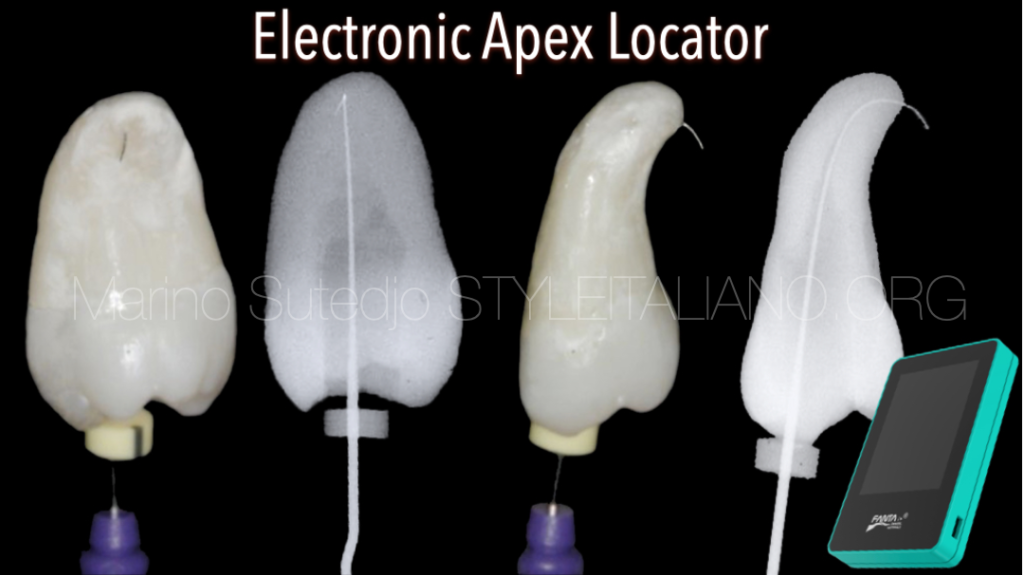
Electronic Apex Locator
28/11/2022
Marino Sutedjo
Warning: Undefined variable $post in /home/styleendo/htdocs/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
Warning: Attempt to read property "ID" on null in /home/styleendo/htdocs/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
Successful endodontic treatment depends on the triad of shaping, thorough cleaning and 3- dimensional obturation of tooth within the confines of canals. To achieve this objective the apical constriction must be detected accurately during canal preparation and precise control over working length during the procedure must be maintained.
There are many methods of working length determination. The radiographs are one of the traditional methods for determination of root canal length. But nowadays an electronic method using an apex locators have definitely served as an effective adjuvant to radiographs.
The outcome of endodontic treatment is influenced significantly by removal of all pulp tissue, necrotic material and microorganisms from the root canal systems. And we need to make sure that these procedures should be confined within the root canal systems. This can only be achieved if the length of the tooth and the root canal is determined with accuracy. Before we proceed with how to determine this length, we need to understand where is the proper point that the root canal systems end.
There are three area that can be considered as the proper point of the terminus of root canal system.
- Radiographic apex: The highest point or tip of the root as seen on the x-ray
- Apical Foramen: The point where the neurovascular bundle enters the root apex.
- Apical Constriction: The narrowest point of the canal
The position of radiographic apex may/may not be the same with apical foramen, but the position of apical foramen will not be the same with apical constriction.
Grove (1930) stated that the proper point to which root canals should end is the junction of the dentin and the cementum and that the pulp should be severed at the point of its union with the periodontal membrane. The cementodentinal junction (CDJ) is the anatomical and histological landmark where the periodontal ligament begins and the pulp ends.
Therefore, we should stop our root canal preparation at the point of CDJ. And this level of CDJ is the same with the level of apical constriction.
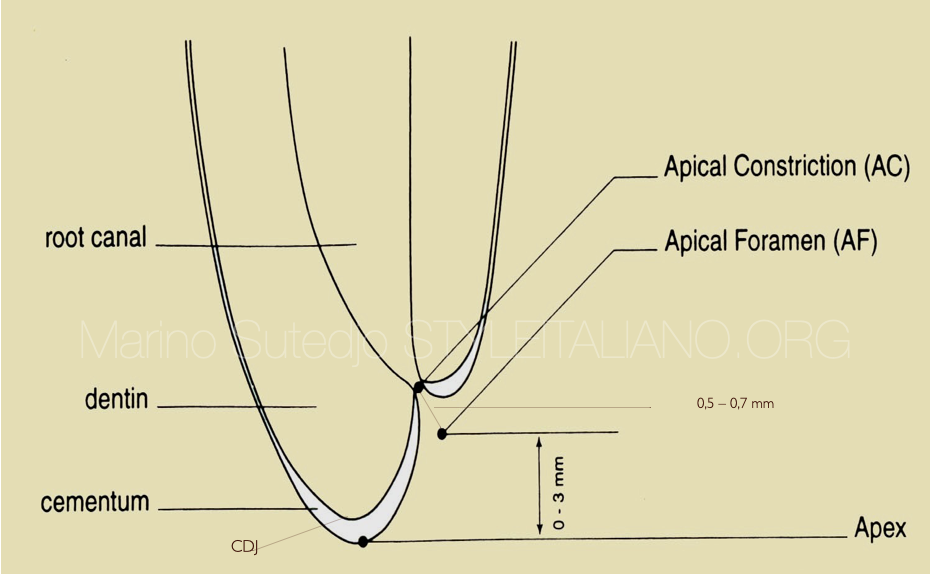
Fig. 1
Radiographic apex, apical foramen and apical constriction. The position of each area can be seen in this image.
Root canal wall that is the dentin will stop at the level of apical constriction (CDJ) and this is where should we stop our preparation
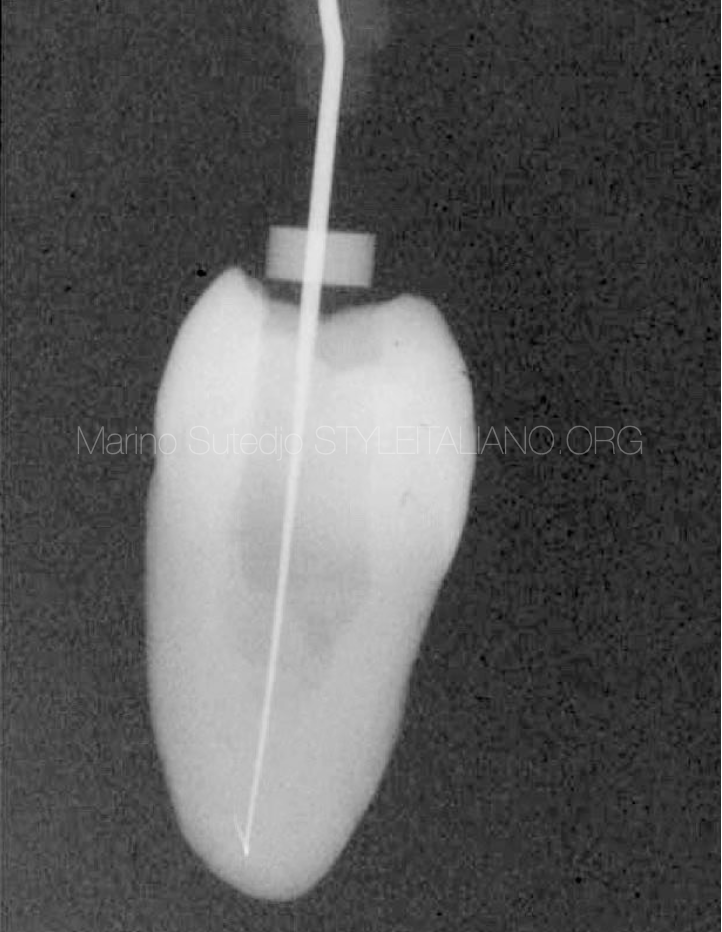
Fig. 2
There are several techniques have been used for determining the apical constriction. Traditionally, the determination will be used by taking radiographs. But nowadays the procedure has become slightly complicated because the apical constriction is a histological landmark that difficult to identified radiographically, and variables in technique, angulations and exposure distort this image leading to errors and multiple exposures which can be lead us in working length determination.
From this Xray, we might think that the working length is a little bit under. But we need to remember that this is a 2D image.
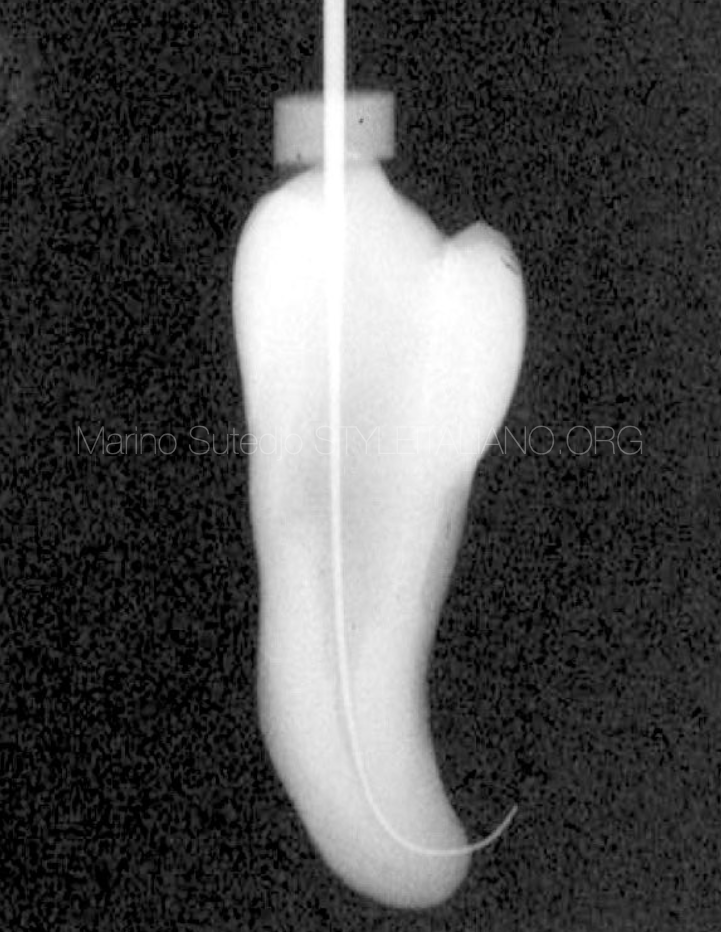
Fig. 3
From the other side we can see that instead of under length this length is already over for few mm.
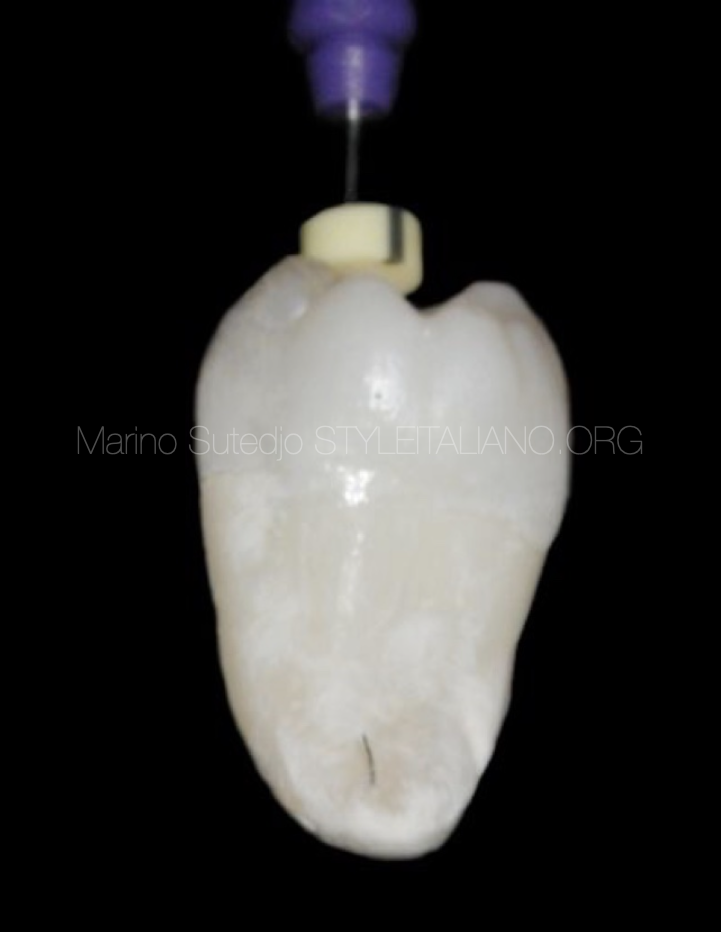
Fig. 4
The apical foramen is not always the same with radiographic apex
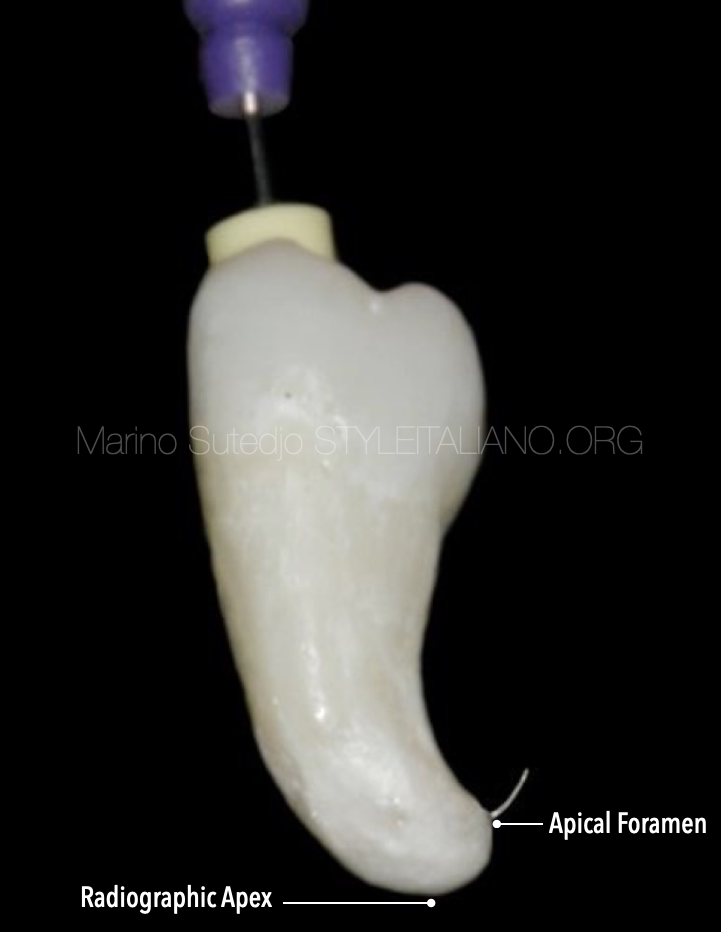
Fig. 5
The apical foramen is not always the same with radiographic apex

Fig. 6
Nowadays, the use of an electronic method to determine working length using an apex locator have proven to be powerful and useful adjunct. The development of the electronic apex locator has helped make the assessment of working length more accurate and predictable.
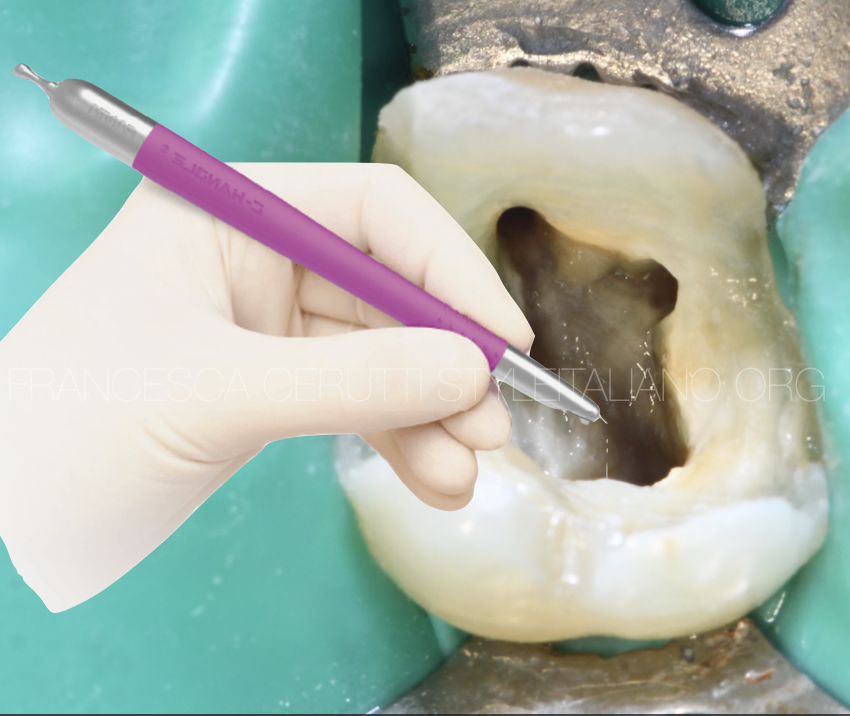
Apex locator is an electronic device used to determine the position of the apical foramen and its location and thus determine the length of the root canal space. Precise name of electronic apex locator (EAL) is Electronic Root Canal Length Measurement Device (ERCLMD) or Electronic Canal Length Measuring Devices. An electronic apex locator has been shown in Fig.6. The work of an Apex Locator is determined by comparing the electrical impedence of periodontal membrane with that of the oral mucosa. An electronic apex locator cord has two ends. One end is called 'lip hook' which is placed in contact with the oral mucosa of the patient. Other end is termed as 'file holder' which is a probe attached to the endodontic instrument in use. The attached file is slowly inserted into the root canal up to the estimated working length. As the file touches the soft tissues of the periodontal membrane, the electrical resistance gauges for both oral mucosa and periodontal membrane would have similar readings and the length of the canal can be determined here.
The development of apex locator has evolved since its first generation to now the 6th generation of apex locator. From resistance type in 1st generation, impedance type in 2nd generation the frequency type in 3rd generation, nowadays the latest generation of electronic apex locators are using multi frequency to be more precise and accurate.
The picture shows an Electronic Apex Locator with Multi frequency. The multi frequency apex locator eliminating necessity of drying the canal and improve precision and accuracy in reading the working length.It provides with a digital read out, graphic illustration and an audible signal.
How we use electronic apex locator clinically
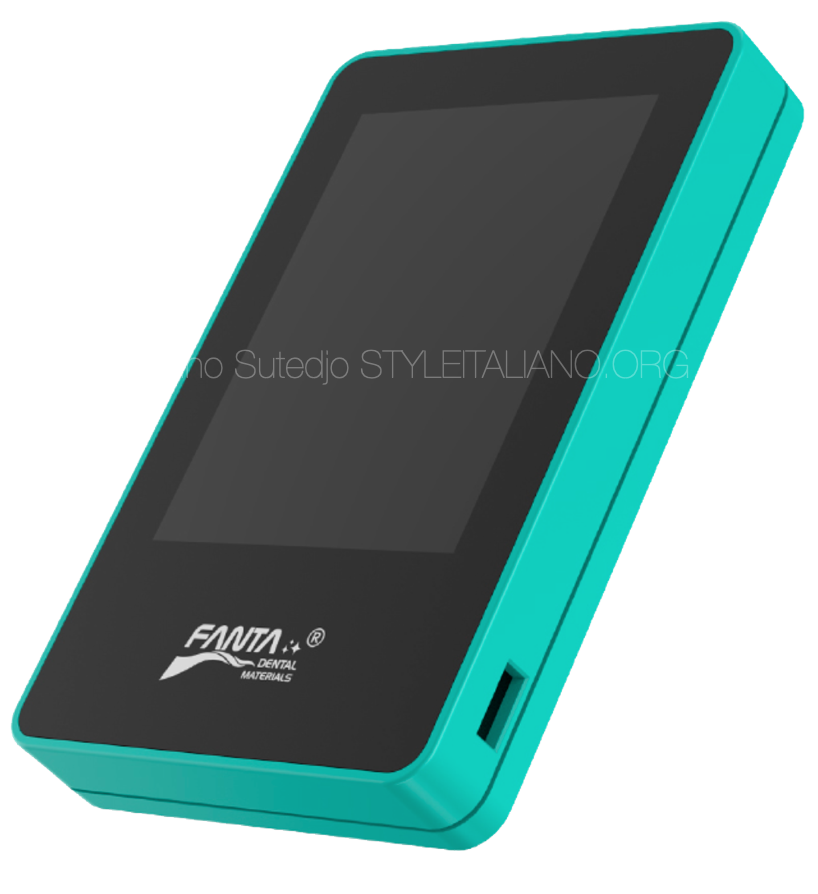

Fig. 7
Other function of Apex Locator are:
- To detect root perforations to clinically acceptable limits
- Determine the location of root and floor perforations
- To detect horizontal fractures
- Recognize any connection between the root canal & periodontal membrane such as root fracture, cracks & internal or external resorption.
This apex locator (wispex) from Fanta dental is a multi frequency apex locator, auto calibration and adjustable reference position for different cases.
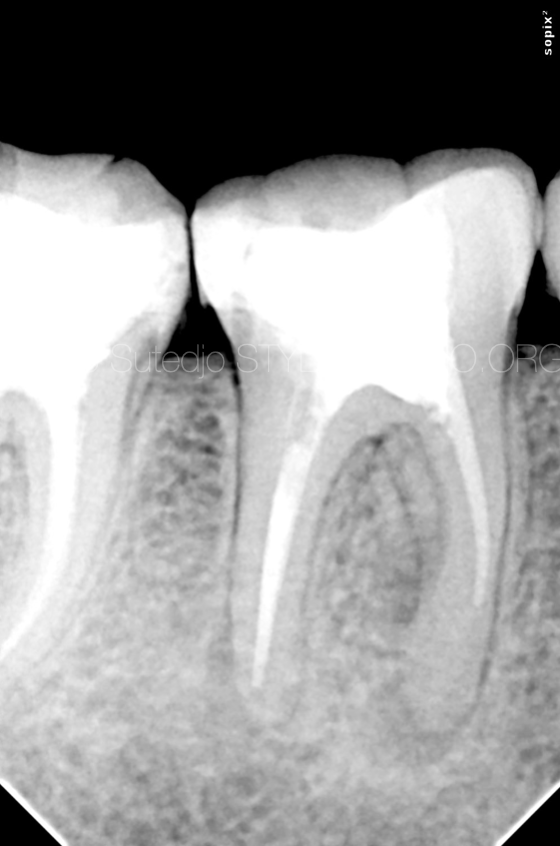
Fig. 8
Case of symptomatic apical periodontitis, lesion was evident on both mesial and distal root. Underfilled root canals more likely is the cause of this endodontic failure
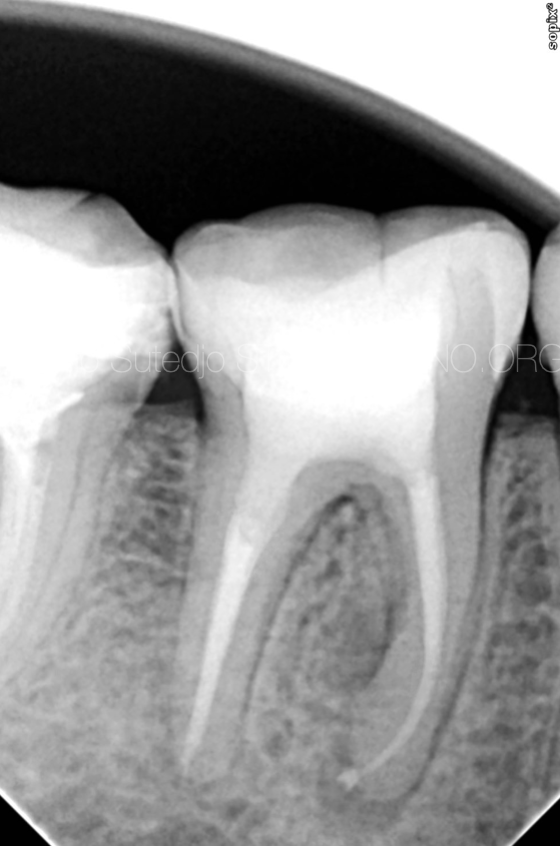
Fig. 9
After root canal retreatment, working length can be reached, shaped, cleaned and packed.
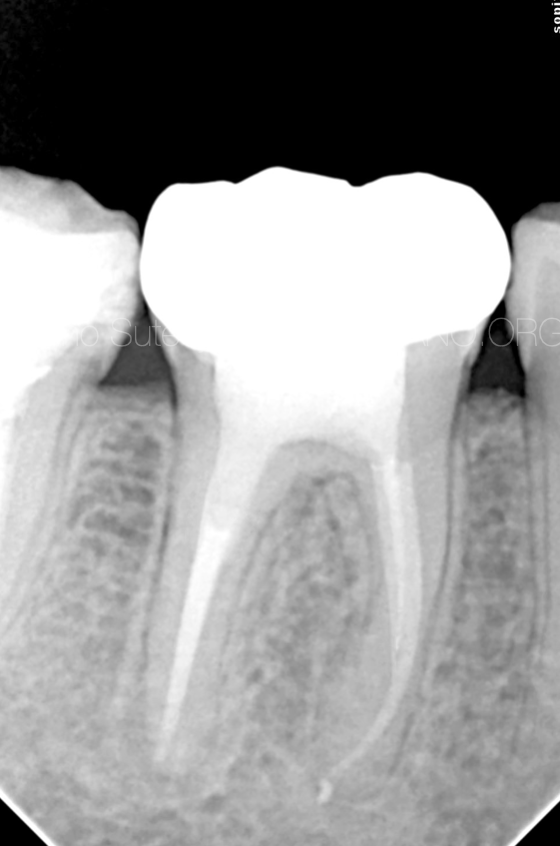
Fig. 10
2 years follow up showed healing lesion
Conclusions
It is undoubtful that higher survival rates were recorded for teeth with root canal fillings of the correct working length. No individual technique is truly satisfactory in determining endodontic working length. But modern electronic apex locators can determine this position with accuracies of greater than 90%. The correct use of an electronic apex locators are user friendly, less time consuming and reliable in most of the clinical situations yet safer compare with the radiographic. However, knowledge of apical anatomy still important for us to understand. Although apex locators can be used as an individual technique to determine working length, but the use of radiographs can not be replace completely, it will serve as an effective adjuvant.
Bibliography
1.Sjögren U, Hagglund B, Sundqvist G, Wing K. Factors affecting the long-term results of endodontic treatment. Journal of Endodontics 16, 498–504, 1990
2.M.P.J. Gordon & N.P. Chandler, “Electronic Apex Locators. Review” International Endodontic Journal 37, 425-437, 2004
3.Grove C. Why canals should be filled to the dentinocemental junction. Journal of the American Dental Association 17, 293–296, 1930
4.Khadse Amruta, Shenoi Pratima, Kokane Vandana ,Khode Rajiv, Sonarkar Snehal, “Electronic Apex Locators-An overview” Indian Journal of Conservative and Endodontics,April-June; 2(2); 35-40, 2017
5.Grossman’s Endodontic Practice, 13th Edition.
6.Fouad AF, Reid LC. Effect of using electronic apex locators on selected endodontic treatment parameters. Journal of Endodontics 26, 364–367, 2000