External resorption Part II
03/04/2025
Fitim Shabani
Warning: Undefined variable $post in /home/styleendo/htdocs/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
Warning: Attempt to read property "ID" on null in /home/styleendo/htdocs/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
Root resorption is the loss of hard dental tissue due to the action of osteoclastic cells. External resorptions present a challenging clinical situation; often, lesions are misdiagnosed and confused. Therefore, we will briefly present the classification of tooth resorption:
Thats why we will se briefly the classification of the tooth resorption: A - Internal tooth resorption 1. Internal surface resorption 2. Internal inflammatory resorption 3. Internal replacement resorption. B – External tooth resorption 1. External surface resorption 2. External inlammatory resorption apical/lateral 3. External replacament resorption 4. External invazive resorption 5. External pressure resorption 6. Orthodontic resorption 7. Physiological resorption 8. Idiopathic resorption.
In this case, we will present a case of external invasive toot resorption on the first mandibular left premolar with symptomatic apical periodontitis.
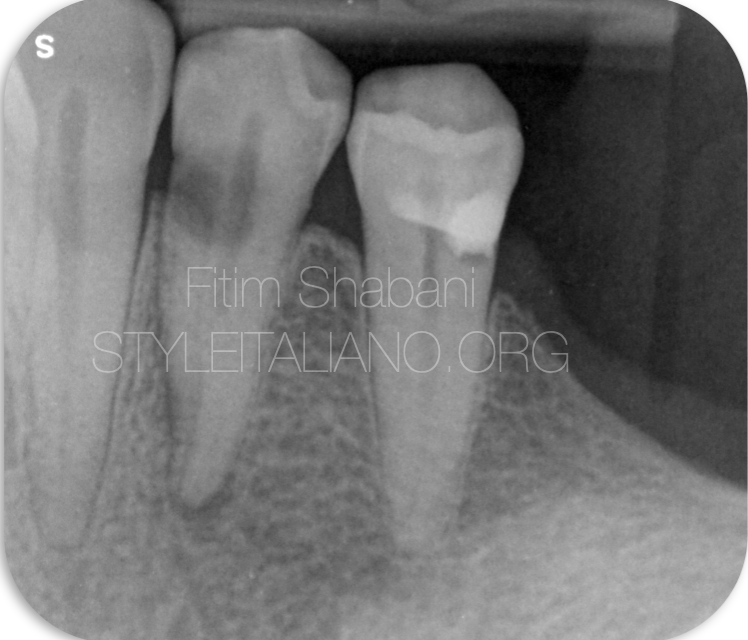
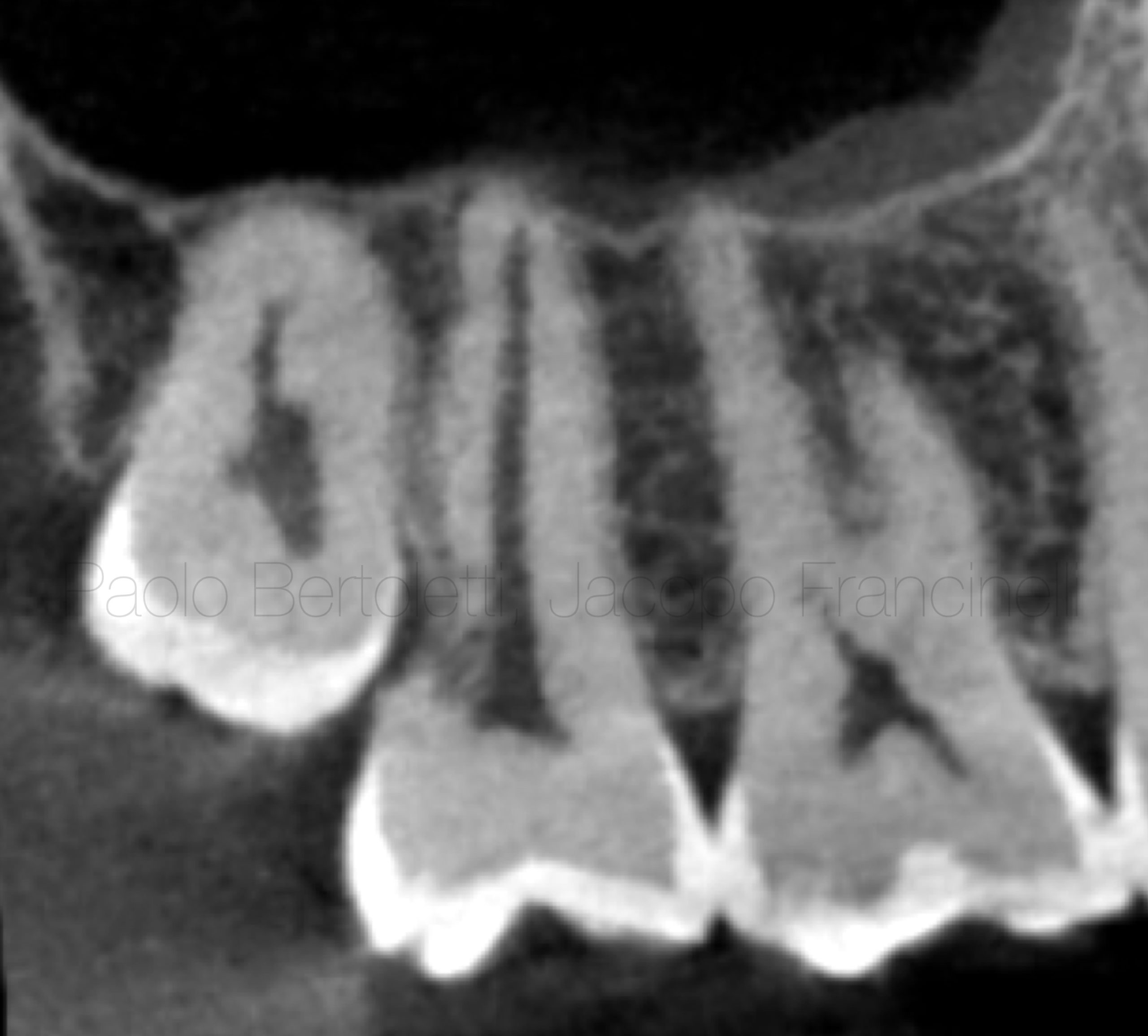
Fig. 1
Clinical case
Clinical data
The patient presents some slight complaints on the lower jaw left.
Dg: External resorption on the mesial/cervical surface, accompanied by symptomatic apical periodontitis.
Treatment plan :
- Reconstruction of the mesial/cervical part of the tooth – surgically
- Endodontic treatment
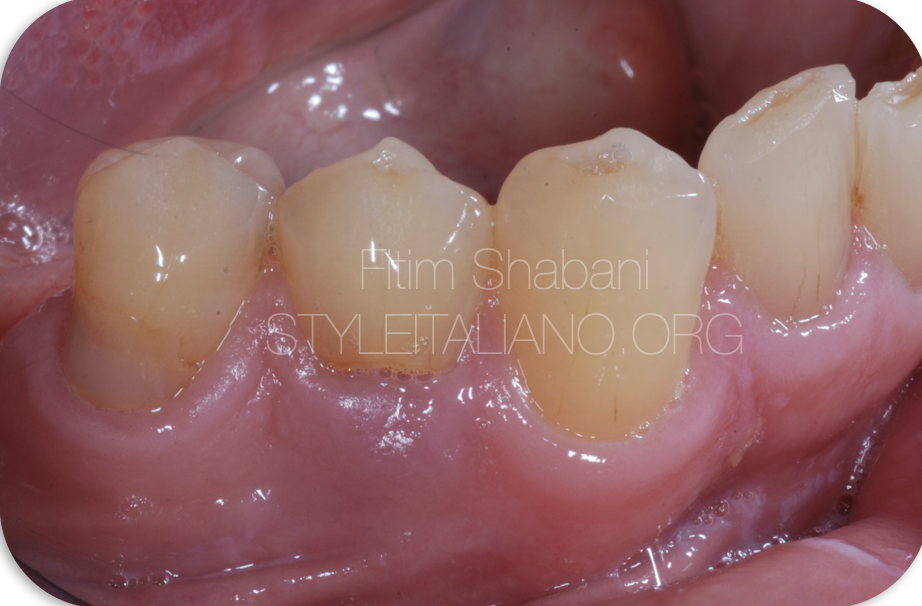
Fig. 2
Initial situation of the case.
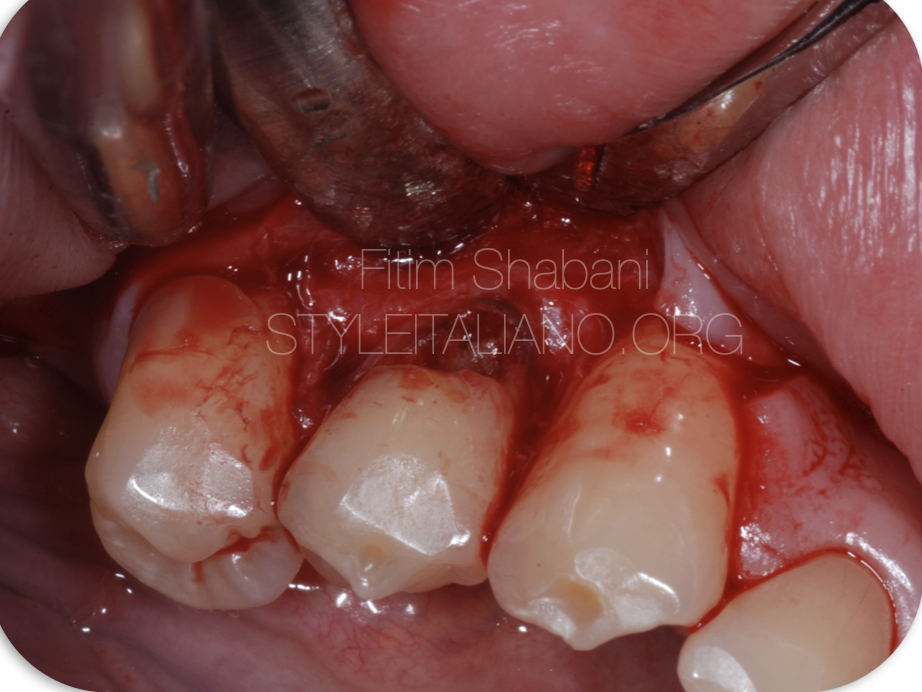
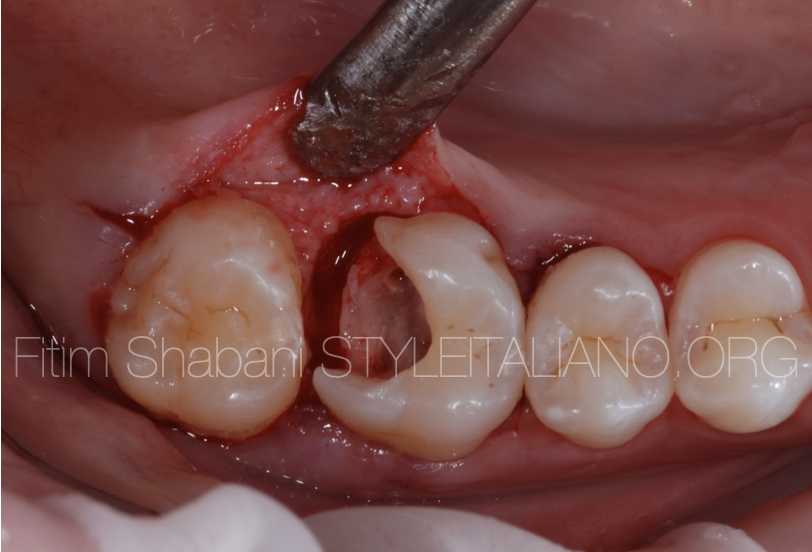
Fig. 3
Surgical approach.
Video of the procedure
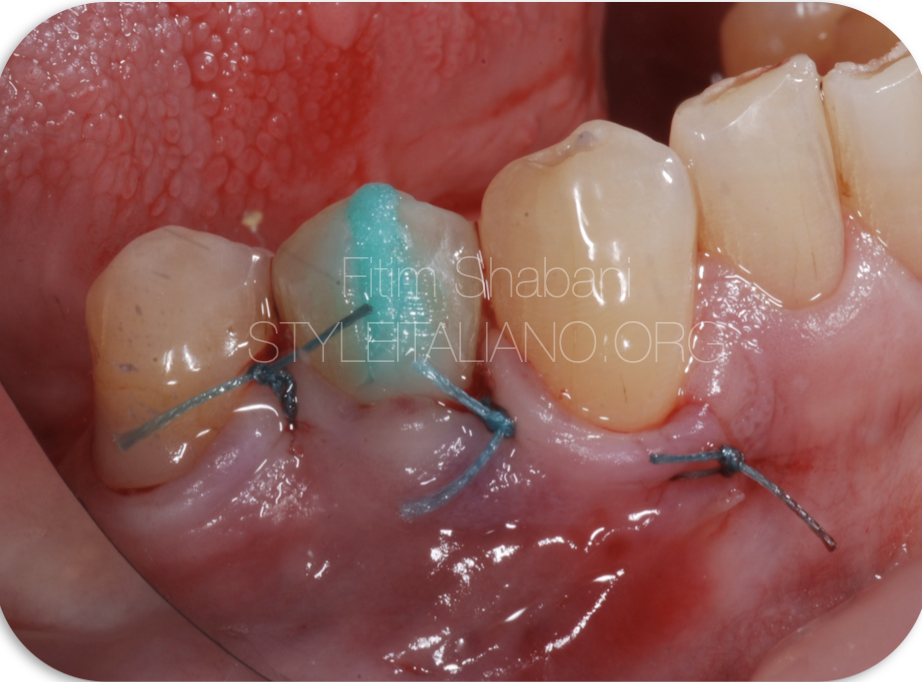
Fig. 4
The view after the reconstruction of the mesial/cervical part of the tooth and pulp extirpation.
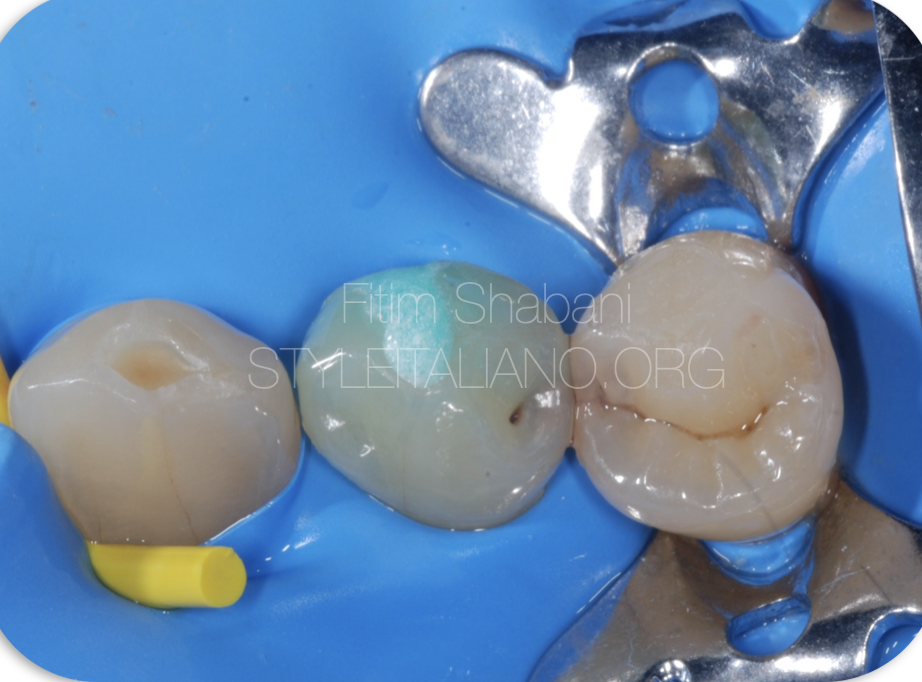
Fig. 5
In the second visit was performed an endodontic treatment.
Video of the endodontic treatment
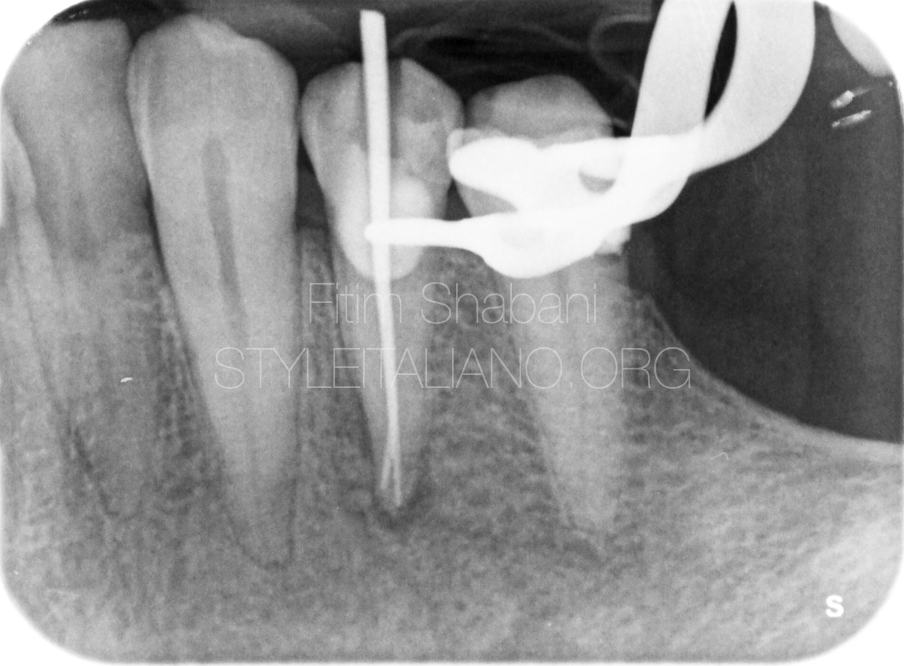
Fig. 6
Fitting a master cone.
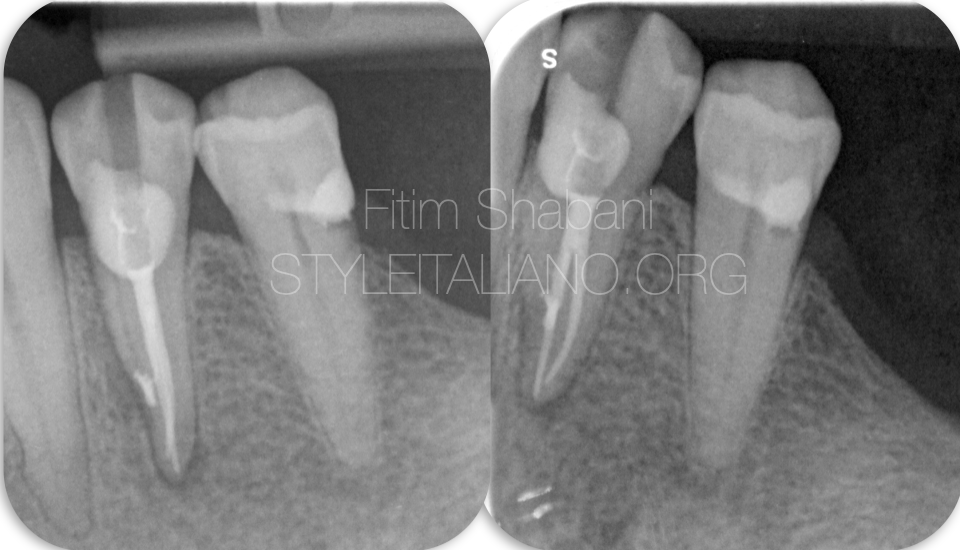
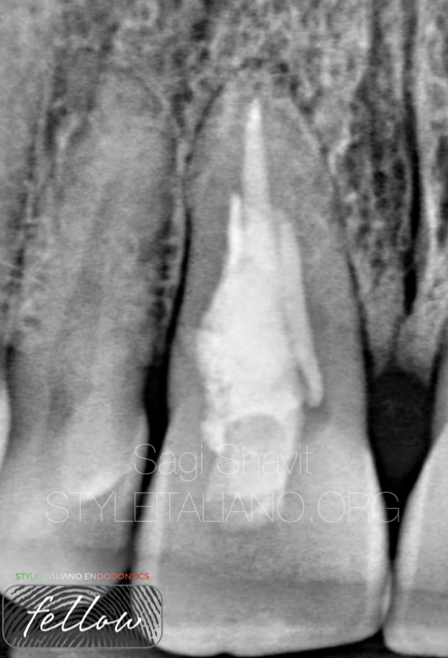
Fig. 7
Xrays after endodontic treatment.
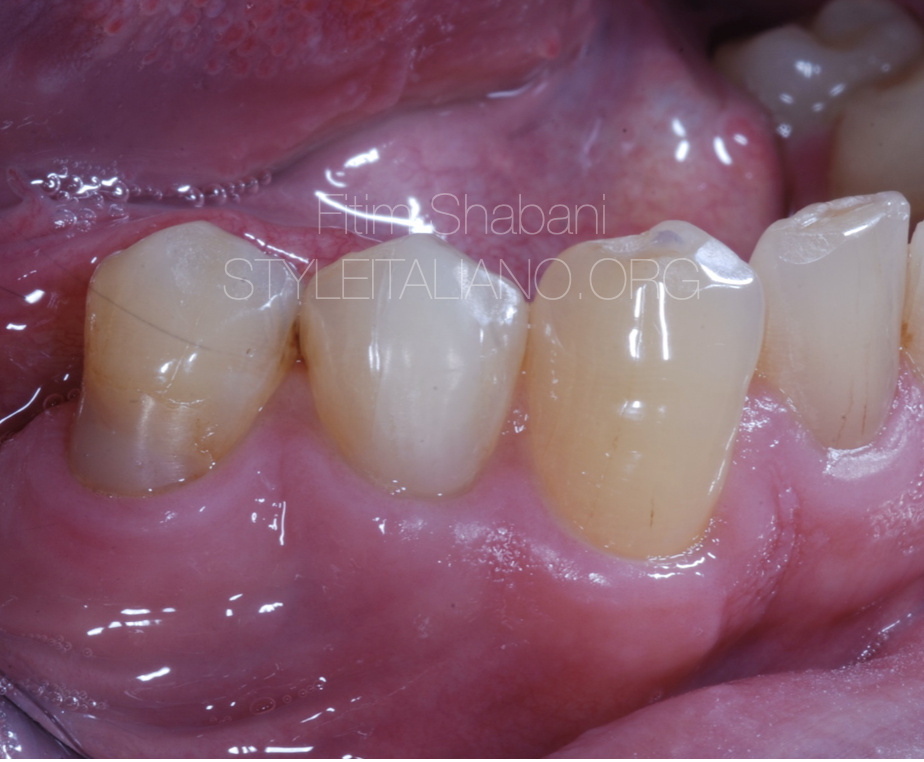
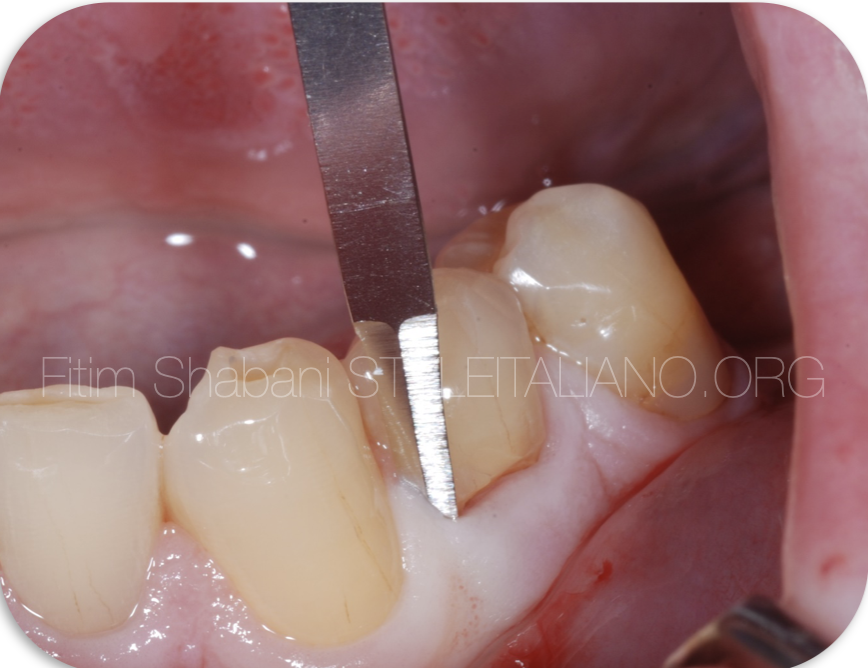
Fig. 8
Final composite restoration. The view after 2 weeks.
Conclusions
Tooth resorption is a pathologic condition that still remains a mystery in many aspects. It may go unnoticed over many years as most cases of resorption are asymptomatic in nature. Early detection of resorption is essential for successful management.
The plan before treatment is of special importance, and almost in all cases a multi-disciplinary approach is needed.
Bibliography
Dr. Marina Fernandes, Ida de Ataide and Rahul Wagle,
Tooth resorption part I - pathogenesis and case series of internal resorption, Case series Jan-Feb 2013.
Dr. Marina Fernandes, Ida de Ataide and Rahul Wagle,
Tooth resorbtion part II – external resorption : Case series, Mar-Apr 2013.
L.Bergmans, J. Van Cleynenbreugel, E. Verbeken, M. Wevers, B. Van Meerbeek, P. Lambrechts
Cervical external root resorption in vital teeth, 25 September 2002.
A. Maini, P. Durning and N. Drage, Resorption: within or without? The benefit of Cone-Beam Computed Tomography when diagnosing a case of an internal/external resorption defect, 2008.
GS Heithersay, Management of tooth resorption, 12 March 2008.
Paul V. Abbott, Shaul Lin
Tooth resorption—Part 2: A clinical classification, 23 May2022