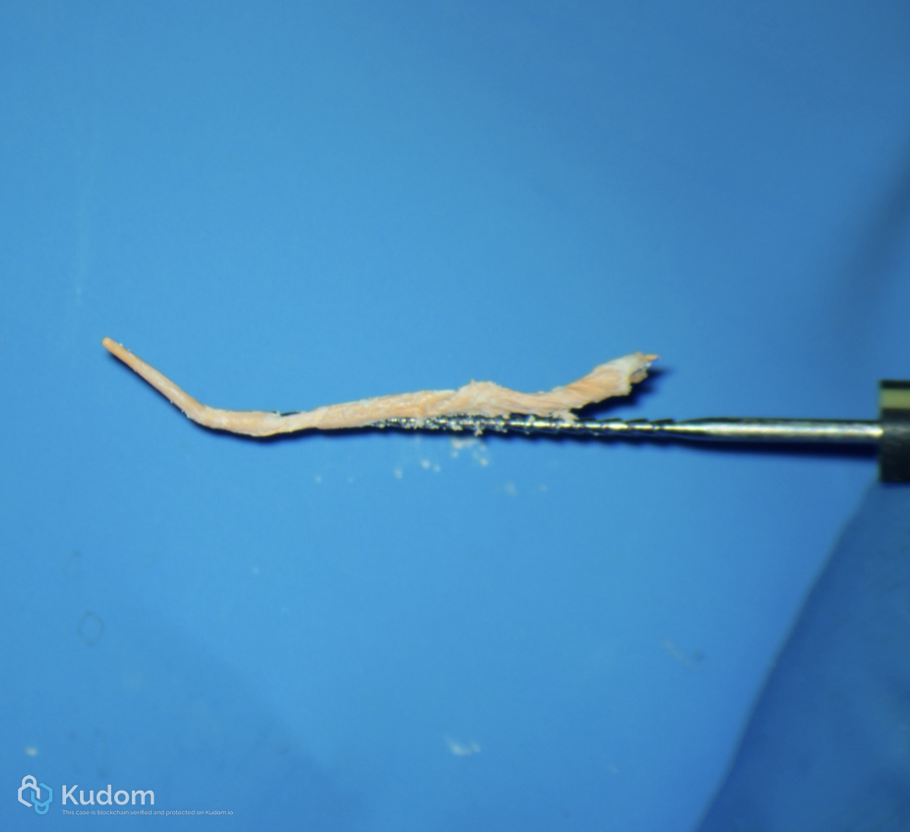
Fig. 6
Removal of the old gutta percha with this sequence:
1) Orifice opiner to remove the coronal third of gutta percha
2) Ultrasonic tip
3) H file (starting from the larger to smallest size)
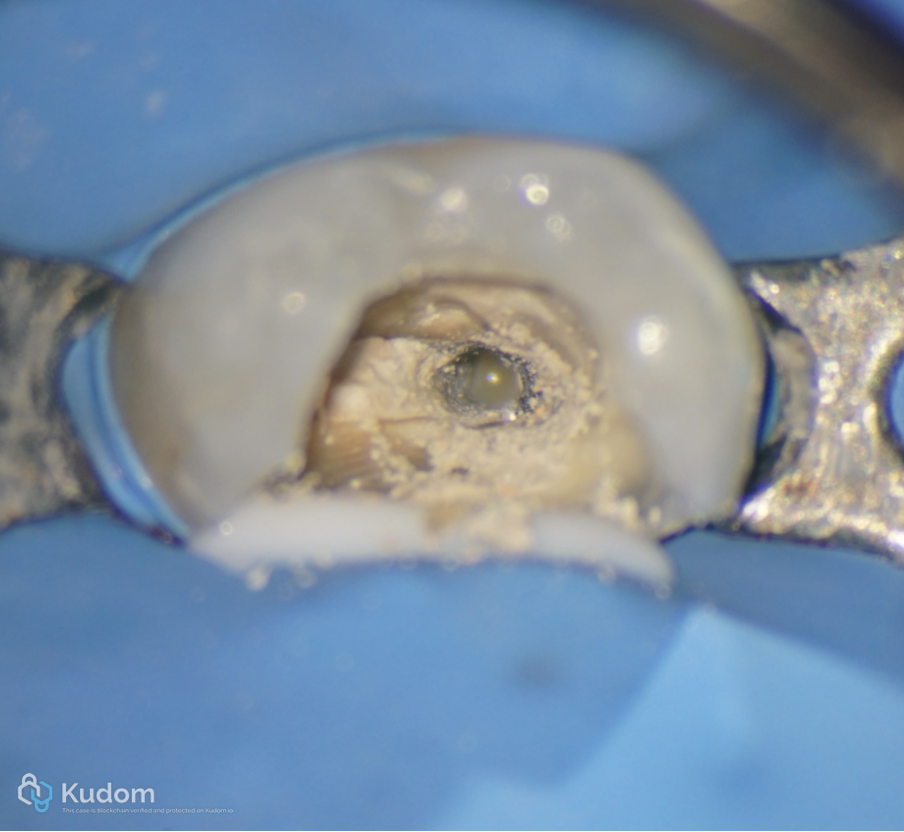
Fig. 7
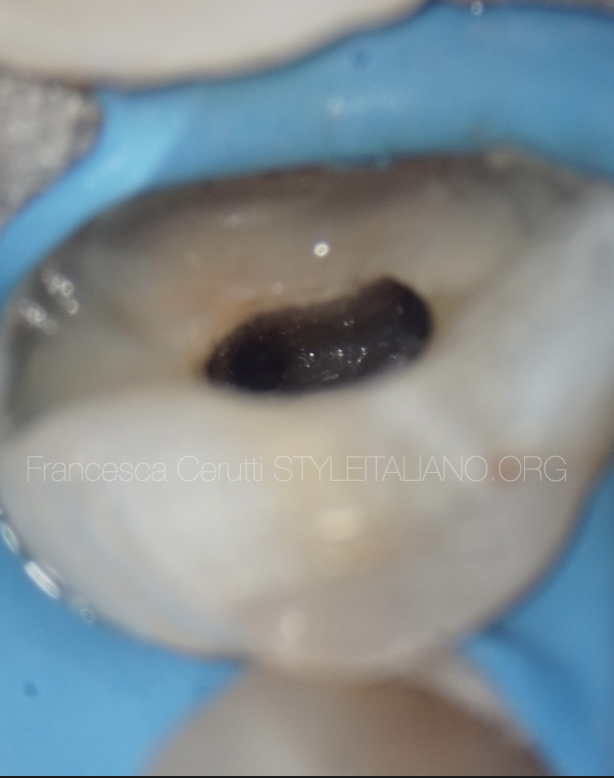
Pus discharge immediately after gutta percha removal
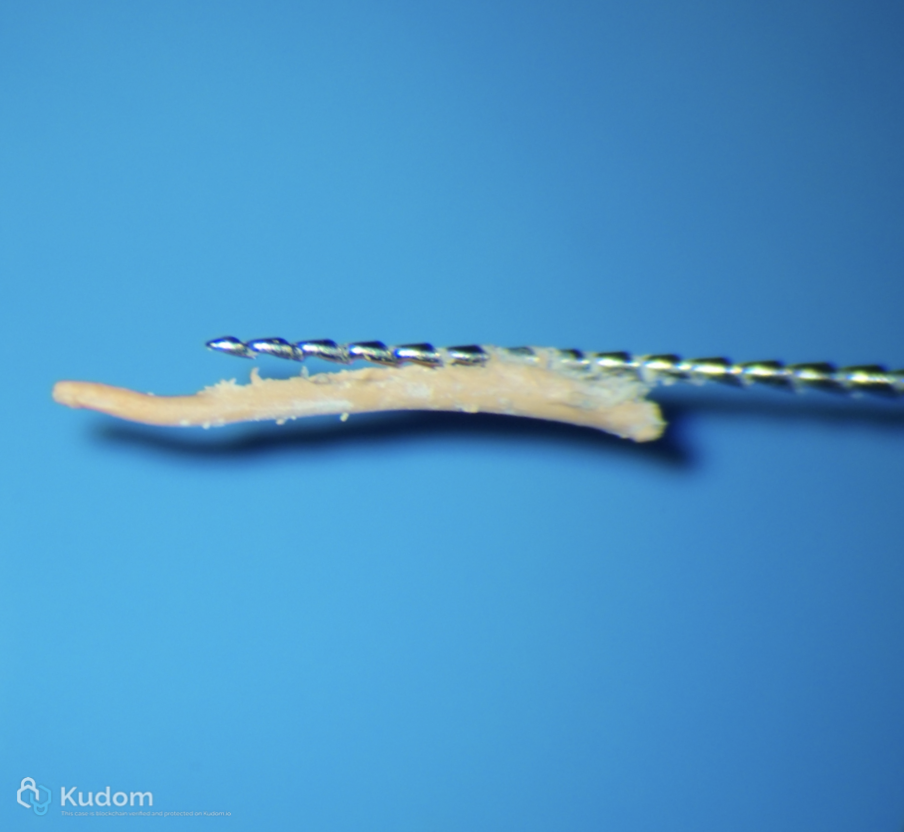
Fig. 8
Remove the second cone with the same sequence
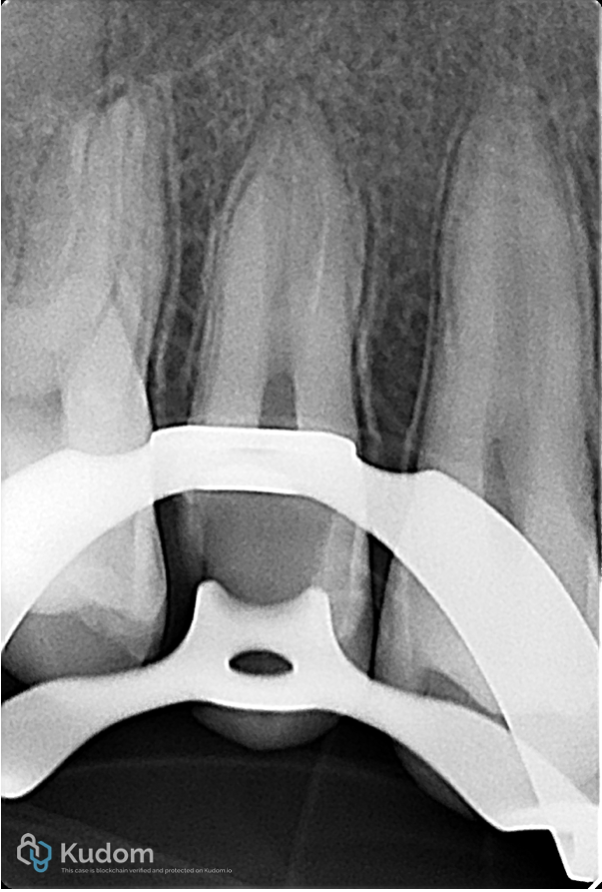
Fig. 9
Clean canals and clean periapical area.
The over obturation cement was removed with ultrasonic tip
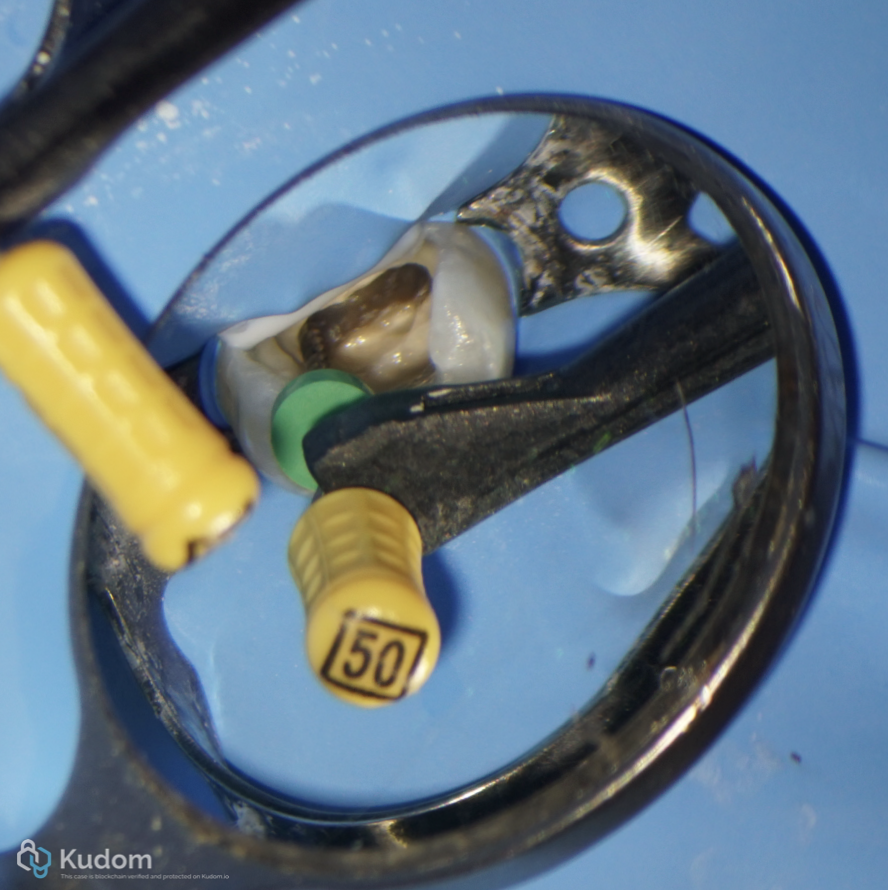
Fig. 10
Working length determination
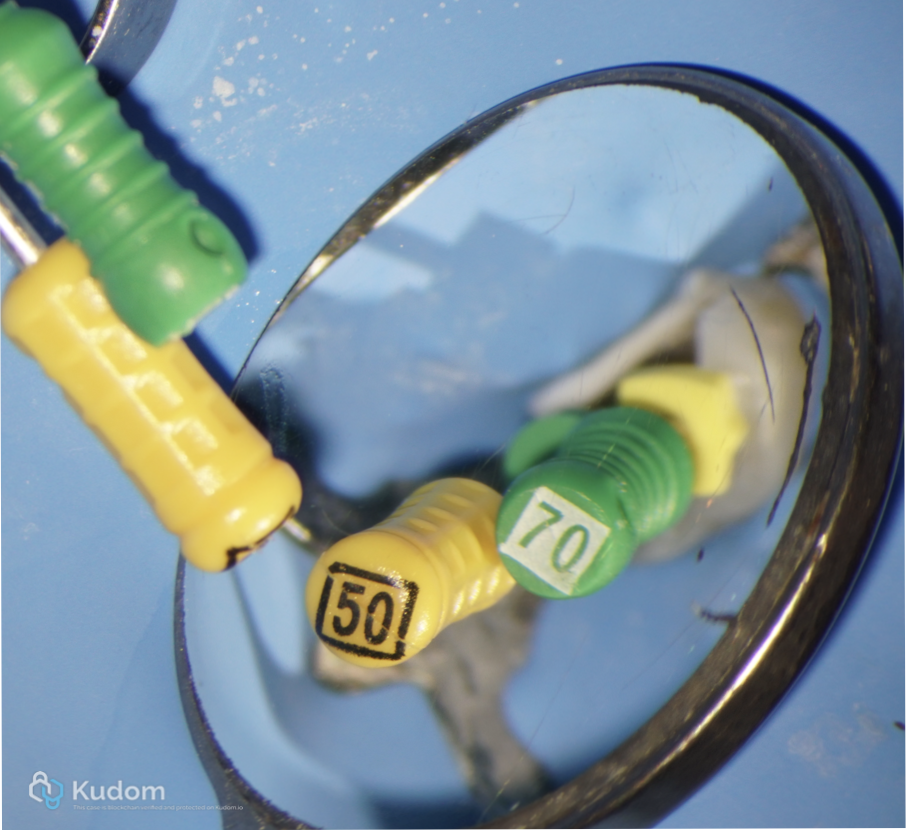

Fig. 11
Apical foramen size was 70 for buccal and 50 for palatal canals.
Foramen size of 60 or more cannot be predictably sealed by Gutta percha and Sealer due to irregular morphology of the foramen.
This is considered as perfect indication for Apical Plug
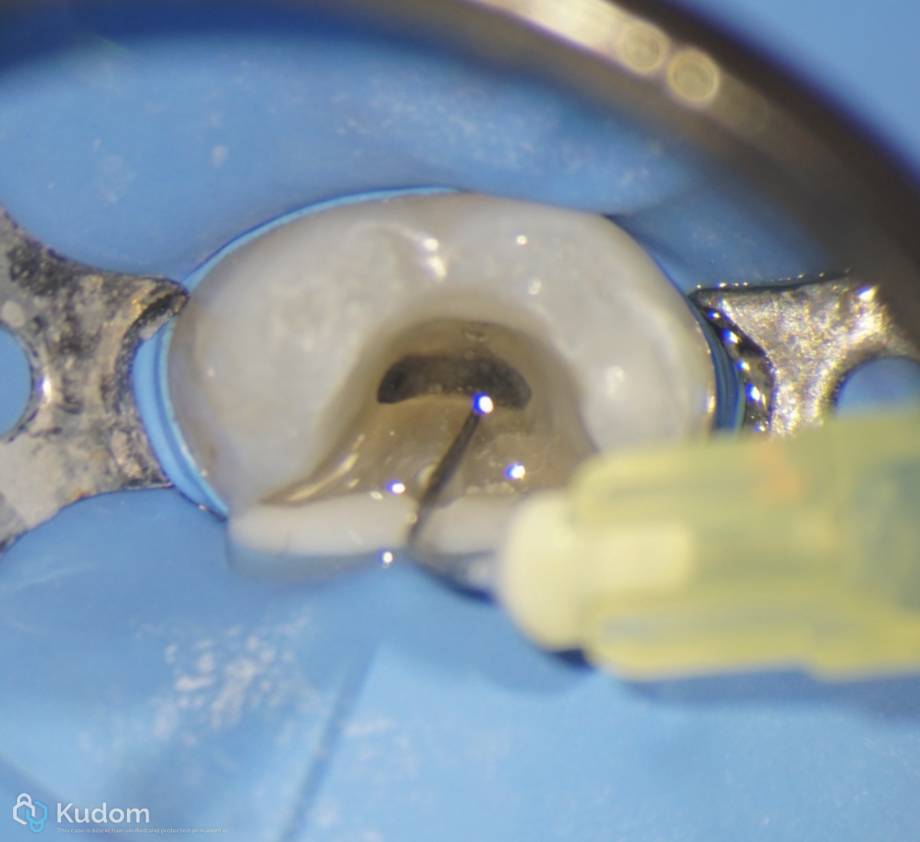
Fig. 12
Irrigation with Sodium hypochlorite
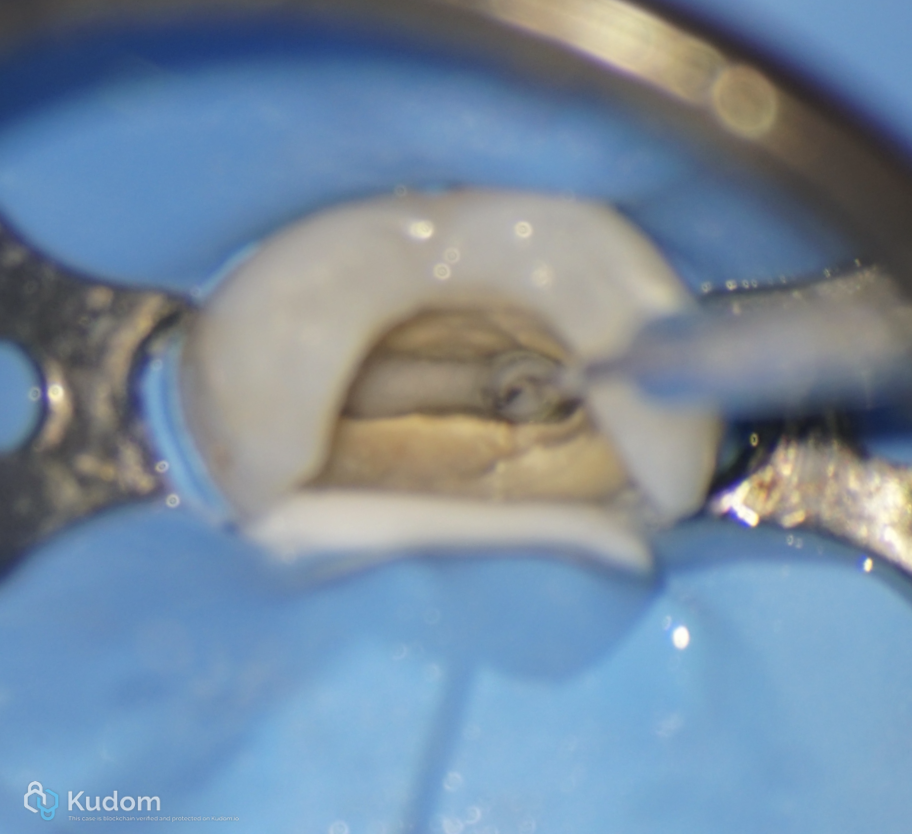
Fig. 13
Ultrasonic activation
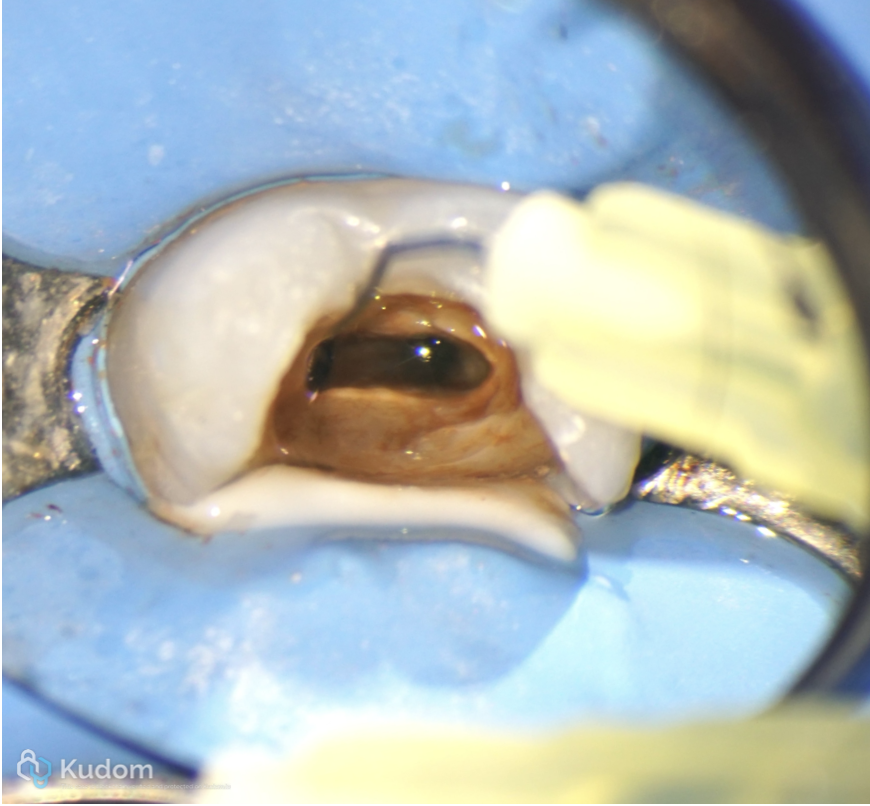
Fig. 14
Final irrigation with chlorhexidine digluconate 2%
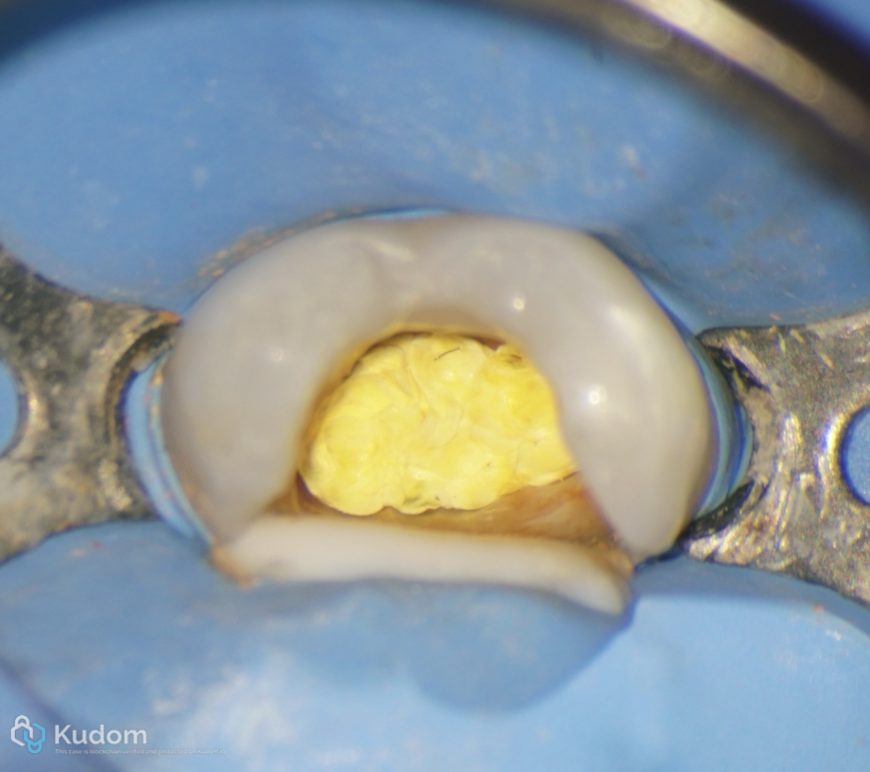
Fig. 15
Teflon tape to seal the canals orifices
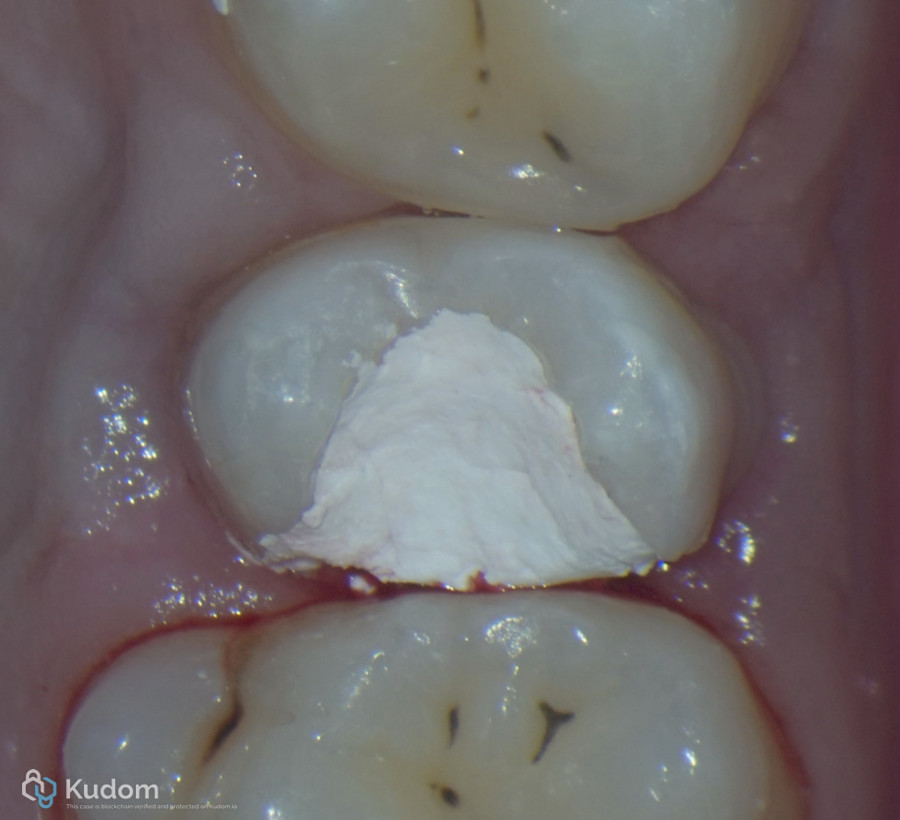
Fig. 16
Temporary filling
Antibiotic prescription:
-lincomycin 600mg vial
-metronidazole 500mg tab
-paracetamol 1000mg tab + ibuprofen 400mg tab (on
need)
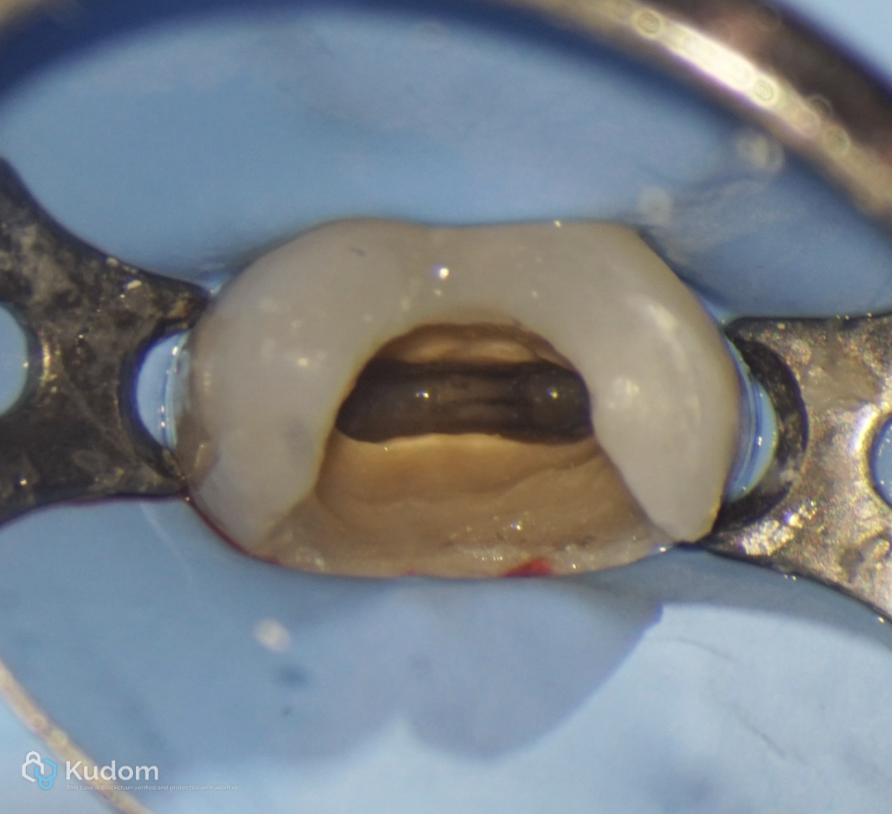
Fig. 17
Second visit
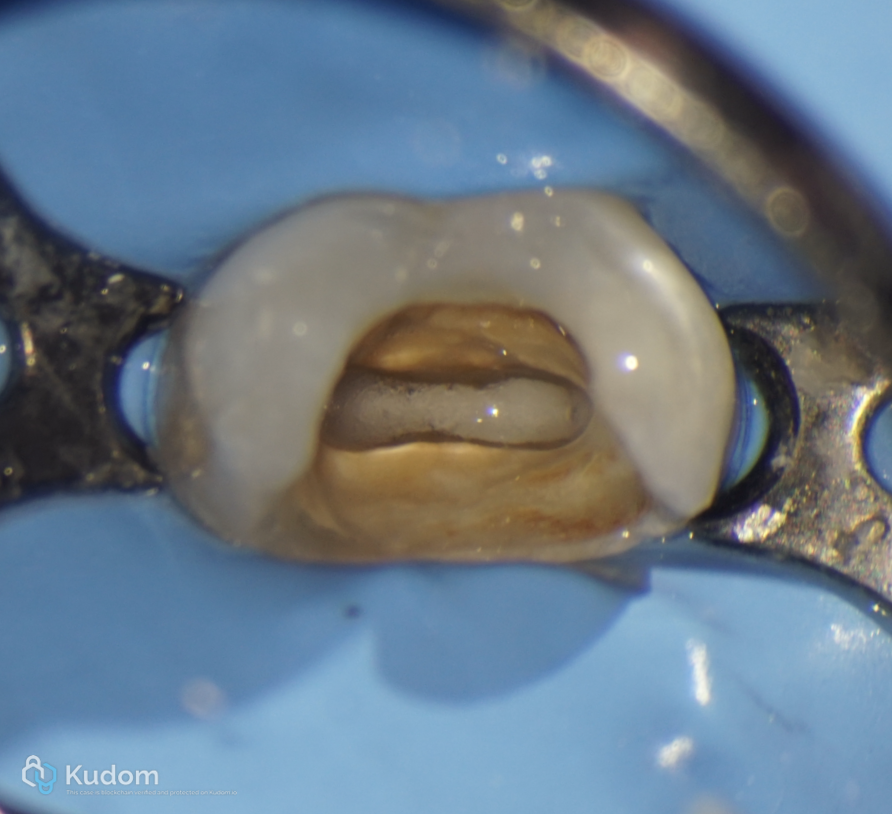
Fig. 18
Full irrigation protocol and activation
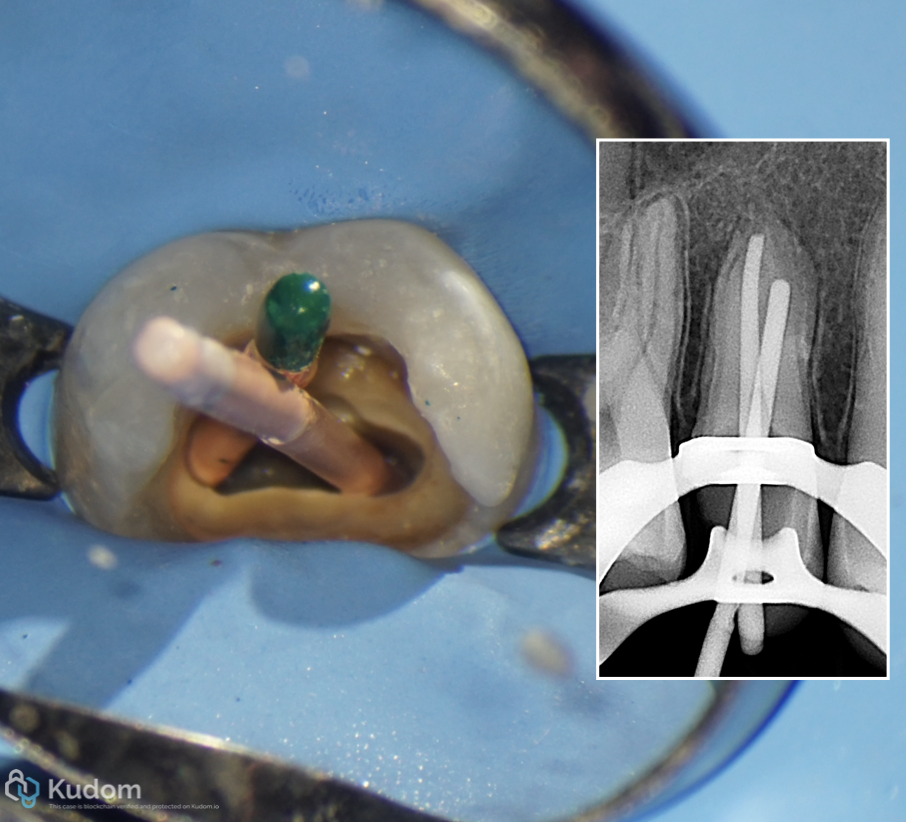
Fig. 19
This cones was used as flexible pluggers for packing and adaptation of MTA apically
Obturation from A to Z
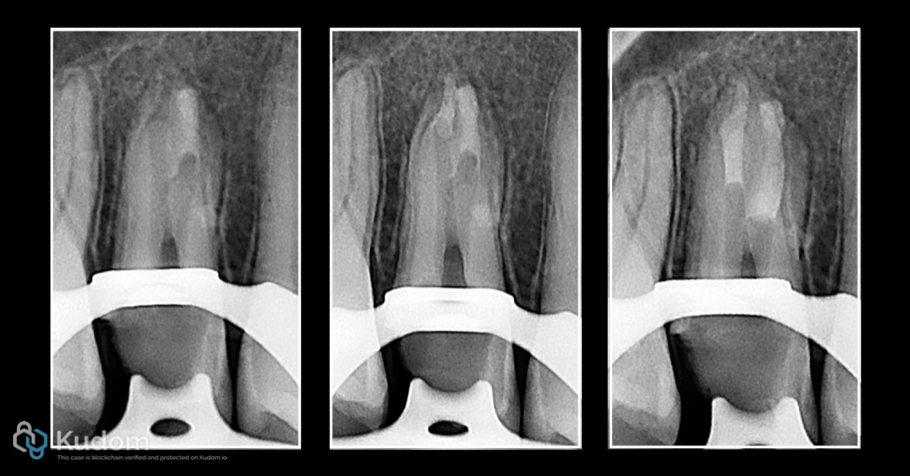
Fig. 20
MTA Apical plug in process
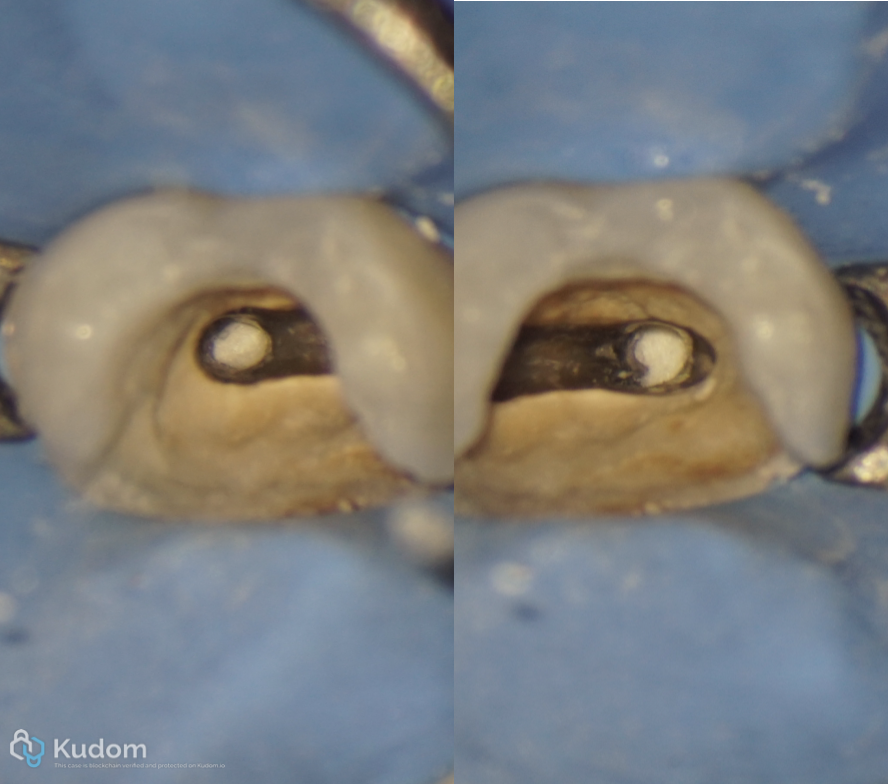
Fig. 21
Apical plug (close up)
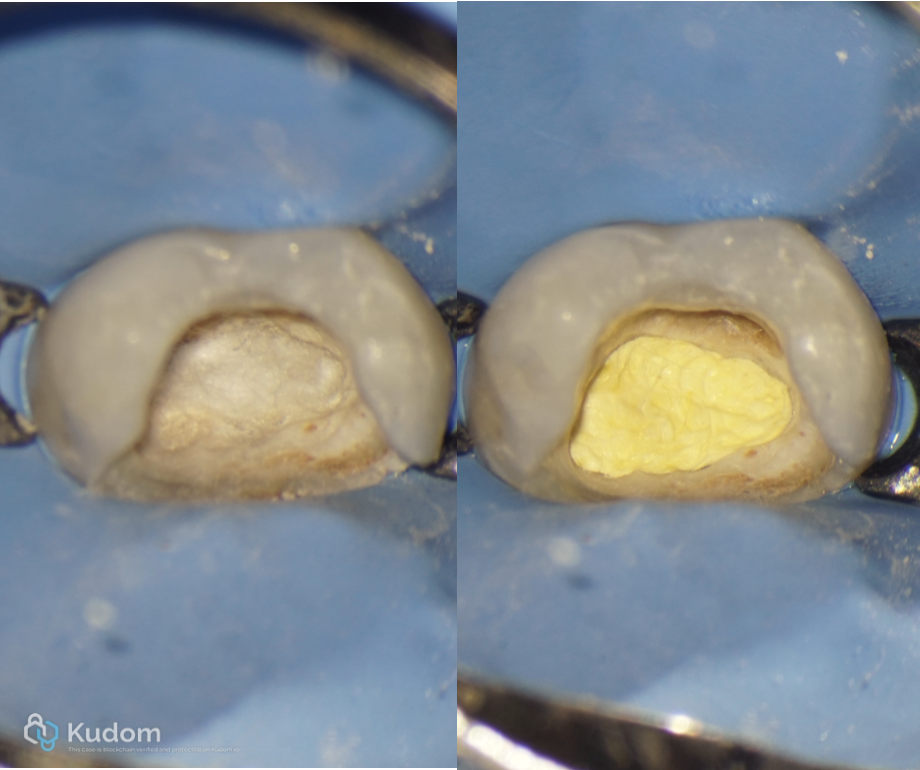
Fig. 22
Wet cotton pallet over the orifices and Teflon tape over it.
End of the second visit
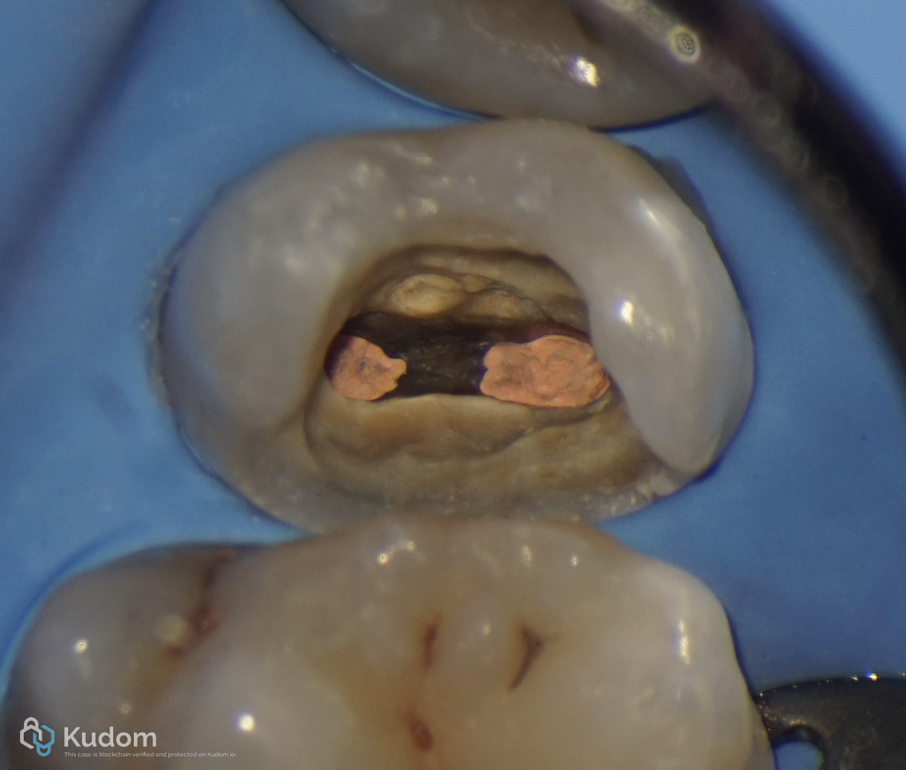
Fig. 23
Third visit
Back filling the remaining of the canals with Gutta percha
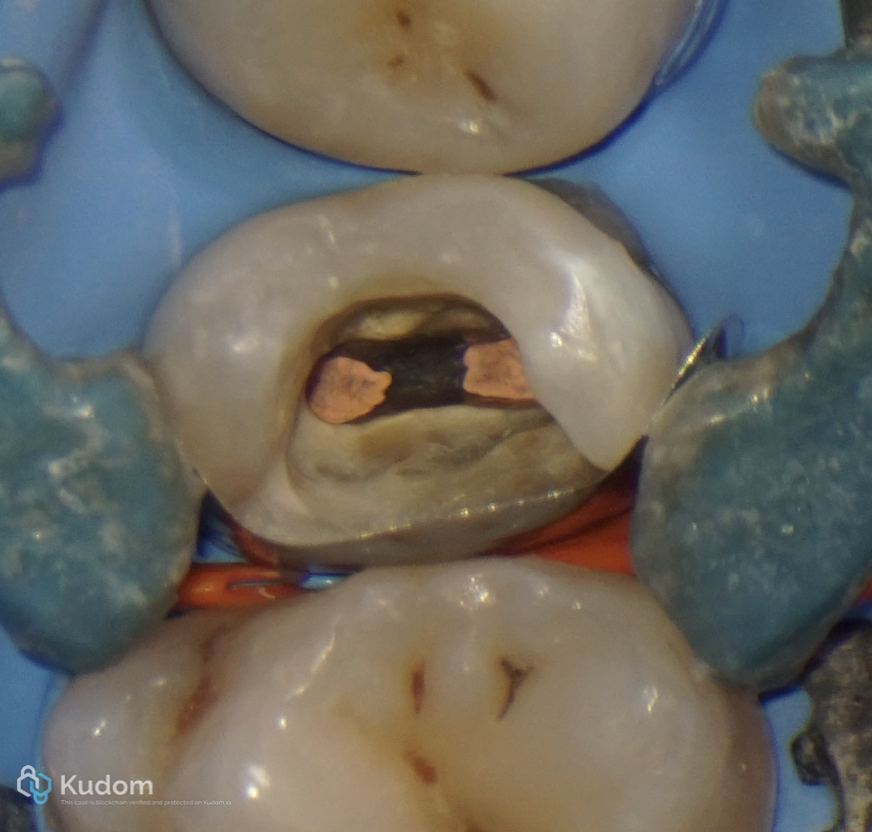
Fig. 24
Sectional-Matrix and pallodent v3 ring were used to restore the proximal wall
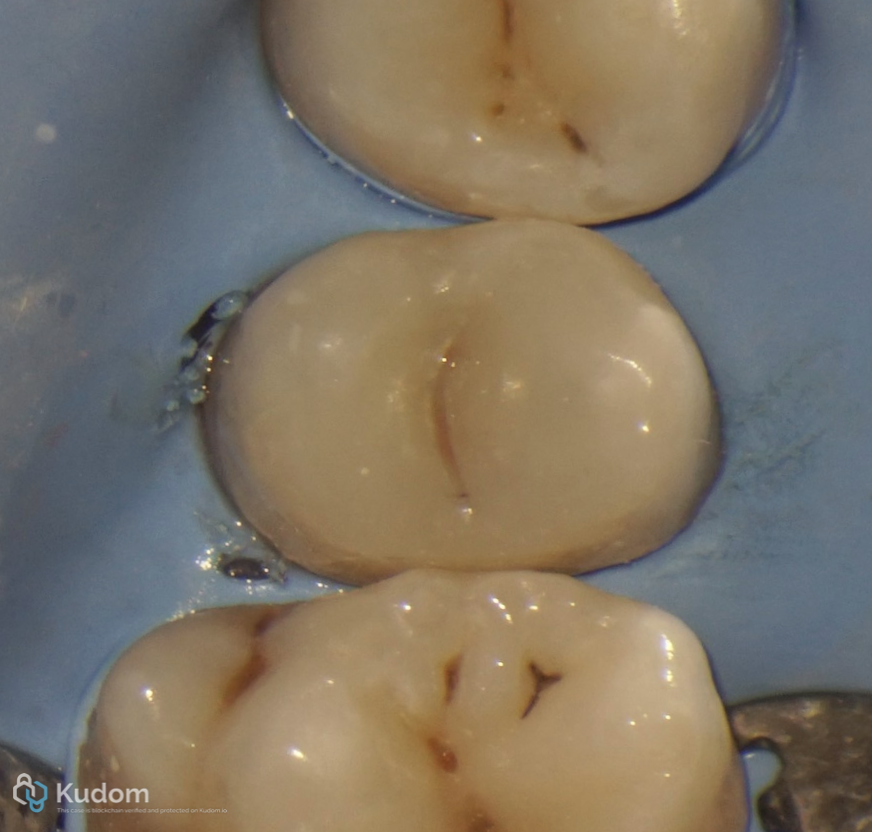
Fig. 25
Final restoration
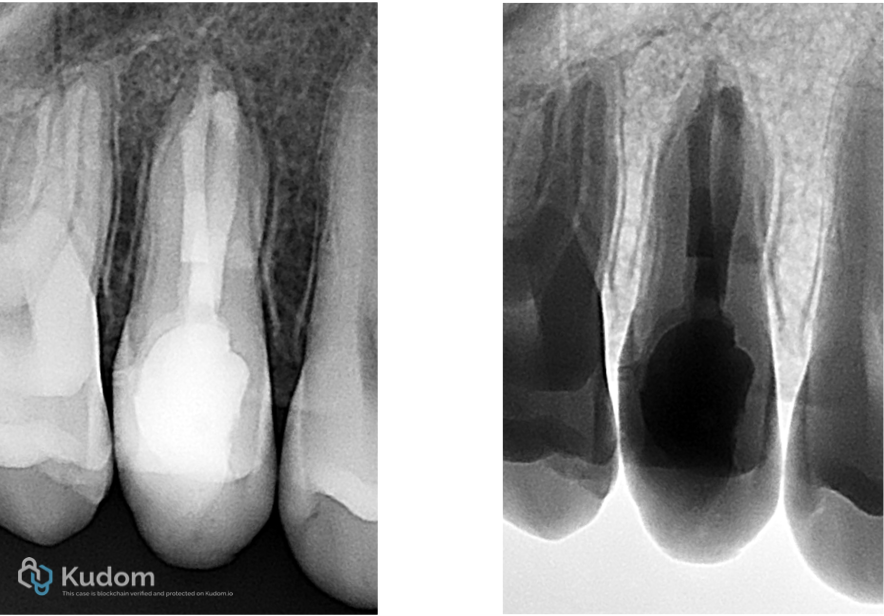
Fig. 26
Post-op Xray
Fig. 27
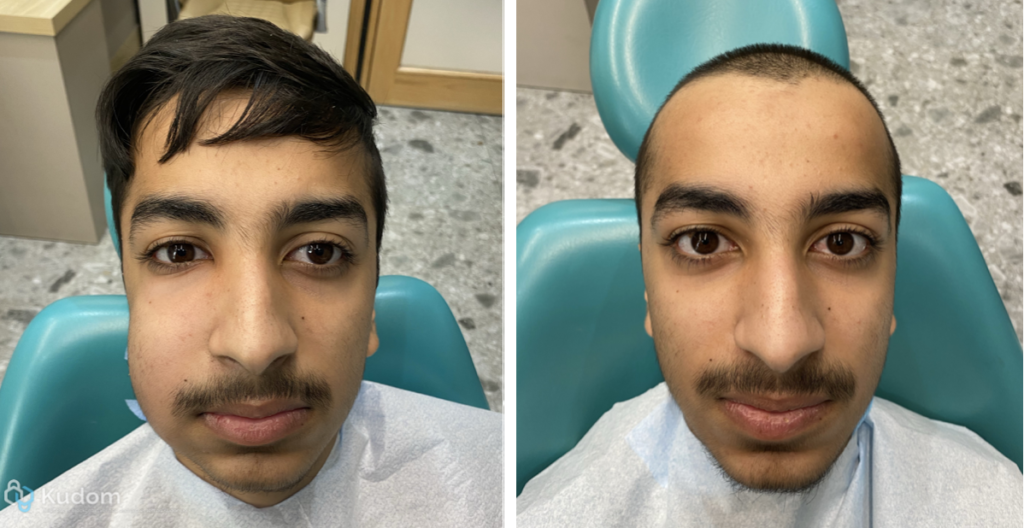
Happy patient with new RCT and new Haircut
Conclusions
Inadequate endodontic treatment can lead to persistent infection and subsequent periapical pathology, presenting clinically as facial swelling. Proper diagnosis, adherence to endodontic principles, and timely management are essential to resolve infection and prevent complications. This case emphasizes the importance of correct canal disinfection and obturation to ensure a favorable outcome and long-term tooth preservation.
Bibliography
Tabassum S, Khan FR. Failure of endodontic treatment: The usual suspects. Reviews the main causes of endodontic failure including poor debridement and obturation. Eur J Dent. 2016;10(1):144–147.
Akbar I. Radiographic study of the problems and failures of endodontic treatment. Analyses radiographic reasons for failed root canal treatments. Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2015;9(2):111–118.
Sawhny A, Singh R, Sharma S, et al. Endodontic Treatment Failure & its Management: A Review. A review of failure mechanisms and retreatment considerations in endodontics. J Clin Diagn Res. 2021;12(1)
Assessment of treatment failure in endodontic therapy. Int Endod J. 2016; Discusses clinical and radiographic assessment of failed endodontic therapy and persistent apical periodontitis.
Success and failure of endodontic treatment: predictability, complications, challenges and maintenance. Provides a broad overview of prognostic factors influencing endodontic success and complications. Br Dent J. 2025;