Finding the MB2 canal
28/02/2022
Fitim Shabani
Warning: Undefined variable $post in /home/styleendo/htdocs/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
Warning: Attempt to read property "ID" on null in /home/styleendo/htdocs/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
In this clinical case I want to emphasize the importance of the instruments and the impact they give us during endodontic treatments, which are often complicated where the help of specific instruments makes the difference.
To achieve a successful endodontic treatment, we must meet three conditions : knowledge, experience and the proper instruments.
The chois of instruments is very important, because the proper instruments facilitate each step of the treatments, while the opposite only complicates it and often leads to mistakes.
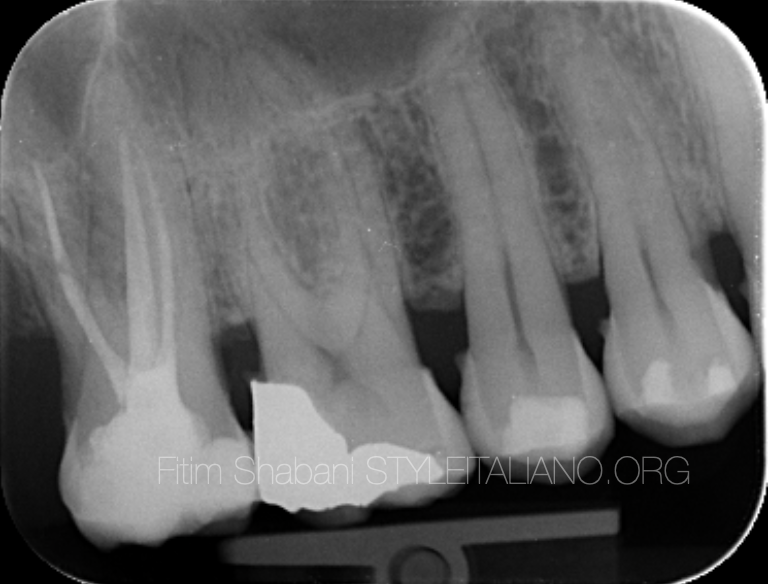
Fig. 1
Clinical case
Clinical data
The first upper right molar
Dg: Irreveresible acute pulpitis
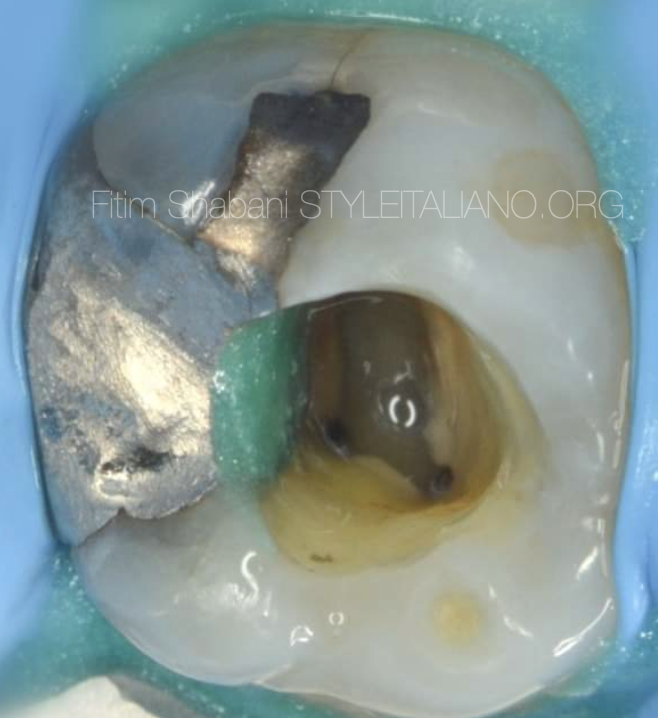
Fig. 2
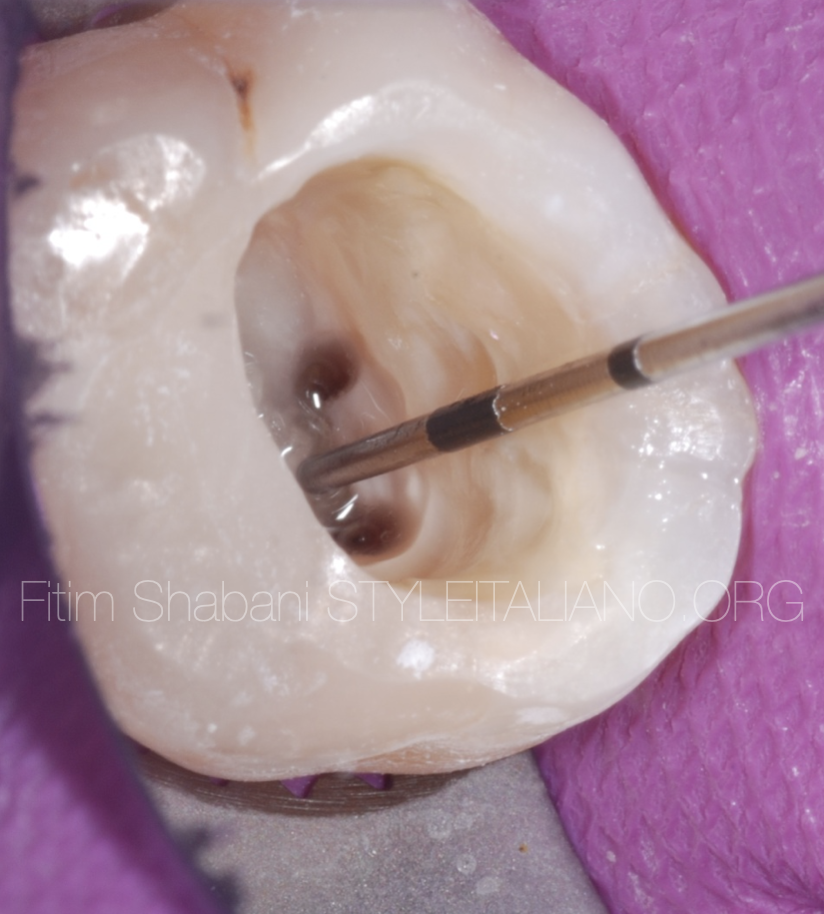
This is the view after endodontic access cavity preparation, shaping the three canals mesio-buccal 1, disto-buccal and palatal.
After that we have to search for the mesio-buccal 2.
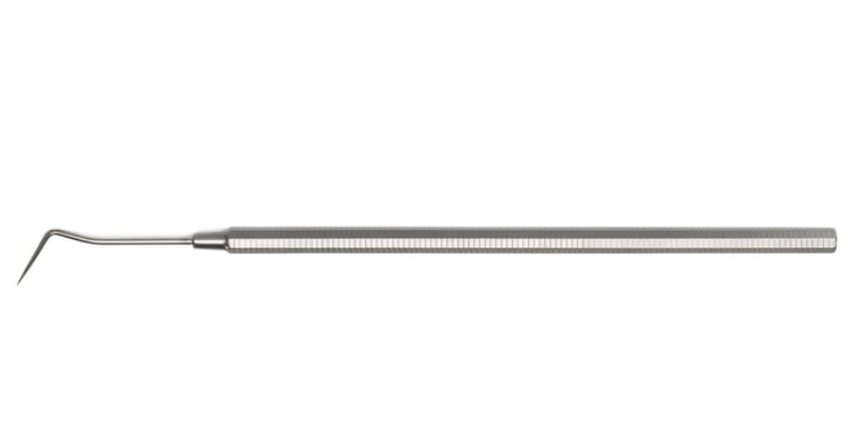

Fig. 3
Always when we explore the entrances of the canals, the first instrument we get is the dental probe.
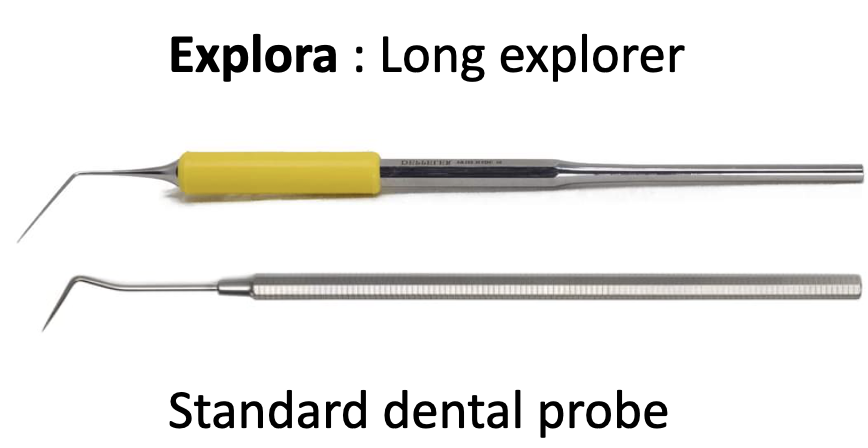
Fig. 4
Explora: long explorer
Compared to the standard probe, Explora is longer, thinner, more flexible, and the work under operating microscope is very easy, because it provides a good view thanks to its length and flexibility of the instrument.
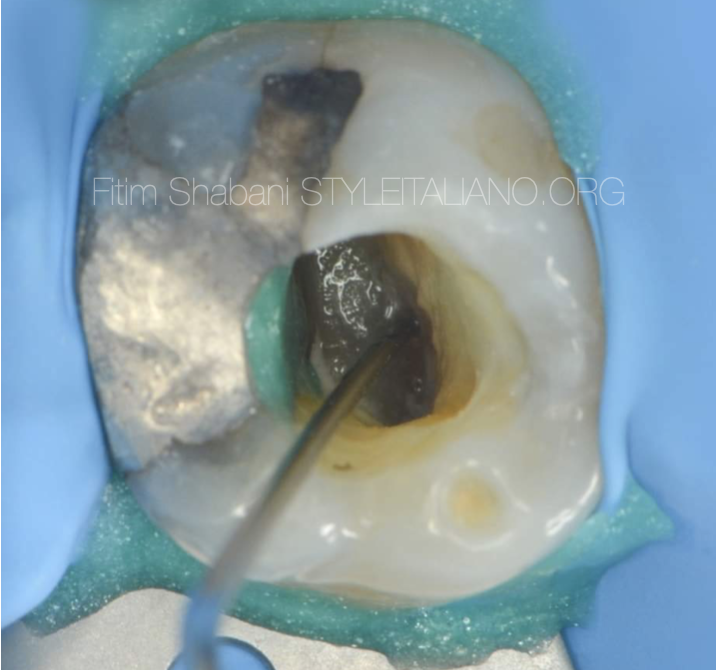
Fig. 5
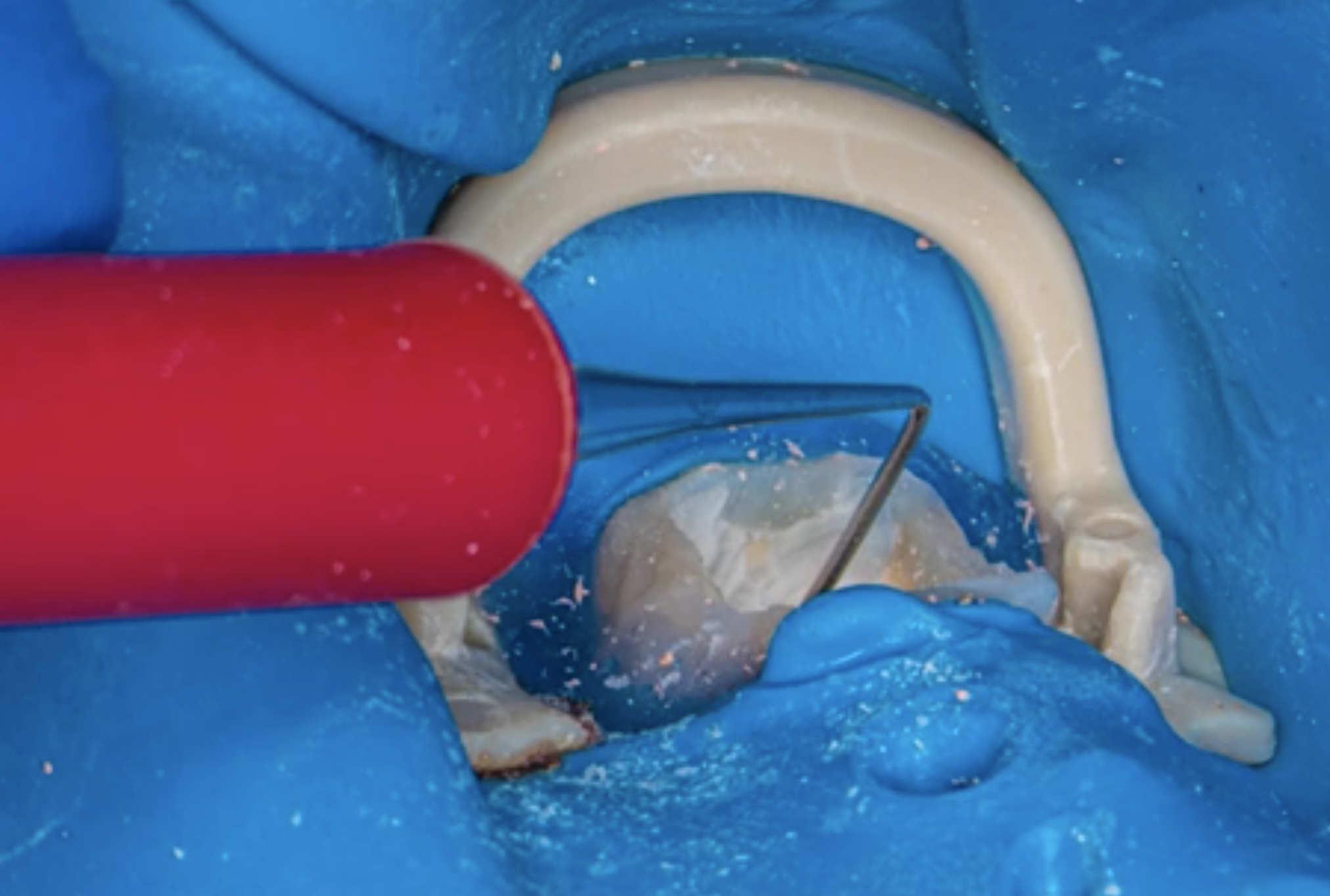
Localization of the canal entrance, the mesio-buccal 2 with Explora.
The very thin tip of the instrument enables easier insertion into the canal entrances, and the good view we have under operating microscope thanks to the flexibility and length of the instrument.
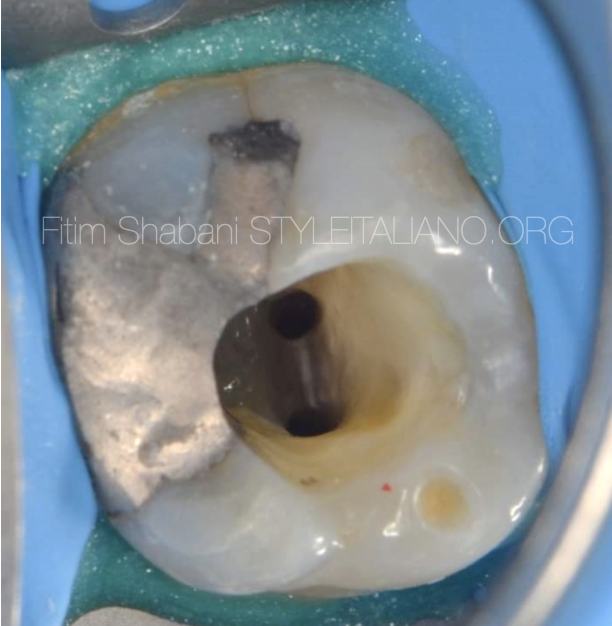
Fig. 6
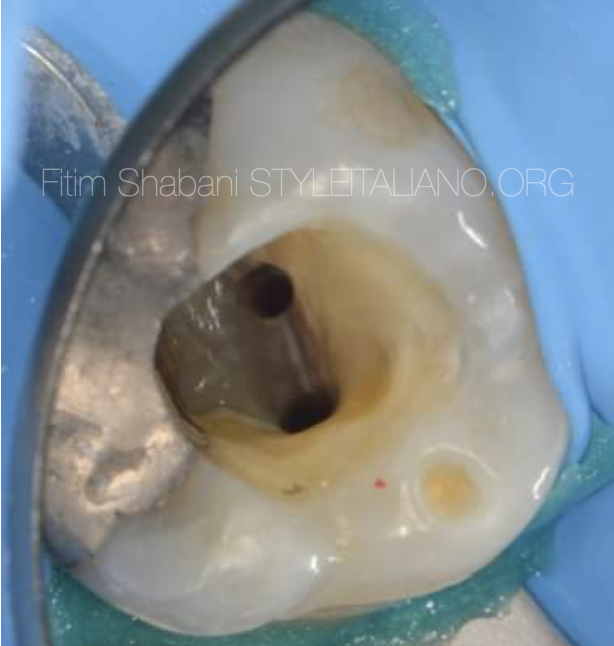
The view after shapping the second mesiobuccal canal.
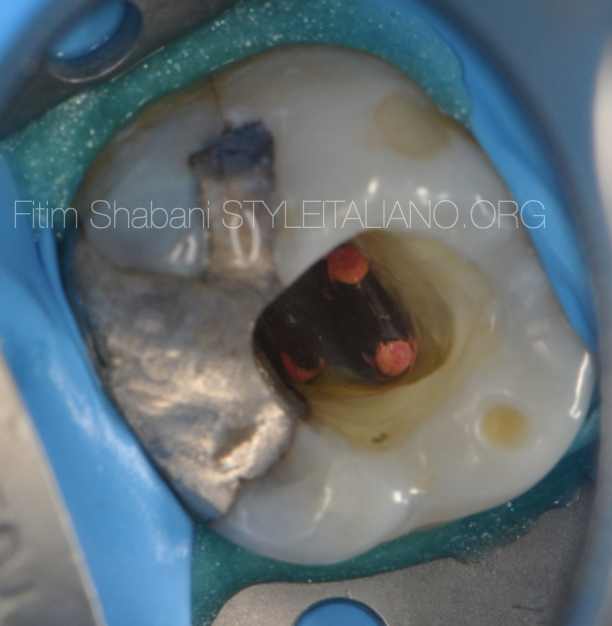

Fig. 7
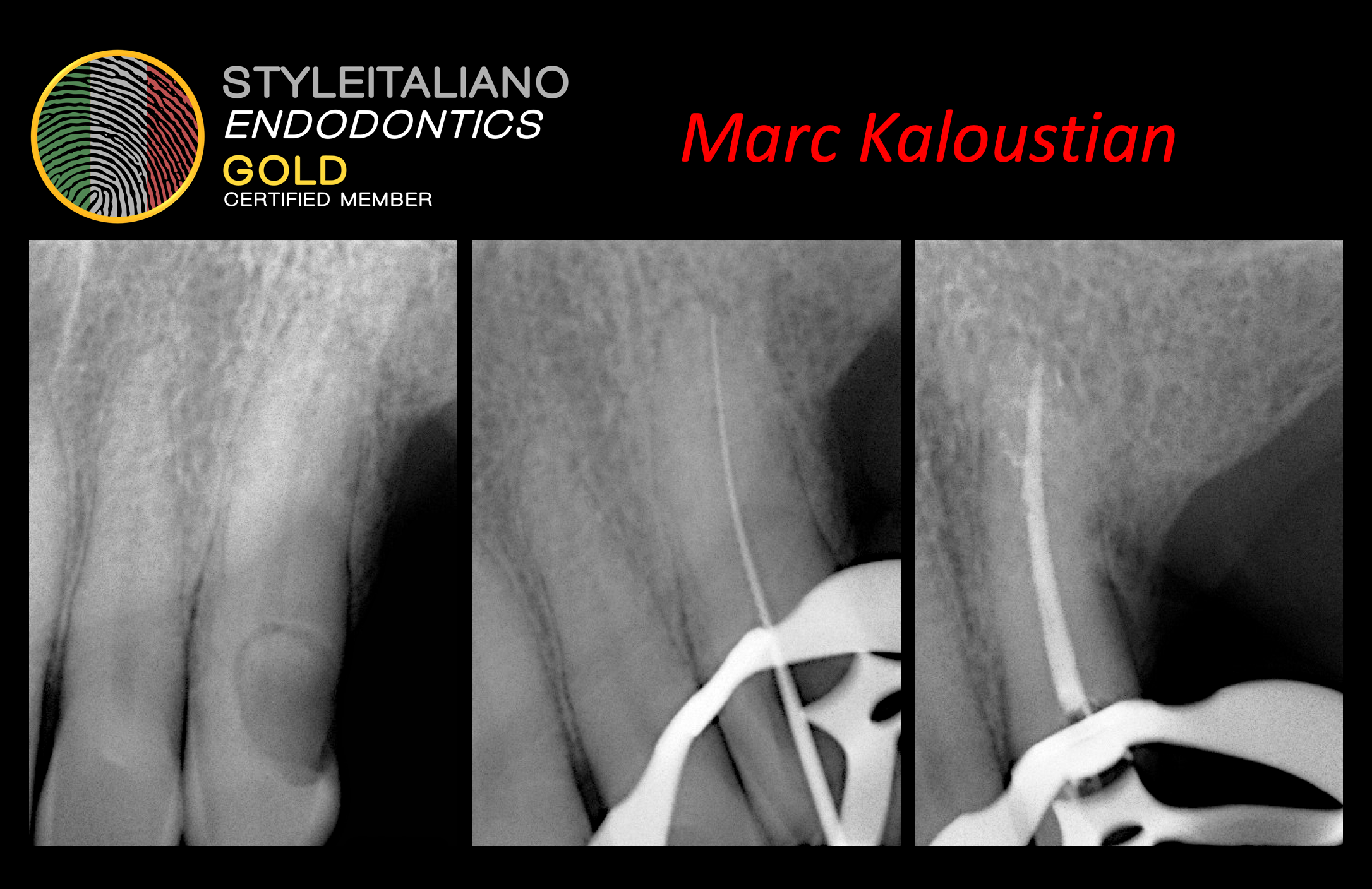
The view after Obturation
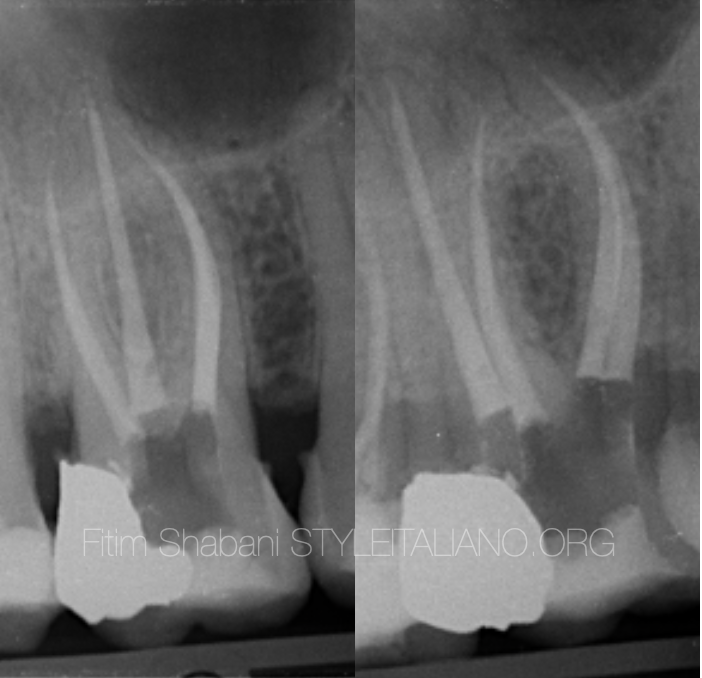
Fig. 8
Final X-ray
Conclusions
It is true that we do endodontic treatments with our knowledge and hands, but they become much easier and safer when we use the proper instruments, which are dedicated to each step of endodontic treatments.
Bibliography
-Louis J. Buhrley, DMD, Michael J. Barrows, DDS, MS, Ellen A. BeGole, PhD, and Christopher S. Wenckus, DDS , Effect of Magnification on Locating the MB2 Canal in Maxillary Molars, Journal of Endodontics 2002
-Marcelo Santos Coelho, Mariane Floriano Lopes Santos Lacerda et Al. Locating the second mesiobuccal canal in maxillary molars: Challenges and solutions, Clinical,cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry 2018
-Adham A.Azim BDS, Katharina A.Azim,MA,Med Allan S.Deutsch, DMD, and George T.-J. Huang, DDS, MSD,Dsc Acquisicion of Anatomic Parameters Concerning Molar Pulp Chamber Landmarks Using Cone-beam Computed Tomography, JOE 2014
-Lieutenant Commander Bernard H. Hofmann, DC, USNR and Captain Jeffrey R. Thorpe, DC, USN, Location of the second mesiobuccal canal of maxillary molars in endodontic therapy, Naval Postgraduate Dental SchoolNational Naval Dental Center Bethesda, Maryland December 2002.
-Paul Krasner, DDS, and Henry J. Rankow, DDS Anatomy of the Pulp-Chamber Floor, Journal of Endodontics
-Mitchell H. Davich, DMD, FACD, FICD The MB2 Canal: Following the Map of the Pulpal Floor, Endodontic therapy Vol 5 Nr 2.