Avulsion Trauma Case management with Dentoclic Fiber Post Build Up
19/08/2022
Marc Habib
Warning: Undefined variable $post in /var/www/vhosts/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/endodontics.styleitaliano.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
Warning: Attempt to read property "ID" on null in /var/www/vhosts/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/endodontics.styleitaliano.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
Traumatic dental injuries occur most frequently in children and young adults.
Proper diagnosis, treatment planning and follow up are very important to assure a favorable outcome.
The purpose of this clinical article is to highlight the advantage of core build up and bonding with ITENA Clinical's Corono-Radicular Restoration Kit in reinforcing tooth structure in view of achieving a better prognosis for a traumatized tooth with external resorption.
An 11 years old patient presented to the clinic with his father after concern of an abscess on his front upper left tooth #21.
Father described a history of trauma and tooth avulsion few months back. Tooth was reimplanted and parents were advised to wait for possible revascularization.
Intra oral examination shows swelling on the gums facing tooth #21 without probing
Radiographic examinations shows tooth 21 with very clear external resorptions
We know that mature avulsed teeth can never revascularize and should be root canal treated after 10 days before pulp necrosis aggravates the inflammatory established status of the ligament
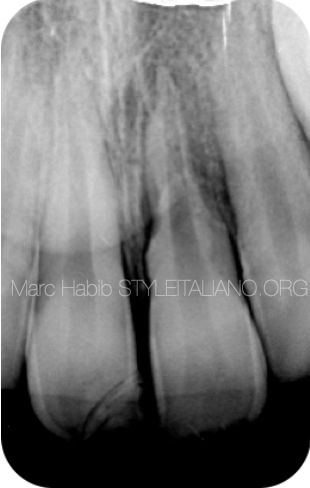
Fig. 1
Dental avulsion is the complete displacement of a tooth from its socket in alveolar bone owing to trauma.
The treatment for permanent teeth consists of reimplantation, immediately if possible. (<15min)
During avulsion there is ischemia of the pulp and the periodontal ligament immediately after expulsion. It is aggravated by drying and bacterial contamination, resulting in a very fast cellular necrosis.
Treatment will depend on the patient's age (tooth development: mature/immature), extra-alveolar time and storage medium.
Delayed reimplantation (> 60 min)of mature tooth without managing removal of necrotic periodontal ligament will induce root external resorption. Moreover, failure to root canal treat within 2 weeks will aggravate the external resorption due to additional necrotic tissue and infection generated from the necrotic pulp tissue.
Over five million teeth are knocked out annually in the United States during sports, automobile accidents, and in the home. A special solution and storage device may be able to be successfully help to reimplant those teeth. Without this kind of solutions and system, only 10 percent of knocked out teeth can be successfully reimplanted, since the periodontal ligament begin to die within 15 minutes after the trauma.
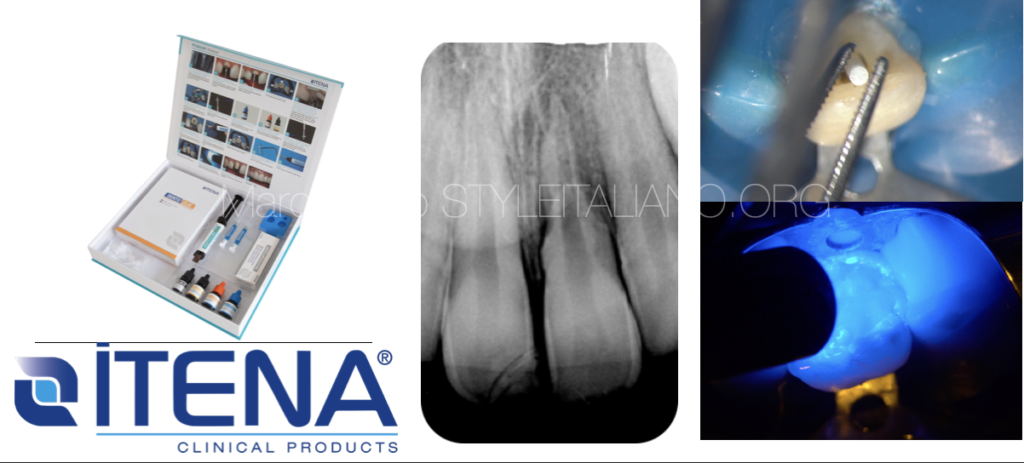
After 10 days, endodontic treatment with calcium hydroxide was performed, the splint was deposited in the same session because a longer immobilization would promote the ankylosis of the tooth.
Renewal of Ca(OH)2 can be done few times but not for one year like it was done previously, since prolonged calcium hydroxide dressings will fragilize the dentine (according to Andreasen et al. fracture strength of calcium hydroxide-filled roots would be reduced to half in about a year due to the root filling). Moreover, Hammarstrom et al. and Lengheden et al. have warned that use of calcium hydroxide in the root canals of teeth with damaged root surfaces might be contraindicated because of its necrotising effect on the cells repopulating the root surface.
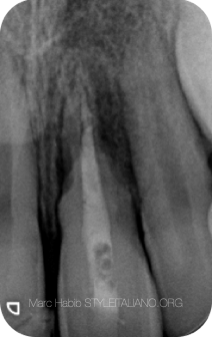
Fig. 2
The definitive filling is carried out after stabilization of the inflammatory processes.
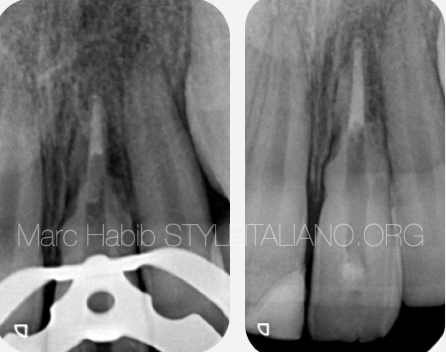
Fig. 3
Post Operative X ray
MTA plug managed in the apical third after 3 weeks of calcium hydroxide dressing
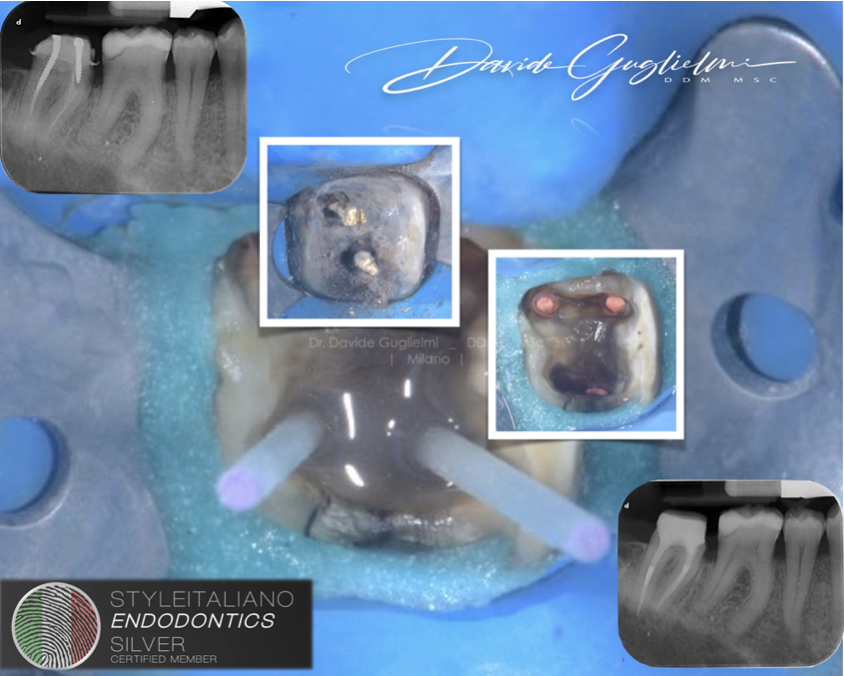
Fiber post preparation
After checking the setting of the MTA plug, fiber post core build up was managed using Itena Clinical's Dentoclic system.
The canal space was not straight in the buccal - palatal aspect, no desire was there to enlarge it. This post was most likely in contact with the canal walls where two grey islands can be observed on the X-ray.
This should be avoided as much as possible.
Post should be loose and reaching the post space available inside the root canal.
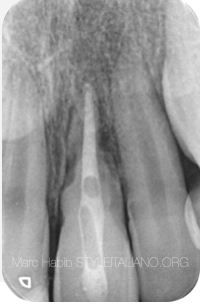
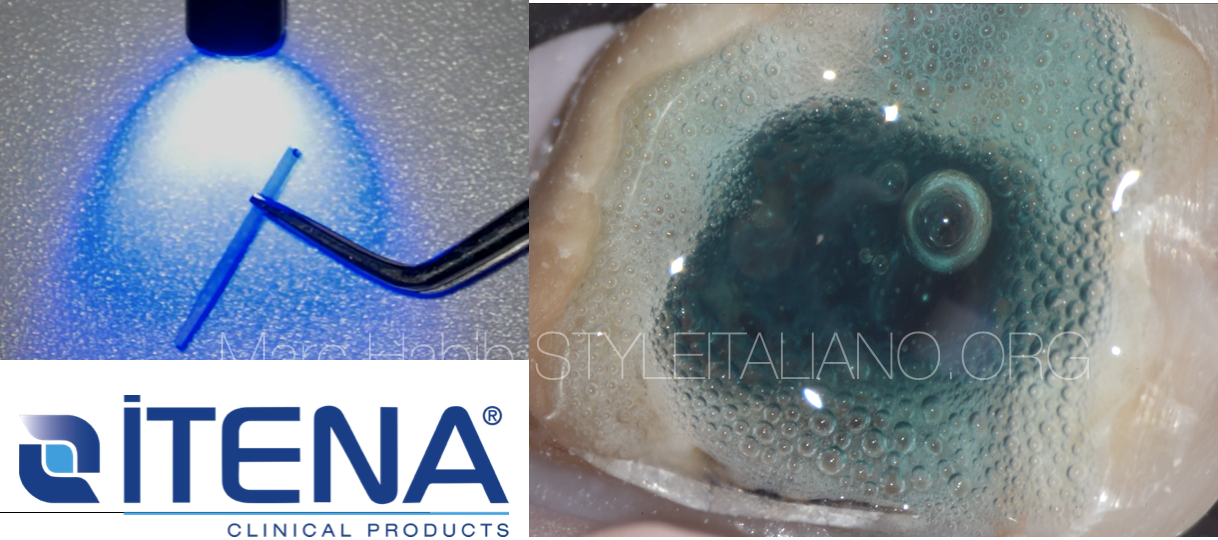
Fig. 4
Core build up material should be in contact with all dentinal walls and the fiber post imbedded in its mass.
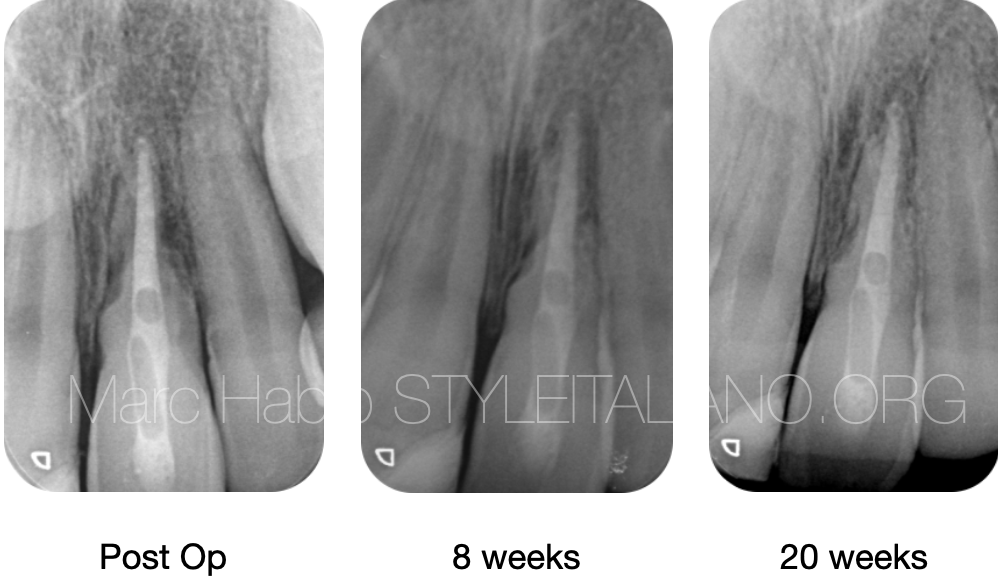
Fig. 5
Follow up X-rays, 8 weeks and 20 weeks
Conclusions
Trauma might fragilize the tooth structure, proper diagnosis and decision making should prevent further tooth loss and initiate healing in order to reach a positive prognosis.
Avulsed mature teeth should always be root canal treated to prevent an aggressive external resorption due to a mixture of necrotic pulp and periodontal tissues. External resorption inflammation is best managed with calcium hydroxide dressing and calcium silicate material as an ideal obturation material to minimize periapical irritation.
Itena Clinical’s Dentocore body consistency provide great ease during core build up with fiber posts, they both create a similar mechanical properties as dentine for the treated tooth preventing fractures and reinforcing the tooth core with maximum preservation of tooth structure
Bibliography
Andreasen JO. The effect of extra-alveolar period and storage
media upon periodontal and pulpal healing after replantation of mature permanent incisors in monkeys. Int J Oral Surg 1981;10:43–51.
Bhuva B, Giovarruscio M, Rahim N, Bitter K, Mannocci F. The restoration of root filled teeth: a review of the clinical literature. Int Endod J. 2021 Apr;54(4):509-535. doi: 10.1111/iej.13438. Epub 2021 Jan 5. PMID:33128279.
Scotti, N., Forniglia, A., Bergantin, E., Paolino, D. S., Pasqualini, D., & Berutti, E. (2013). Fibre post adaptation and bond strength in oval canals. International Endodontic Journal, 47(4), 366–372. doi:10.1111/iej.12156
Cvek M, Cleaton-Jones P, Austin J, Lownie J, Kling M, Fatti
P. Effect of topical application of doxycycline on pulp revascularization and periodontal healing in reimplanted mon- key incisors. Endod Dent Traumatol 1990;48:56.
Tay, F. R., & Pashley, D. H. (2007). Monoblocks in Root Canals: A Hypothetical or a Tangible Goal. Journal of Endodontics, 33(4), 391–398. doi:10.1016/j.joen.2006.10.00
Trope,M .(2011) Avulsion of permanent teeth: theory to practice REVIEW ARTICLE , Dental Traumatology 2011; doi: 10.1111/j.1600-9657.2011.01003.x
Andreasen JO, Farik B, Munksgaard EC. Long-term calcium hydroxide as a root canal dressing may increase the risk of root fracture. Dent Traumatol 2002 18: 134137.
Lengheden A, Blomlof L, Lindskog S. Effect of delayed calcium hydroxide treatment on periodontal healing in contaminated replanted teeth. Scand J Dent Res 1991 99: 147153.
Hammarstrom L, Blomlof L, Feiglin B, et al. Replantation of teeth and antibiotic treatment. Endod Dent Traumatol 1986 2: 5157.