The extra root
27/11/2025
Fellow
Warning: Undefined variable $post in /var/www/vhosts/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/endodontics.styleitaliano.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
Warning: Attempt to read property "ID" on null in /var/www/vhosts/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/endodontics.styleitaliano.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
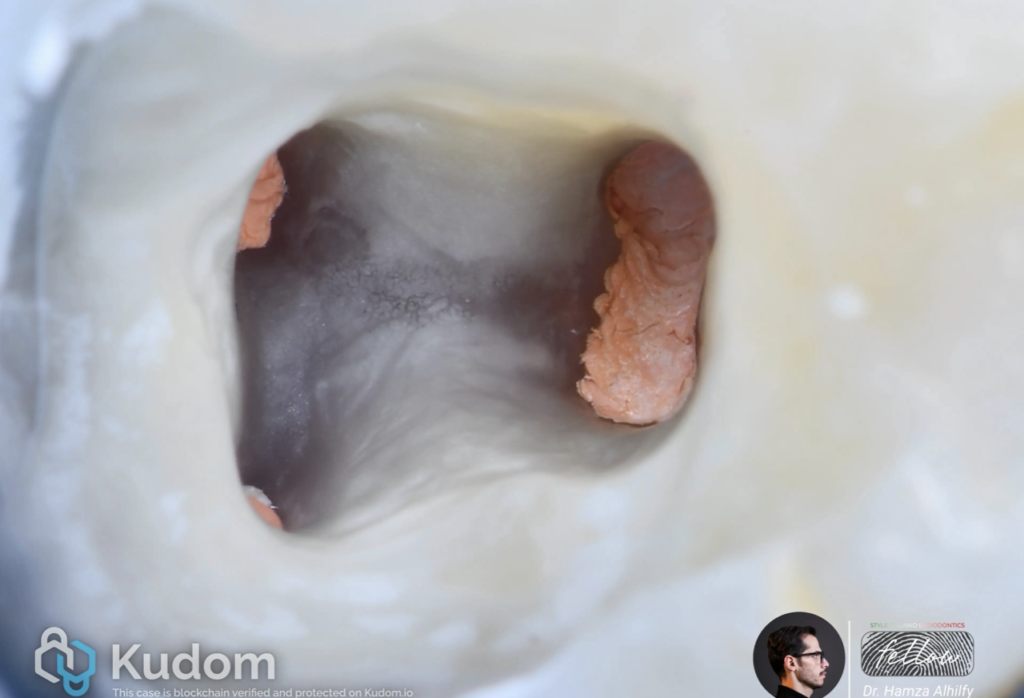
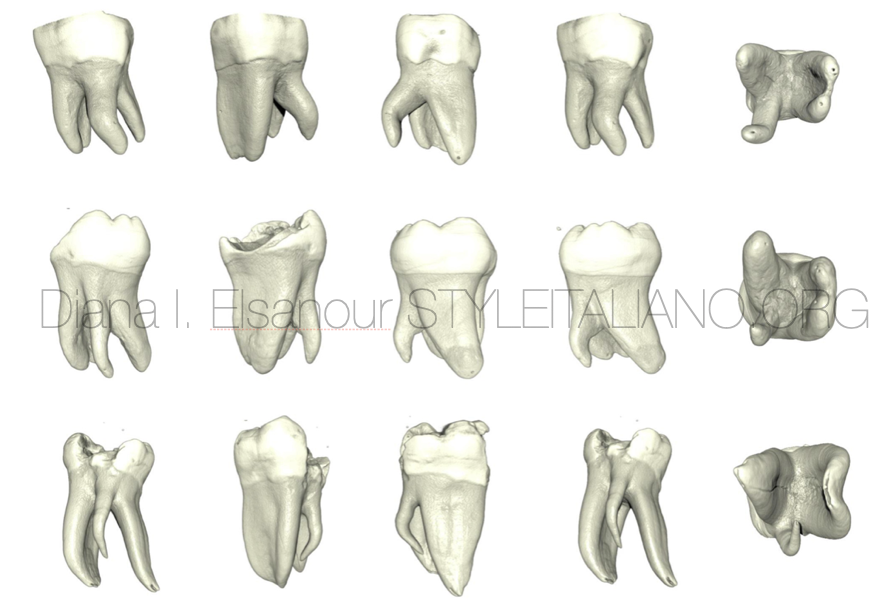
In endodontics, the terms "radix entomolaris" and "paramolaris" refer to specific anatomical variations of the roots of molar teeth, particularly in relation to their root canal systems. Identifying a radix ento/paramolaris is crucial for successful endodontic therapy, as failure to locate and treat all root canals can lead to treatment failure and persistent apical periodontitis. The radix
entomolaris (RE) is a supernumerary root located distolingually in mandibular molars whereas the radix paramolaris (RP) is an extra root located mesiobuccally.{1}
In the cases below I will show you different situations of (RE) and ( RP) .
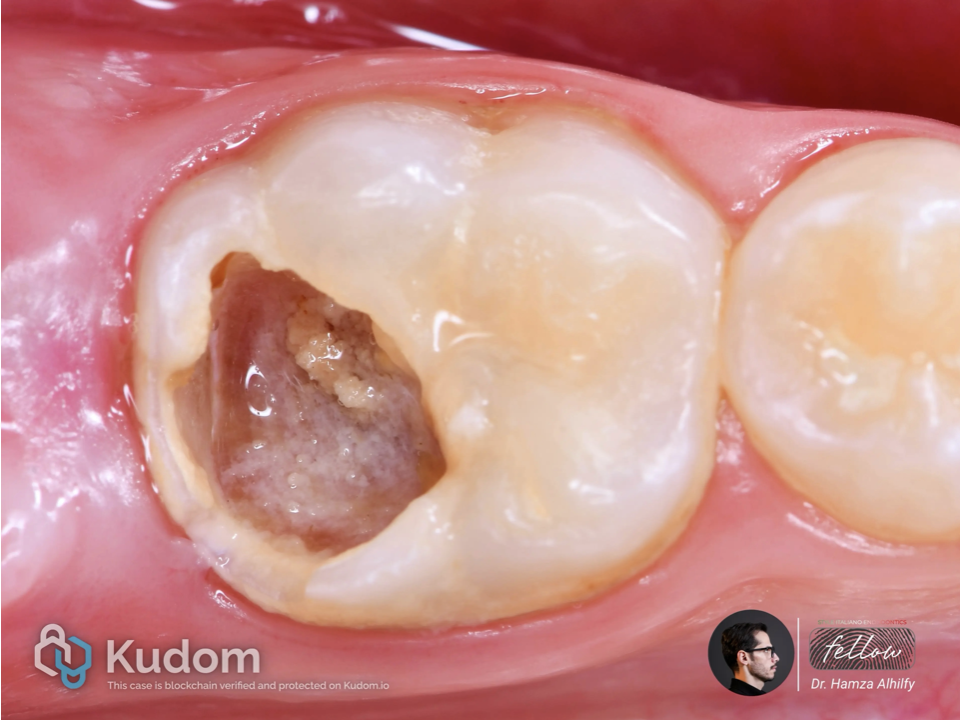
Fig. 1
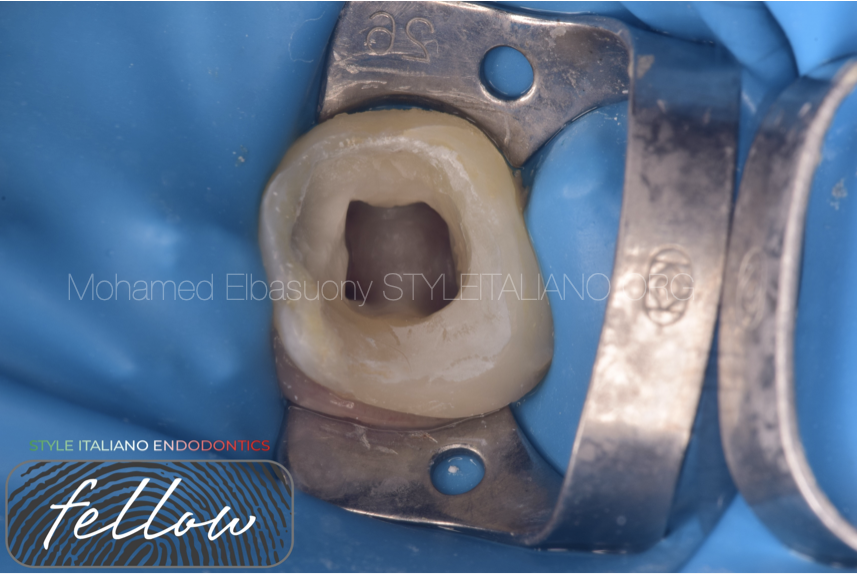
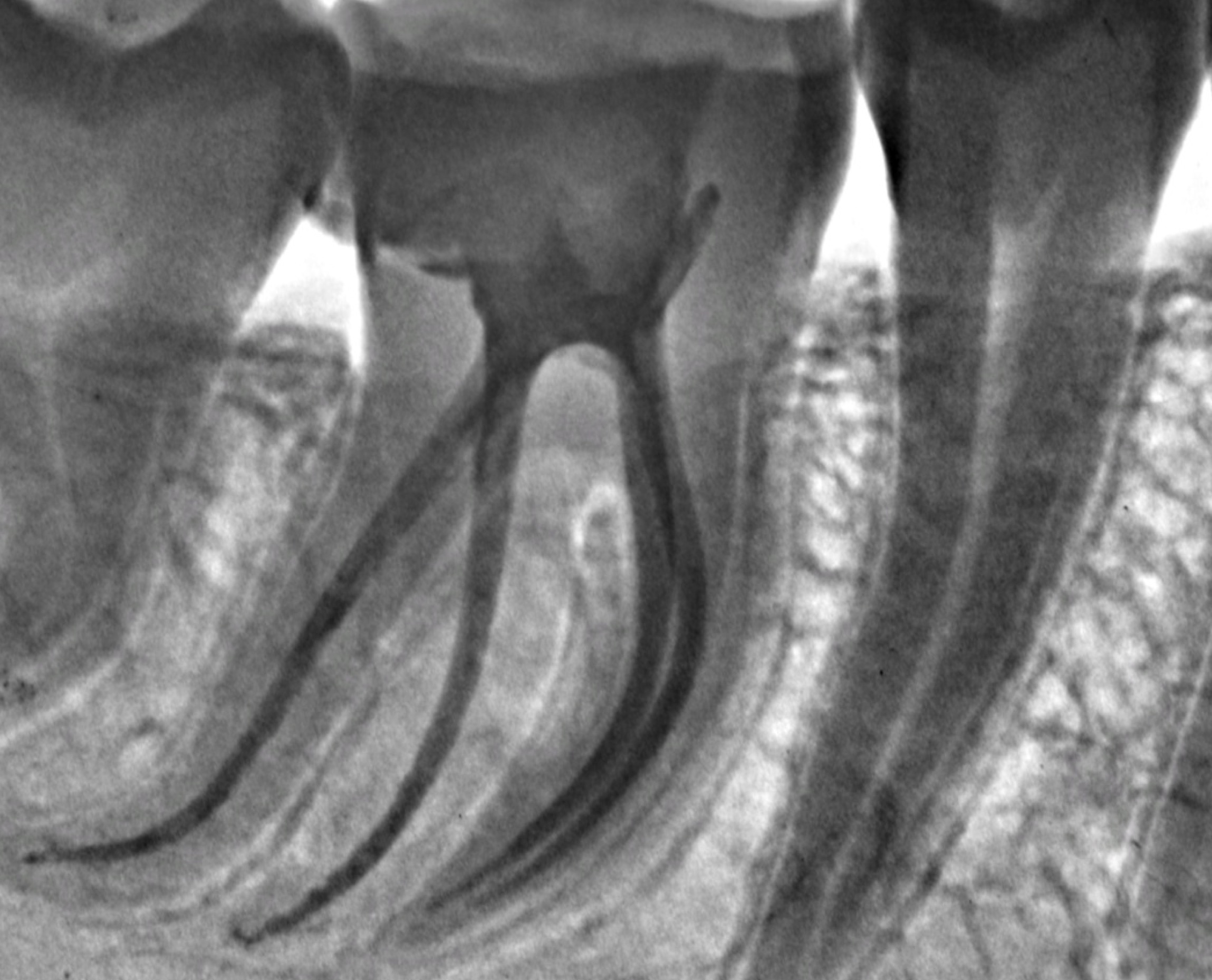
A lower left first molar suffering from acute irreversible pulpits . Preoperative x-ray shows (RE) extra root.
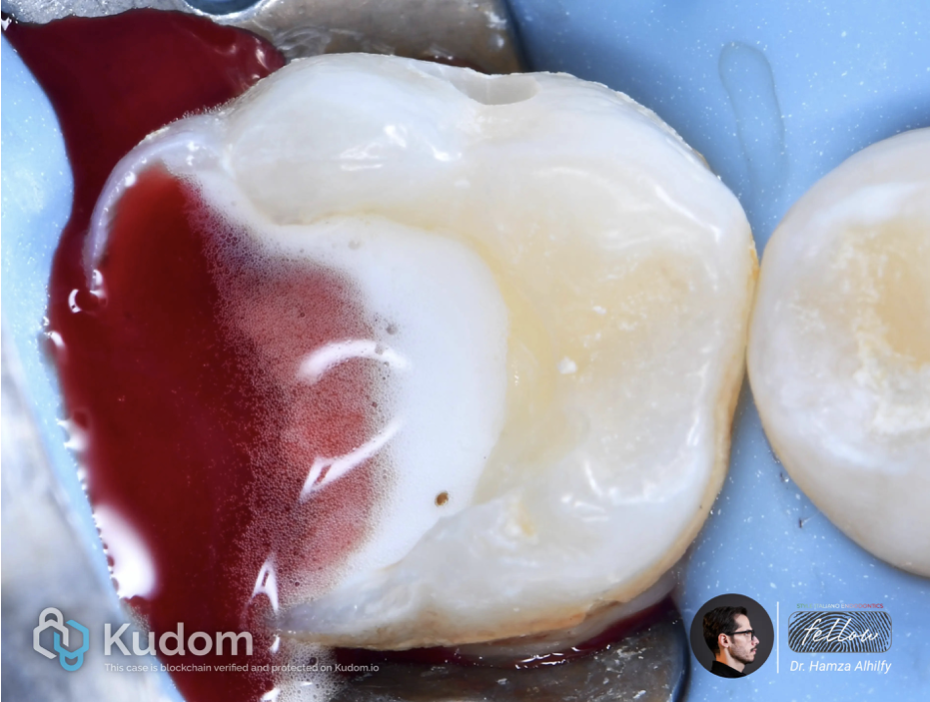
Fig. 2
After caries removal pulp chamber exposed and sever hemorrhage occurs . The image view NaoCl and blood combination.
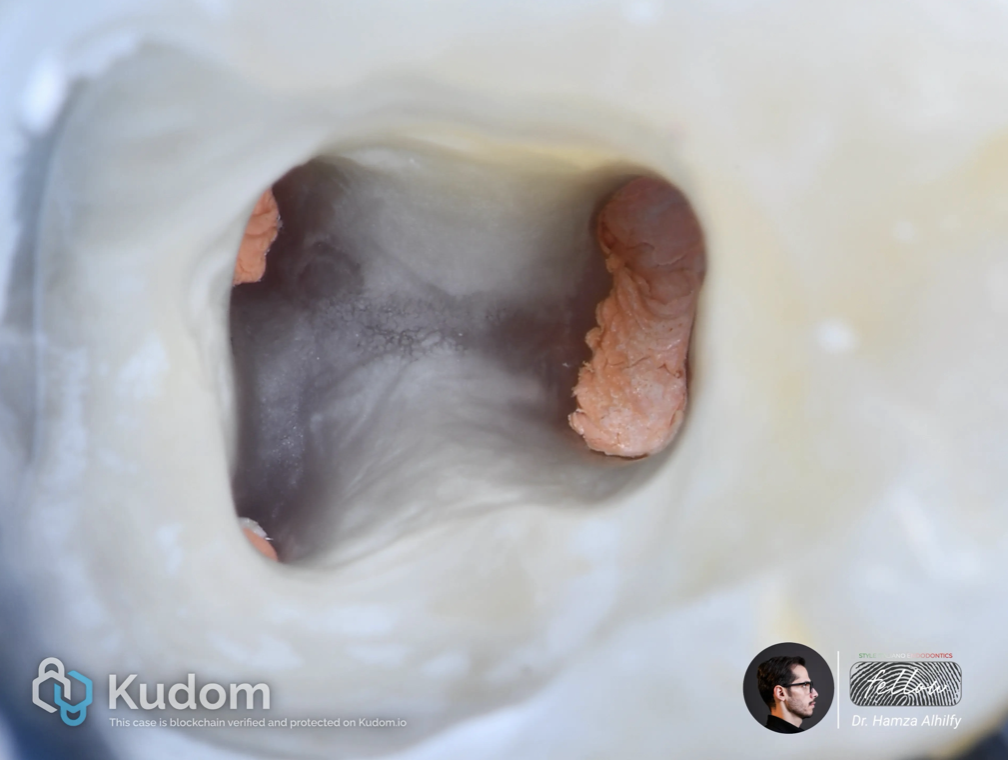
Fig. 3
Root canal treatment performed in single visit with the restoration.
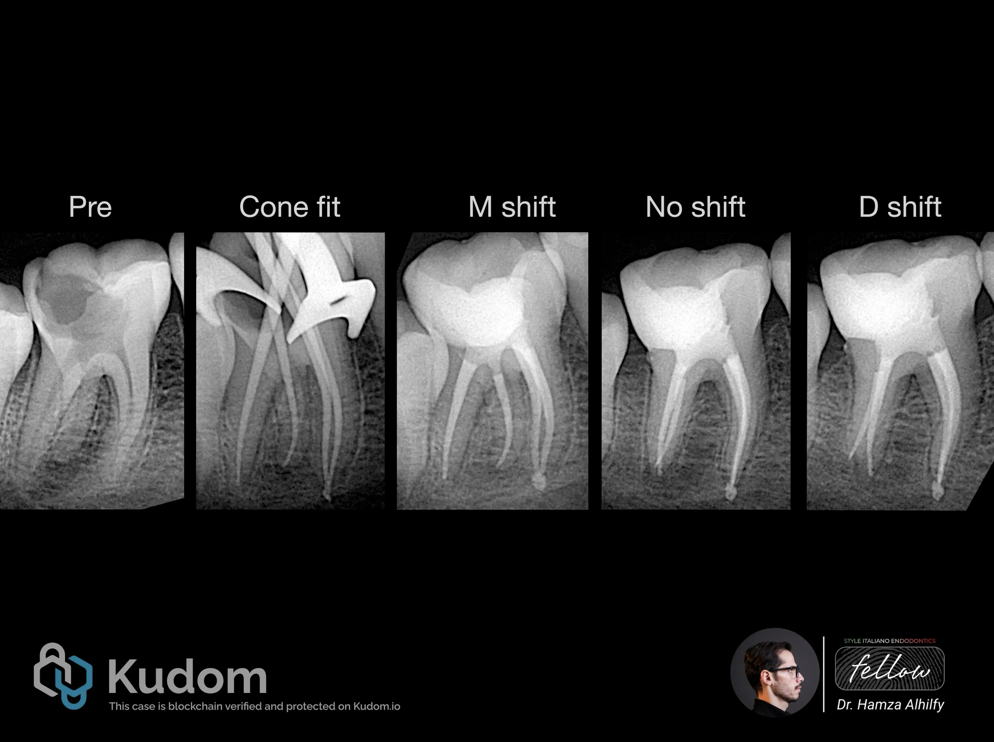
Fig. 4
Peri apical x-rays images for the single visit R C T .
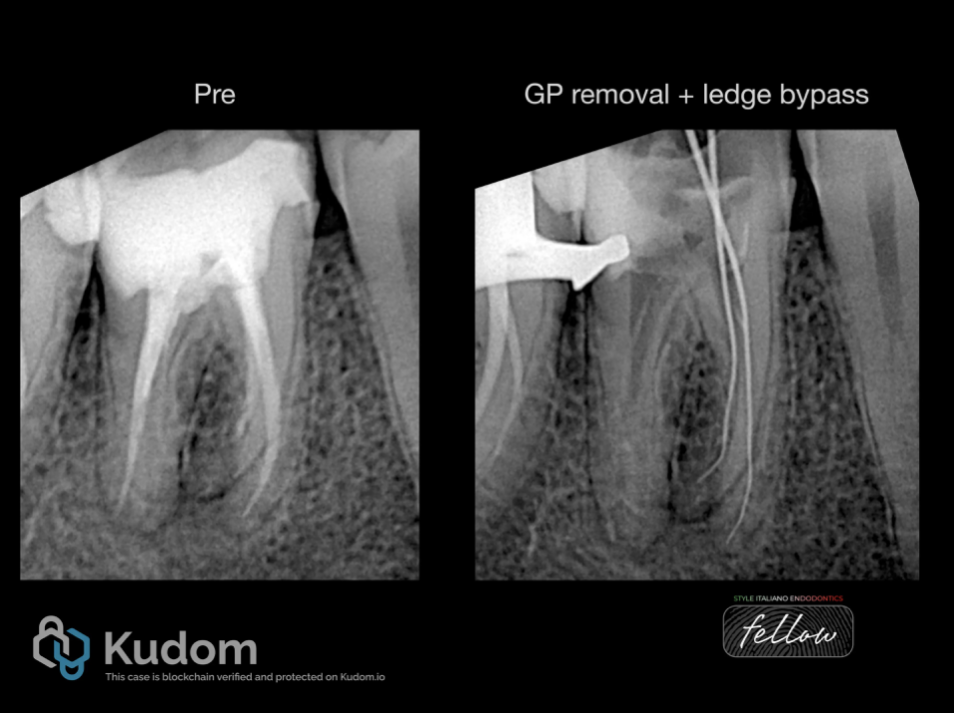
Fig. 5
Another lower first molar with shows a different anatomical variation with (RP) . The tooth previously improperly treated with short obturation and missed DL canal leading to periapical periodontitis.
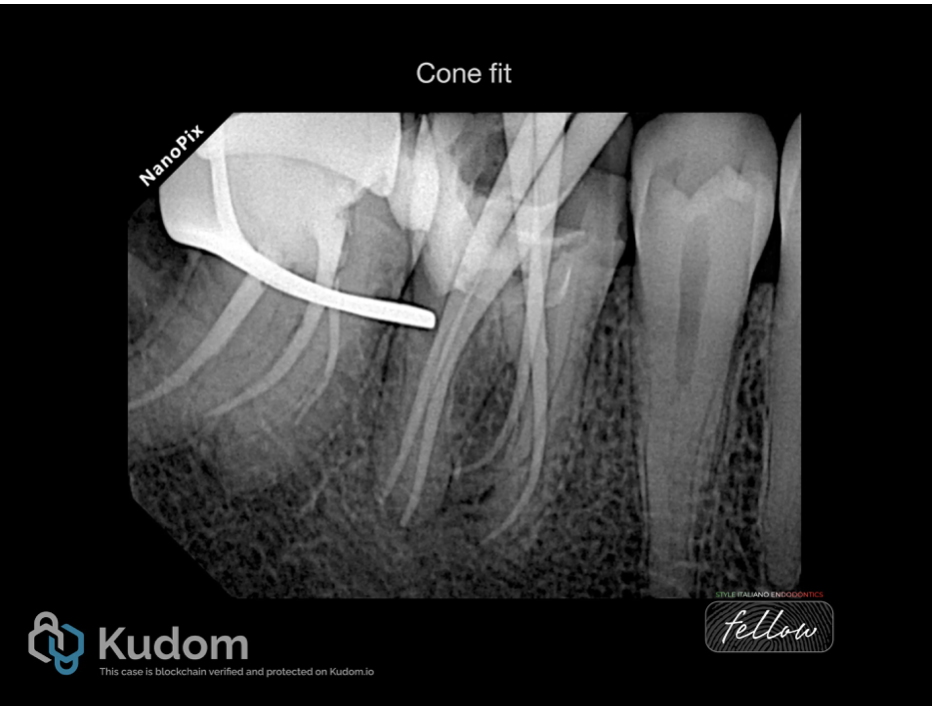
Fig. 6
After removing the old root canal filling and ledge bypass in the (RP) , A proper shaping and cleaning performed and cone fit x-ray image taken.
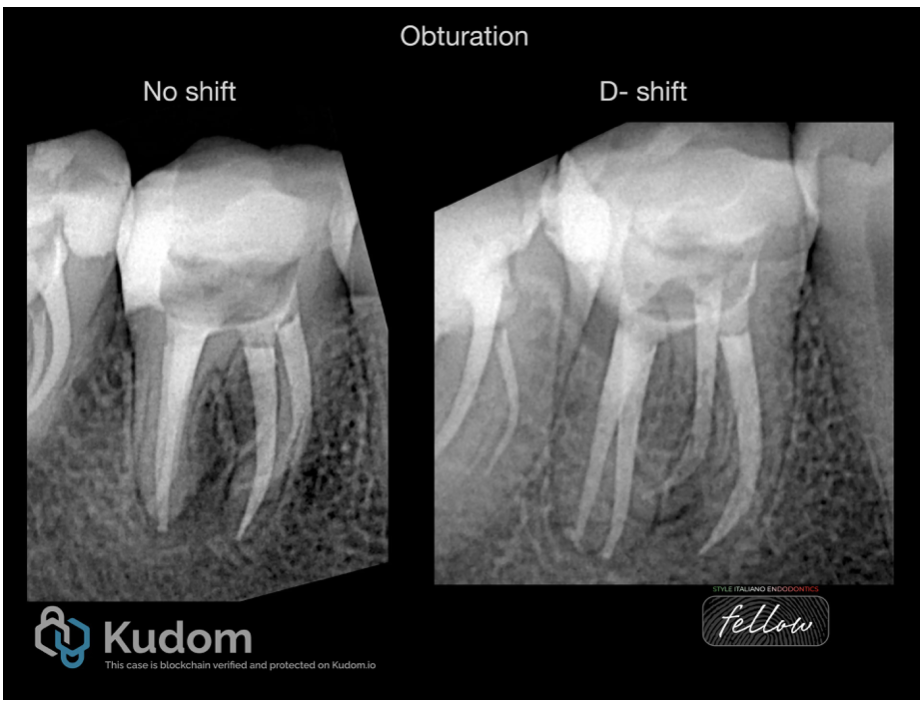
Fig. 7
Obturation done in the same visit. The image shows different shifts .
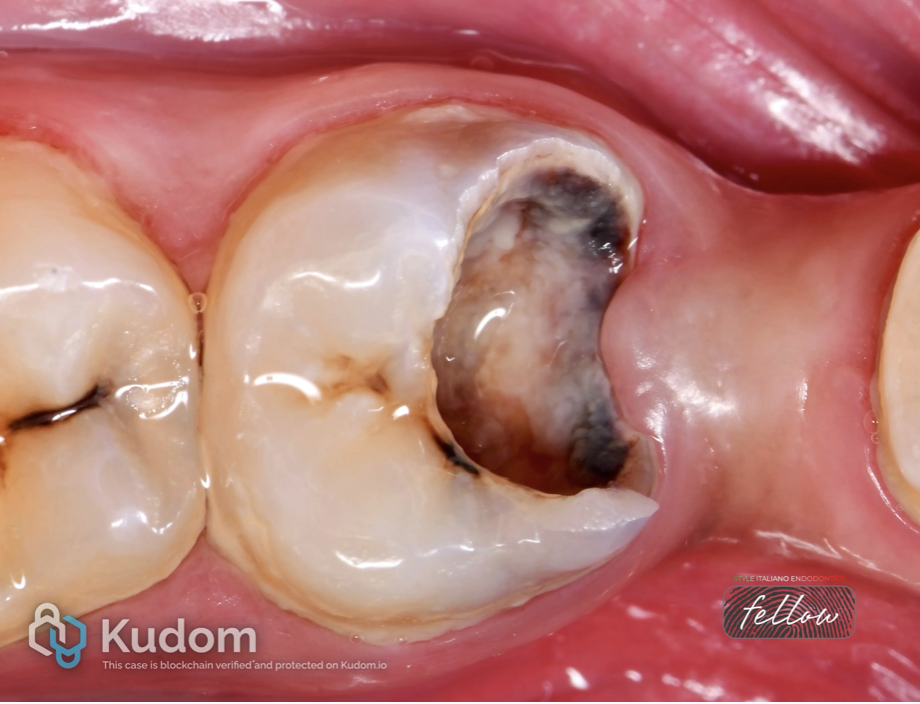
Fig. 8
Lower right first molar with irreversible pulpitis.
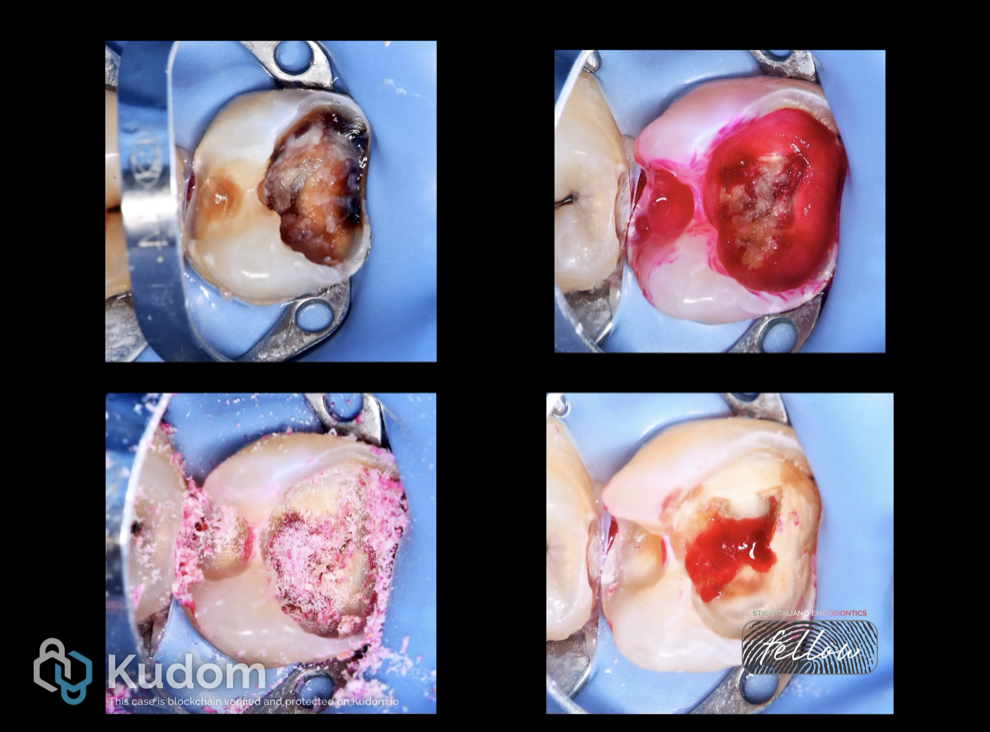
Fig. 9
Access opening done in the first visit.
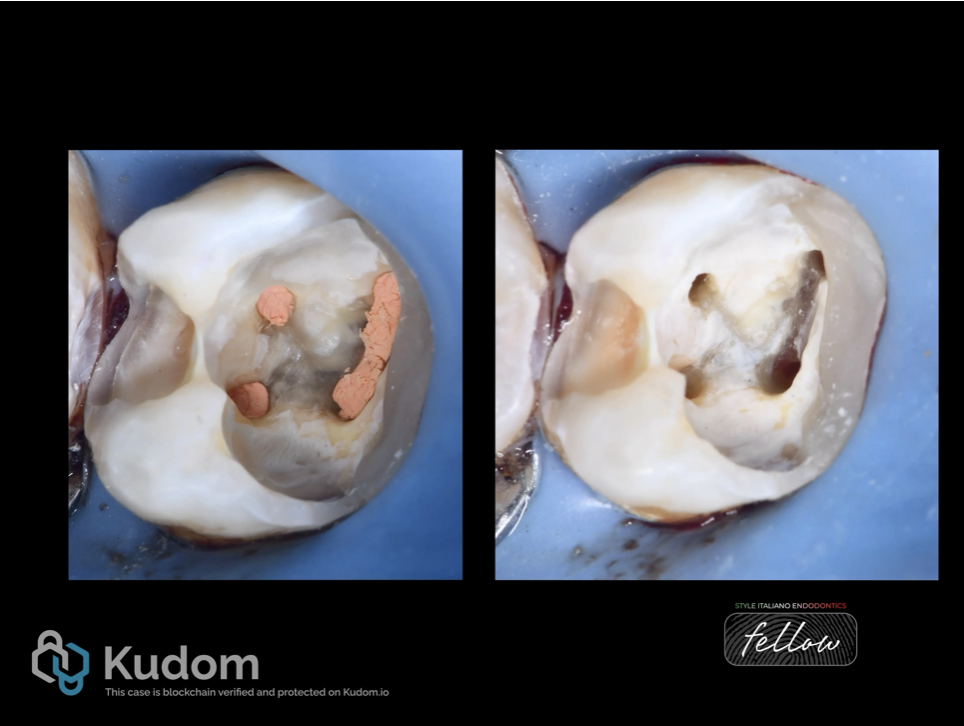
Fig. 10
In the second visit DME and obturation done .
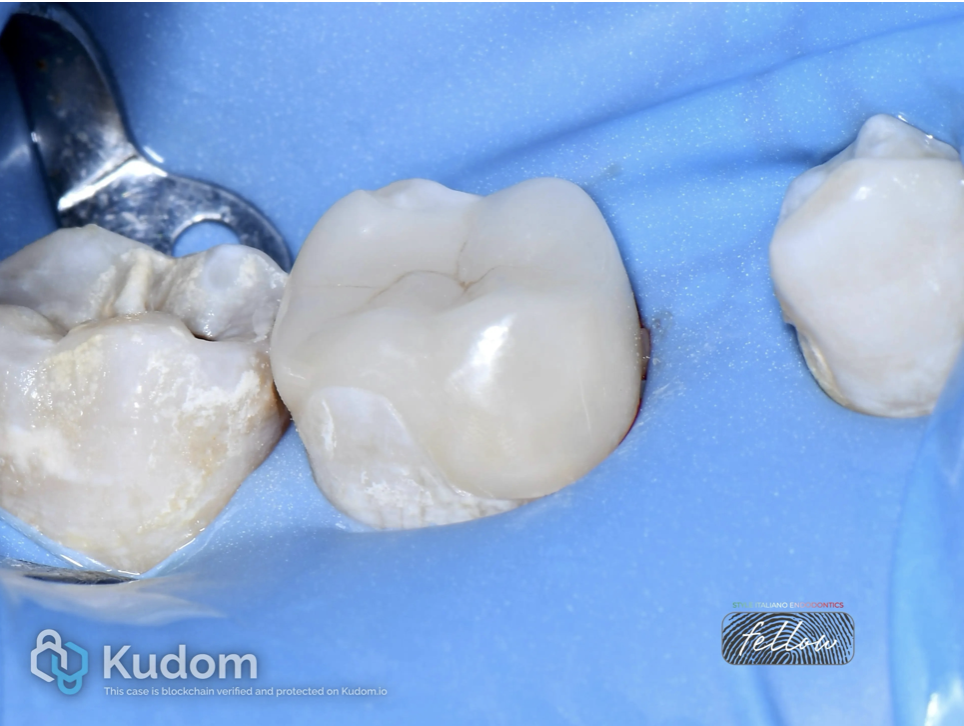
Fig. 11
Indirect e-max only as restoration.
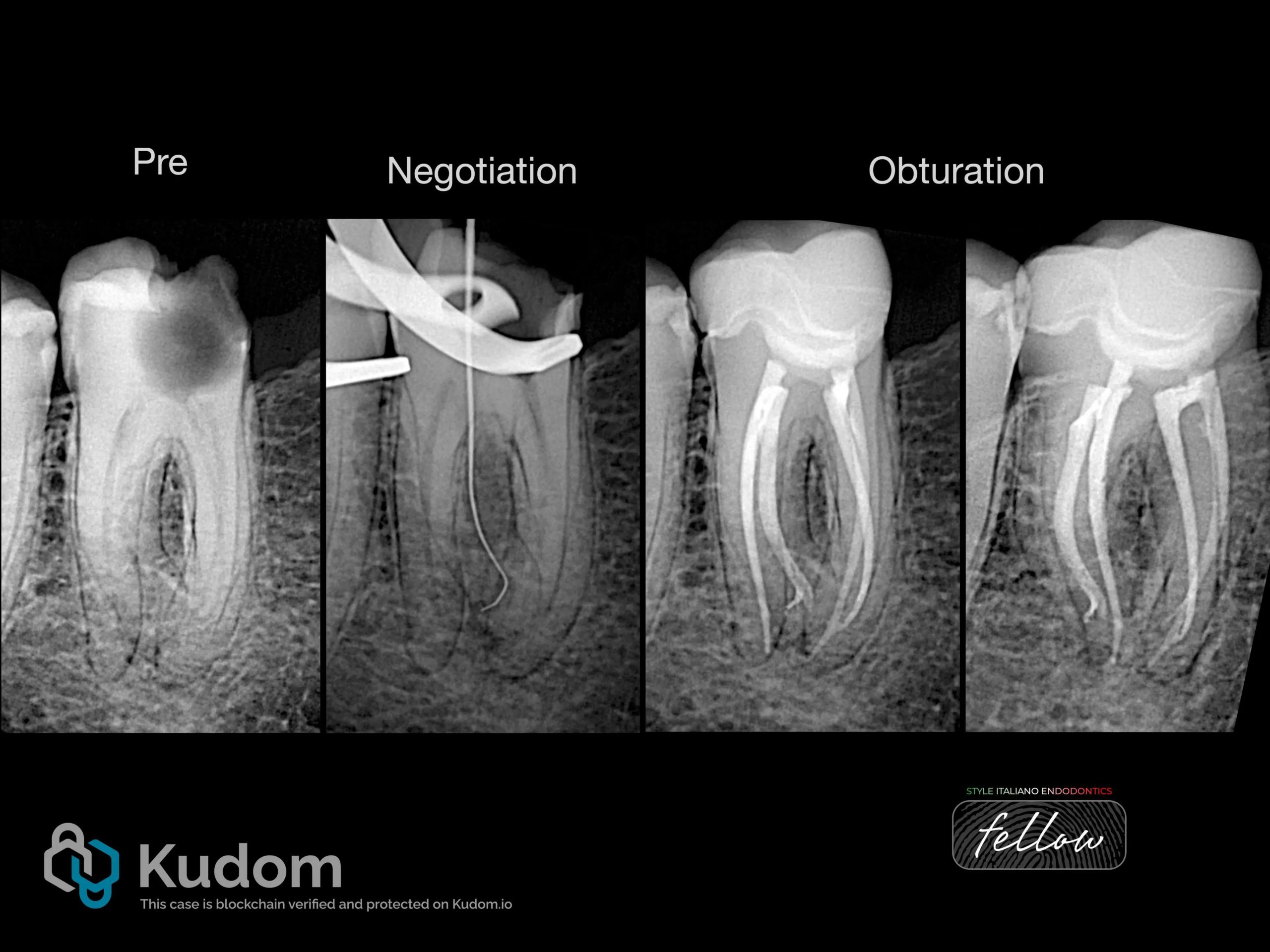
Fig. 12
X-rays of the case

Fig. 13
About the author
Hamza Alhilfy
Dr. Hamza Alhilfy
Graduated from Al-zahrawy dental college in Iraq .
5 years experience in dentistry especially endodontic treatments
Conclusions
Radix para and into molaris are anatomical variations that we must discover before work in diagnosis with the preoperative x-ray image or by the help of CBCT. Leaving such variation untreated could cause root canal treatment failure. So we should take our time with in diagnosis and reading the preoperative x-ray image properly.
Bibliography
Cohen's Pathways of the Pulp 12th Edition.
Calberson FL, De Moor RJ, Deroose CA. The radix entomolaris and paramolaris: clinical approach in endodontics. J Endod. 2007 Jan;33(1):58-63. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2006.05.007. Epub 2006 Jul 26. PMID: 17185133.
Harinkhere CK, Pandey SH, Patni PM, Jain P, Raghuwanshi S, Ali S, Bilaiya S. Radix entomolaris and radix paramolaris in mandibular molars: a case series and literature review. Gen Dent. 2021 May-Jun;69(3):61-67. PMID: 33908881.
Rokni HA, Alimohammadi M, Hoshyari N, Charati JY, Ghaffari A. Evaluation of the Frequency and Anatomy of Radix Entomolaris and Paramolaris in Lower Molars by Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) in Northern Iran, 2020-2021: A Retrospective Study. Cureus. 2023 Oct 11;15(10):e46854. doi: 10.7759/cureus.46854. PMID: 37954728; PMCID: PMC10637391.