BlueShaper PRO: Two heat treatments in a single instrument, DUAL WIRE technology.
22/09/2024
José Aranguren
Warning: Undefined variable $post in /home/styleendo/htdocs/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
Warning: Attempt to read property "ID" on null in /home/styleendo/htdocs/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
We will describe and analyze the new BlueShaper PRO system for rotary surgical preparation of root canals with the new Dual Wire technology.
It includes a basic set of 4 files: Z1, Z2, Z3, and Z4, as well as the Blue Shaper PRO system with a D0 of 0.14mm, 0.17mm, 0.19mm, and 0.25mm respectively, with variable taper ranging from 2 to 10%.
The only difference with the classic Blue Shaper system is that Blue Shaper PRO features a double heat treatment (Dual Wire) in all its instruments.
This Dual Wire technology gives all instruments greater cutting capacity (20% more cutting), greater torsional resistance (28% more resistance), and greater penetrability in the canal (2% more penetration). At the same time, it maintains the same flexibility and resistance to cyclic fatigue as conventional Blue Shaper.
All of them have 3mm of Gold heat treatment (Dual Wire) at the apex in their PRO presentation, with all the advantages explained above.
For wider root canals, the Z5, Z6, and Z7 files are also included in their PRO version with 3mm of Gold heat treatment.
The company markets gutta-percha cones BlueShaper PRO (ZARC, Gijon, Spain) that correspond to files Z3, Z4, Z5, Z6, and Z7. This Blue Shaper PRO system is the first and only system with dual heat treatment in a single instrument.
This technology is called Dual Wire and is patented by ZARC4ENDO (ZARC, Gijon, Spain).
Keywords: BlueShaper, rotary instrumentation, multi-alloy system, Dual Wire, heat treatment.
Fig. 1
This Dual Wire technology gives all instruments greater cutting capacity (20% more cutting), greater torsional resistance (28% more resistance), and greater penetrability in the canal (2% more penetration). At the same time, it maintains the same flexibility and resistance to cyclic fatigue as conventional Blue Shaper.
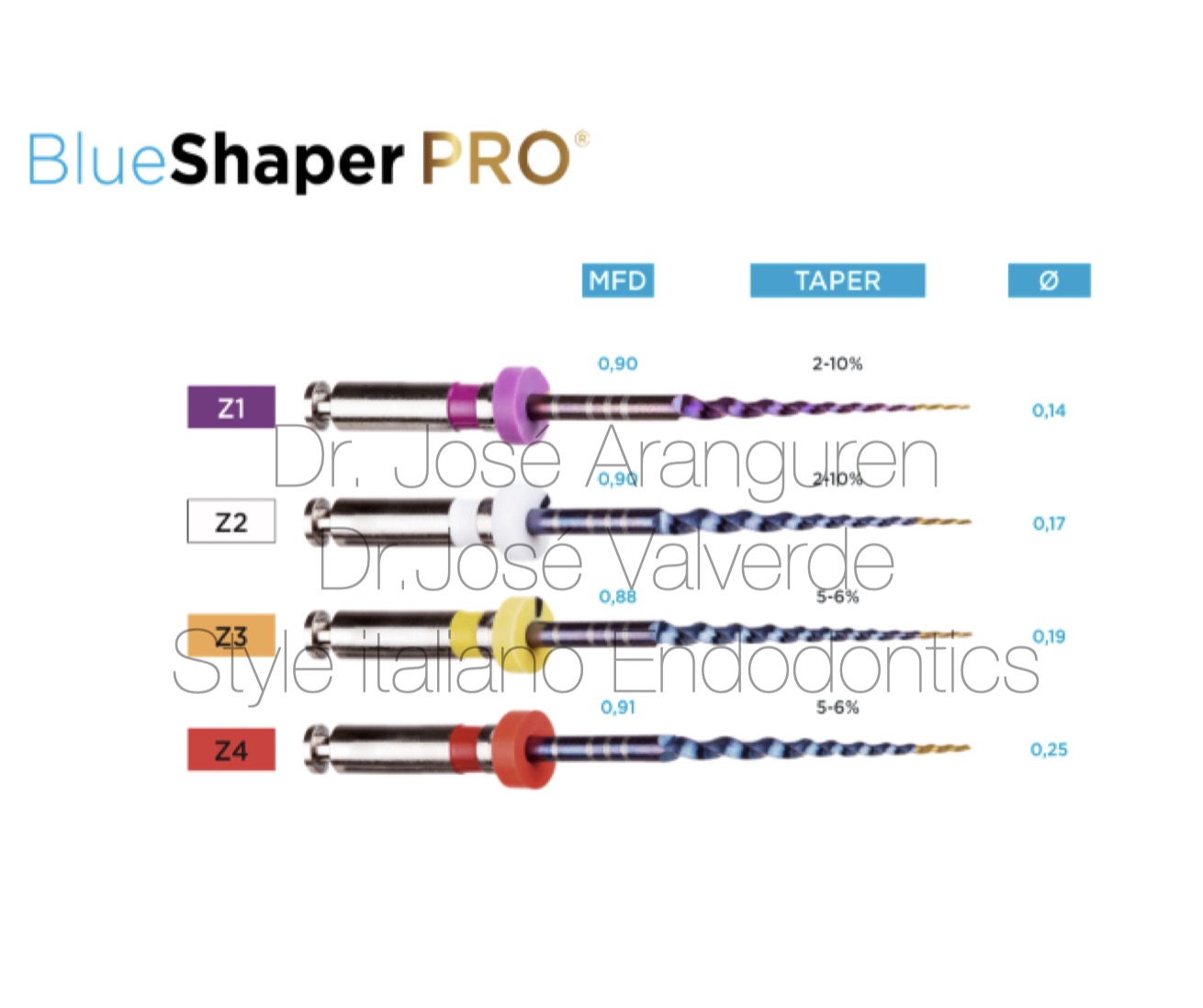
Fig. 2
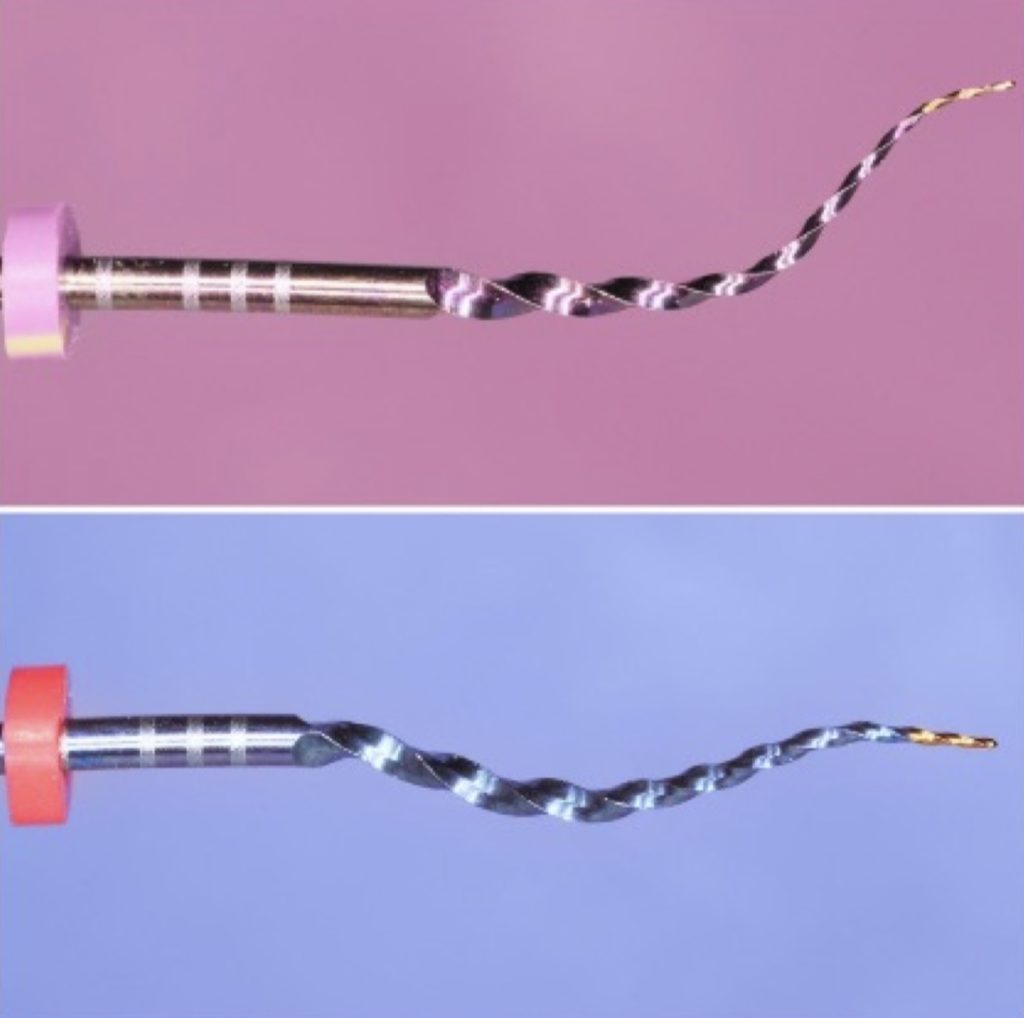
Files Z1, Z2, Z3 y Z4. Double-alloy System Blue- Shaper PRO.

Fig. 3
3 mm at the tip of more Austenitic alloy provides the file better penetration inside the canal maintaining the same flexibility.

Fig. 4
Scanning electron microscopy: convex triangular cross-section of file Z1.
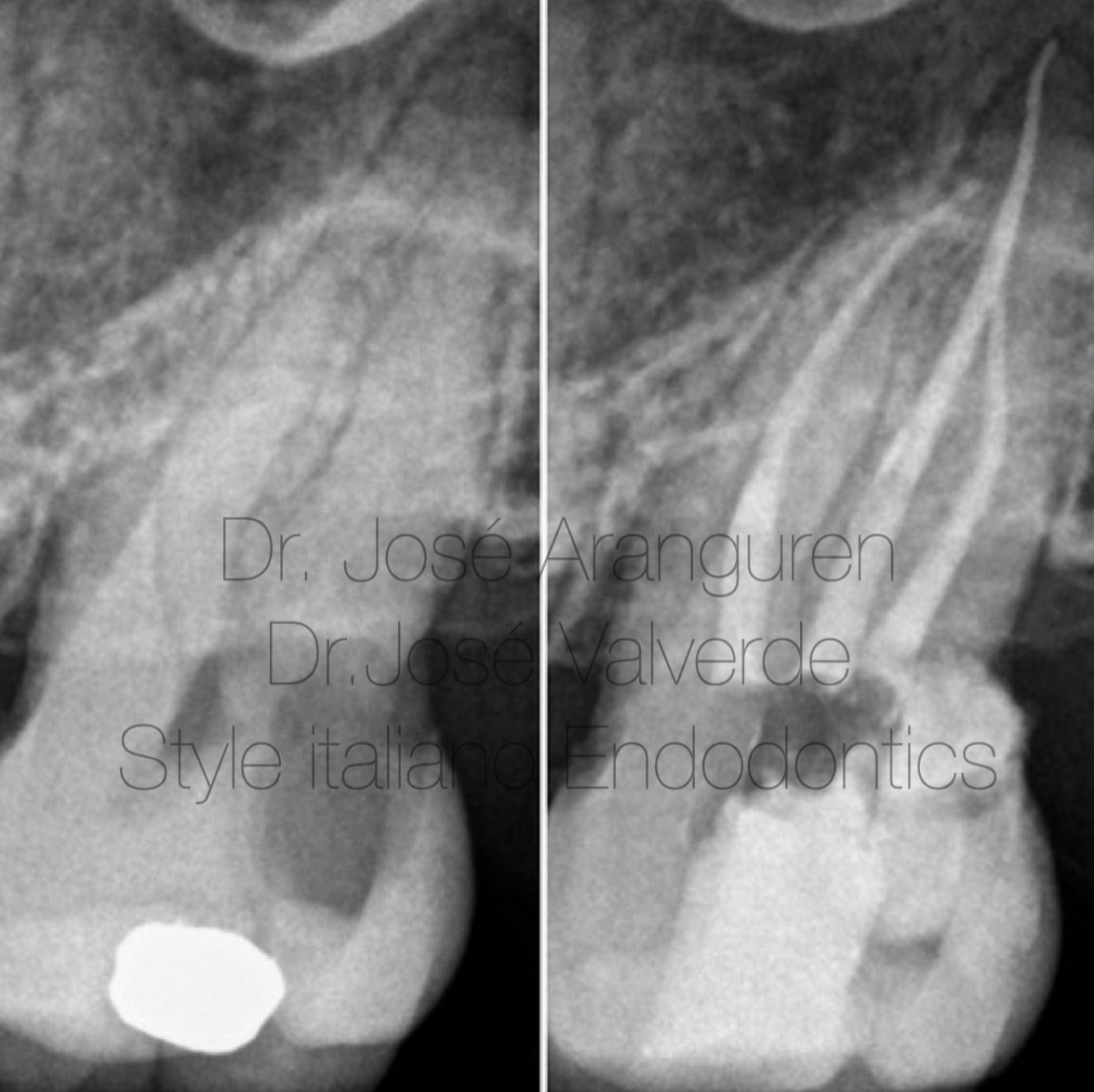
Fig. 5
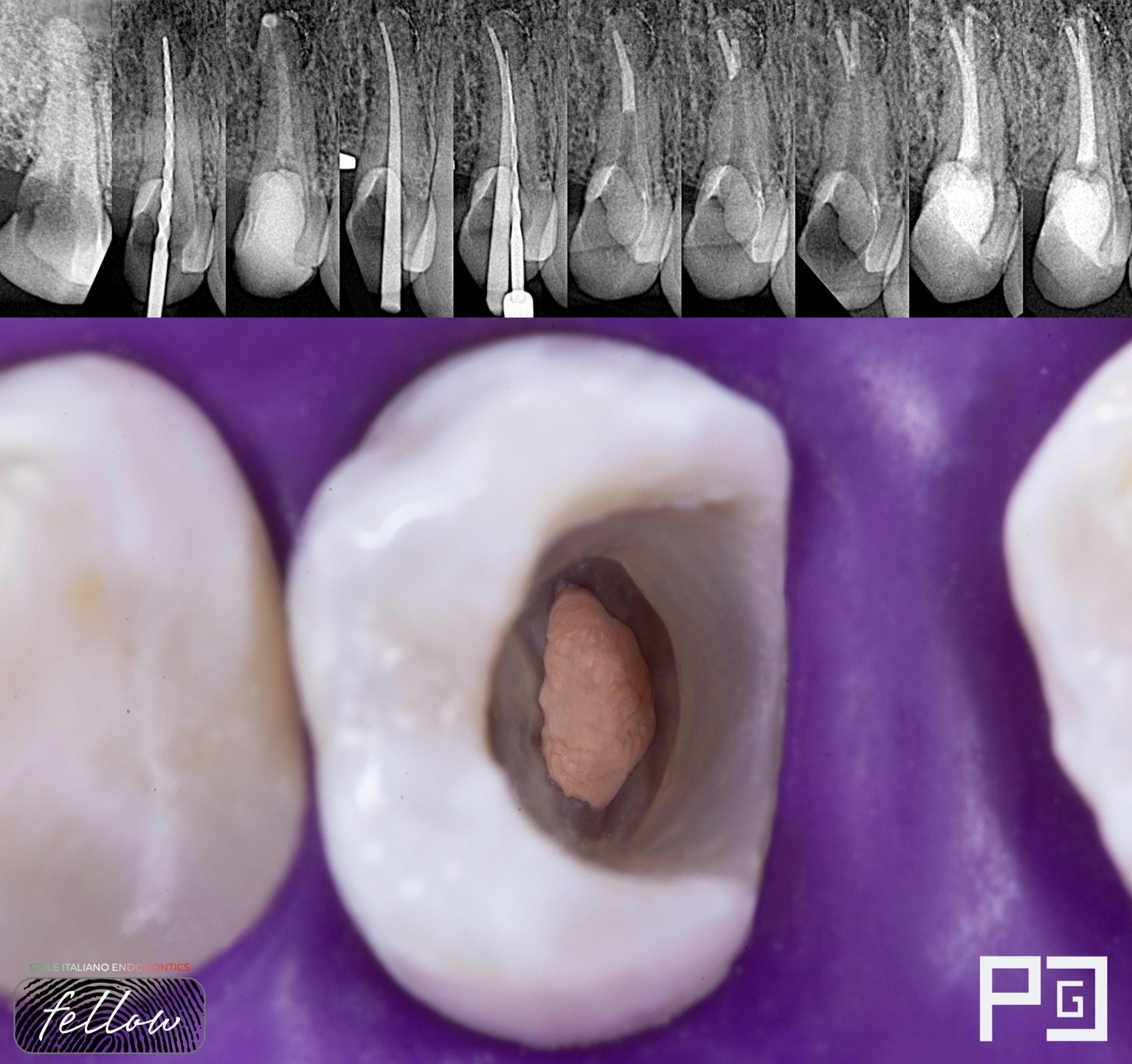
Preoperative X-ray of a molar with moderate curvatures. B: Post-operative X-ray.
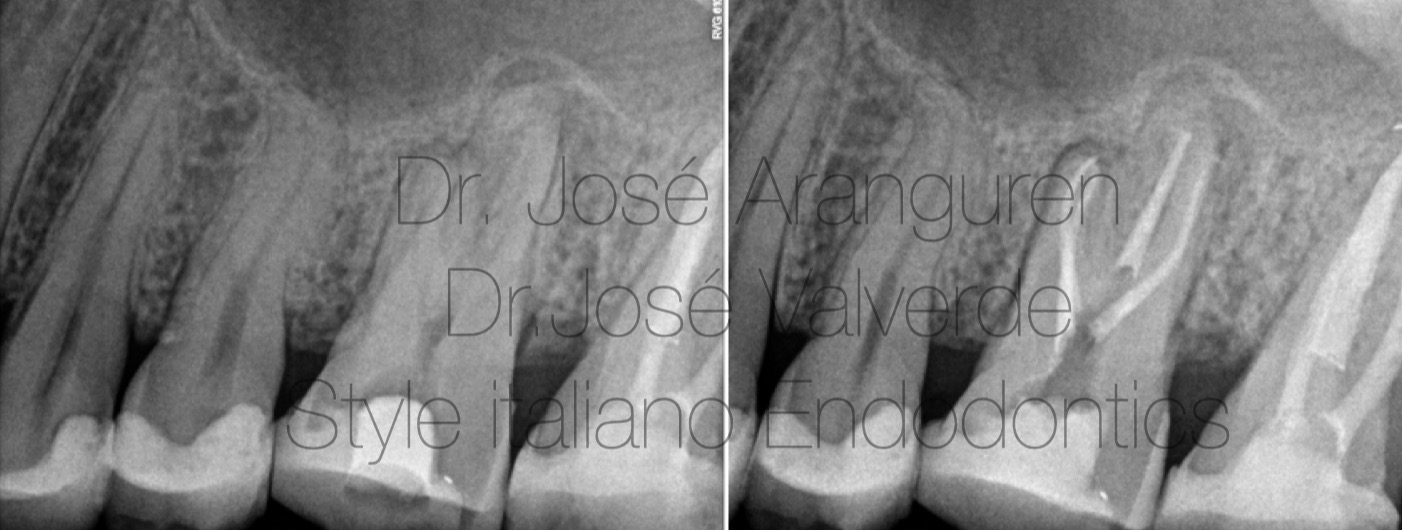
Fig. 6
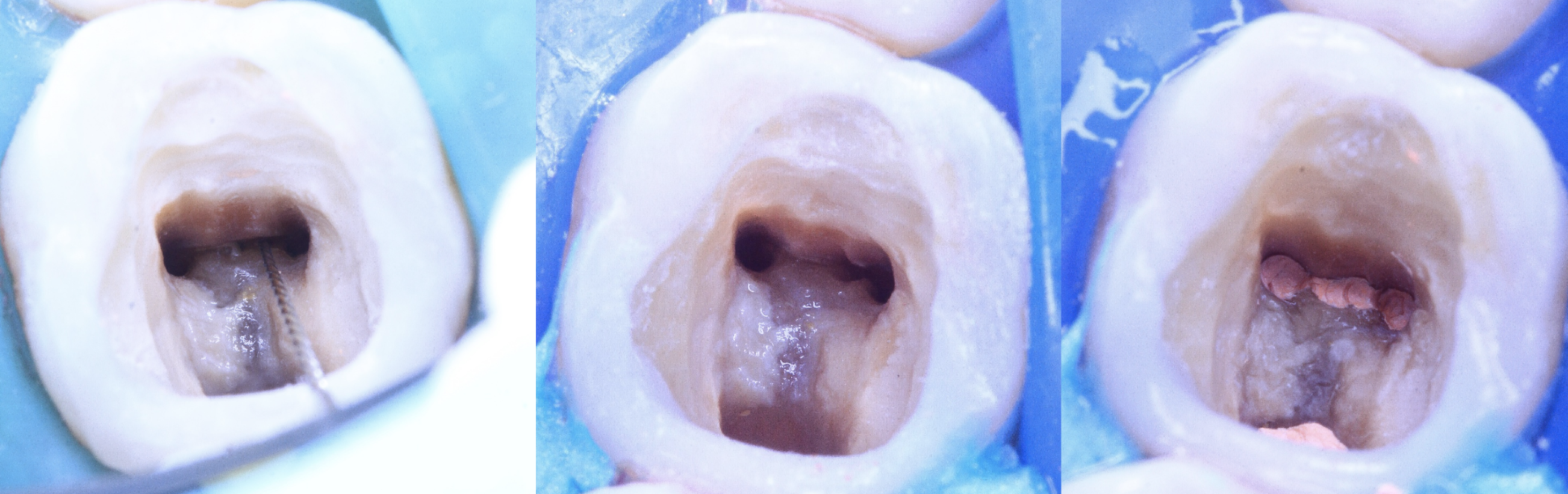
Root canal treatment in a taurodontic anatomy.
Left: Preoperative x-ray.
Right: Postoperative x-ray.
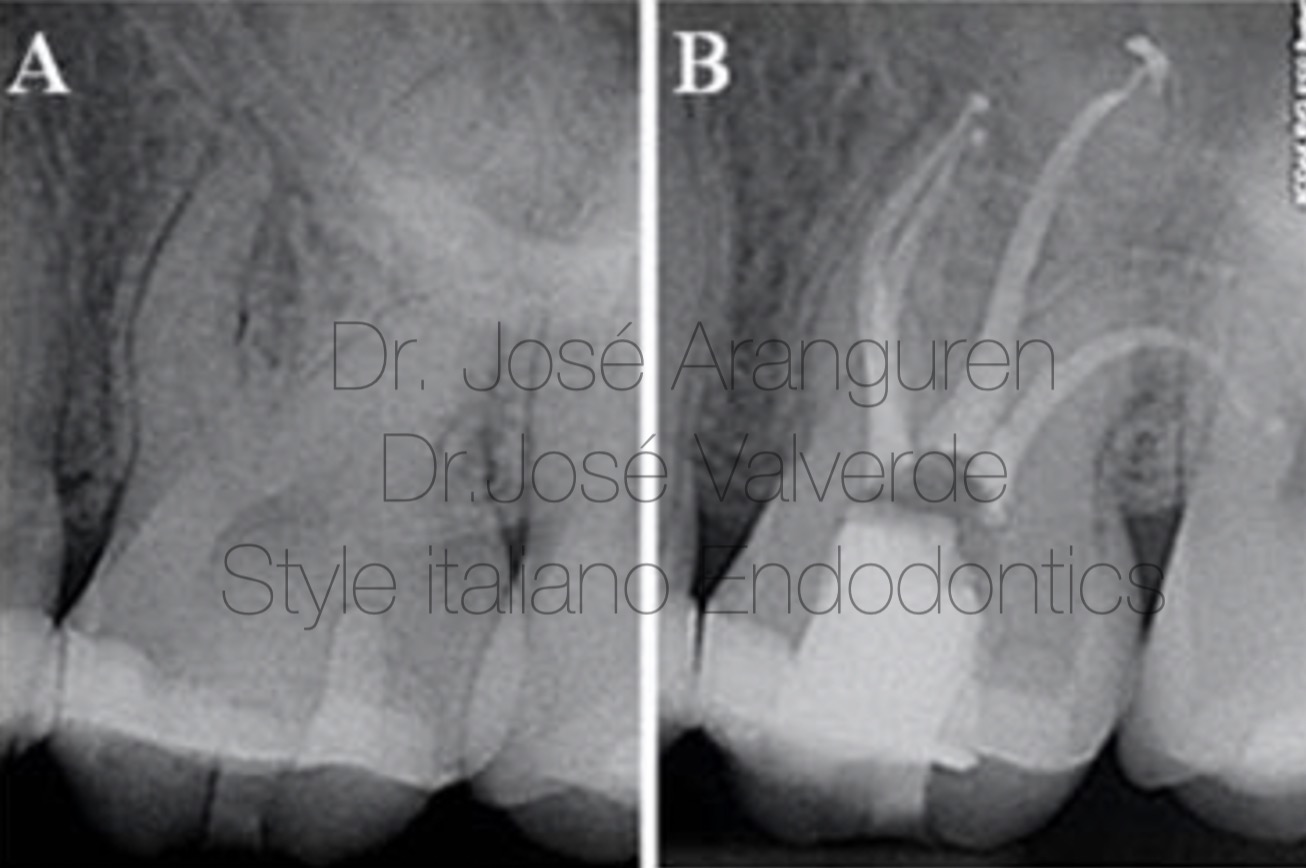
Fig. 7
A: Preoperative X-ray of an upper first molar with a severe curvature at the distobuccal root.
B: Postoperative x-ray.
Conclusions
The BlueShaper Pro multi-alloy file system, with Dual Wire technology, is a system that maintains the same flexibility and adaptation to the canal as the classic Blue Shaper, significantly improving cutting capacity (20%), torsional resistance (28%), and penetration into the canal. Making it a much more effective and versatile system.
Bibliography
Bibliography
1. Schilder H. Cleaning and shaping the root canal. Dent Clin North Am 1974;12:26996.
2. Weine FS. Endodontic therapy, 5a ed., St. Louis, Mosby 1996, pp. 30592.
3. Soares IJ, Goldberg F. Endodoncia. Técnica y fundamen- tos. Porto Alegre, Artmed, 2001, pp. 14554.
4. Sattapan B, Palamara JEA, Messer HH. Torque during ca nal instrumentation using rotary nickel-titanium files. J En- dod 2000;26:15660. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004770 20000300000007
5. Shen Y, Zhou H, Zheng T, Peng B, Haapasalo M. Current challenges and concepts of the thermomechanical treat ment of nickeltitanium instruments. J Endod 2013;39:163 72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2012.11.005
6. Gao Y, Gutmann JL, Wilkinson K, Maxwell R, Ammon D. Evaluation of the impact of raw materials on the fa tigue and mechanical properties of ProFile Vortex rotary instruments. J Endod 2012;38:398401. https://doi.or g/10.1016/j.joen.2011.11.004
7. Ye J, Gao Y. Metallurgical characterization of MWire nickeltitanium shape memory alloy used for endodontic rotary instruments during low-cycle fatigue. J Endod 2012;38:1057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2011.09.028
8. Mohammadi Z, Soltani MK, Shalavi S, Asgary S. A Re view of the various surface treatments of NiTi instru ments. Iran Endod J 2014;9:235–40.
9. Ebihara A, YahataY, Miyara K, Nakano K, Hayashi Y, Suda H. Heat treatment of nickeltitanium rotary endo dontic instruments: effects on bending properties and shaping abilities. Int Endod J 2011;44:843–9. https://doi. org/10.1111/j.1365-2591.2011.01891.x
10. Miyai K, Ebihara A, Hayashi Y, Doi H, Suda H, Yoneya ma T. Influence of phase transformation on the torsional and bending properties of nickeltitanium rotary endodon tic instruments. Int Endod J 2006;39:119–26. https://doi. org/10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01055.x
11. Shen Y, Huang X, Wang Z, Wei X, Haapasalo M. Low en vironmental temperature influences the fatigue resistance of nickel-titanium files. J Endod 2018;44:626–9. https:// doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2017.11.004
12. Zupanc J, Vahdat-Pajouh N, Schäfer E. New thermo mechanically treated NiTi alloys- a review. Int Endod J 2018;51:1088–103. https://doi.org/10.1111/iej.12924
13. Martins JNR, Silva EJNL, Marques D, Belladonna F, SimõesCarvalho M, Vieira VTL, et al. Design, meta llurgical features, mechanical performance and canal preparation of six reciprocating instruments. Int Endod J 2021;54:1623–37. https://doi.org/10.1111/iej.13529
14. Martins JNR, Silva EJNL, Marques D, Pereira MR, Viei ra VTL, ArantesOliveira S, et al. Design, metallurgical features, and mechanical behaviour of NiTi endodontic instruments from five different heat-treated rotary sys tems. Materials 2022;15:1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/ ma15031009
15. DeDeus G, Silva EJNL, Vieira VTL, Belladonna FG, Elias CN, Plotino G, et al. Blue thermomechanical treat ment optimizes fatigue resistance and flexibility of the reciproc files. J Endod 2017;43:462–6. https://doi.or g/10.1016/j.joen.2016.10.039
16. Pereira ESJ, Gomes RO, Leroy AMF, Singh R, Peters OA, Bahia MGA, et al. Mechanical behavior of M-wire and conventional NiTi wire used to manufacture rotary endodontic instruments. Dental Materials 2013;29:e318– e324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dental.2013.10.004
17. Lopes HP, GambarraSoares T, Elias CN, Siqueira Jr. JF, Inojosa IF, Lopes WSP, et al. Comparison of the mecha nical properties of rotary instruments made of conven tional nickel-titanium wire, M-Wire, or nickel-titanium alloy in Rphase. J Endod 2013;39:516–20. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.joen.2012.12.006
18. Zupanc J, Vahdat-Pajouh N, Schäfer E. New thermo mechanically treated NiTi alloys- a review. Int Endod J 2018;51:1088–103. https://doi.org/10.1111/iej.12924
19. Silva EJNL, Tameirao MDN, Belladonna FG, Neves AA, Souza EM, DeDeus G. Quantitative transportation assessment in simulated curved canals prepared with an adaptive movement system. J Endod 2015;41:1125–9. ht tps://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2015.02.028
20. Özyürek T, Gündoğar M, Uslu G, Yılmaz K, Staffoli S, Nm G, et al. Cyclic fatigue resistances of Hyflex EDM, Wa veOne gold, Reciproc Blue and 2Shape NiTi rotary files in different artificial canals. Odontology 2018;106:408–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s102660180340y
21. Alcalde MP, Duarte MAH, Bramante CM, de Vasconse los BC, TanomaruFilho M, GuerreiroTanomaru JM, et al. Cyclic fatigue and torsional strength of three different thermally treated reciprocating nickeltitanium instru ments. Clin Oral Investig 2018;22:1865–71. https://doi. org/10.1007/s0078401722958. Publicado electrónica mente antes de su impresión el 9 de diciembre de 2017.
22. Kim JW, Ha JH, Cheung GSP, Versluis A, Kwak SW, Kim HC. Safety of the factory preset rotation angle of recipro cating instruments. J Endod 2014;40:1671–5. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.joen.2014.06.002
23. Silva E, Oliveira de Lima C, Vieira V, Antunes H, Lima Moreira EJ, Versiani M. Cyclic fatigue and torsional resis tance of four martensitebased nickel titanium reciproca ting instruments. Eur Endod J 2020;5:231–5. https://doi. org/10.14744/eej.2020.16878
24. Alcalde MP, TanomaruFilho M, Bramante CM, Duarte MAH, GuerreiroTanomaru JM, CamiloPinto J, et al. Cy clic and torsional fatigue resistance of reciprocating sin gle files manufactured by different nickel-titanium allo ys. J Endod 2017;43:1186–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. joen.2017.03.008
25. Elsaka SE, Elnaghy AM, Badr AE. Torsional and bending resistance of WaveOne Gold, Reciproc and Twisted File Adaptive instruments. Int Endod J 2016;50:1077–83. ht tps://doi.org/10.1111/iej.12728
26. Plotino G, Grande NM, Cotti E, Testarelli L, Gambarini G. Blue treatment enhances cyclic fatigue resistance of vor tex nickel-titanium rotary files. J Endod 2014;40:14513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2014.02.020
27. Plotino G, Grande NM, Testarelli L, Gambarini G, Cas tagnola R, Rossetti A, et al. Cyclic fatigue of Reciproc and Reciproc Blue Nickel-titanium reciprocating files at diffe rent environmental temperatures. J Endod 2018;44:1549 52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2018.06.006
28. Silva EJNL, Vieira VTL, Hecksher F, Dos Santos Oliveira MRS, dos Santos Antunes H, Moreira EJL. Cyclic fati gue using severely curved canals and torsional resistance of thermally treated reciprocating instruments. Clin Oral Investig 2018;22:26338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784 01823629
29. Shim KS, Oh S, Kum KY, Kim YC, Jee KK, Chang SW. Mechanical and metallurgical properties of va rious nickeltitanium rotary instruments. BioMed Res Int 2017;2017:4528601. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4528601
30. Kaval ME, Capar ID, Ertas H. Evaluation of the cyclic fati gue and torsional resistance of novel nickeltitanium rotary files with various alloy properties. J Endod 2016;42:1840 3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2016.07.015
31. Varghese NO, Pillai R, Sujathen UN, Sainudeen S, An tony A, Paul S. Resistance to torsional failure and cy clic fatigue resistance of ProTaper Next, WaveOne, and Mtwo files in continuous and reciprocating motion: An in vitro study. J Conserv Dent 2016;19:22530. https://doi. org/10.4103/09720707.181937
32. Silva EJNL, Giraldes JFN, de Lima CO, Vieira VTL, Elias CN, Antunes HS. Influence of heat treatment on tor sional resistance and surface roughness of nickeltitanium instruments. Int Endod J 2019;52:1645–51. https://doi. org/10.1111/iej.13164