Necrodontics - saving hopeless teeth
05/12/2020
Bartłomiej Karaś
Warning: Undefined variable $post in /var/www/vhosts/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/endodontics.styleitaliano.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
Warning: Attempt to read property "ID" on null in /var/www/vhosts/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/endodontics.styleitaliano.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
Both non-surgical and surgical retreatment procedures are performed when the primary treatment fails and we are trying to preserve the tooth. Usually the next attempt after the primary treatment is non-surgical retreatment and follow up. In some cases when we estimate that non-surgical procedures will not be helpful we can perform surgical retreatment with apicectomy.
Sometimes the cases that we want to treat are that challenging that they require both procedures at the same time. This article was written to show the possibility of the alternative method of treatment hopeless teeth.
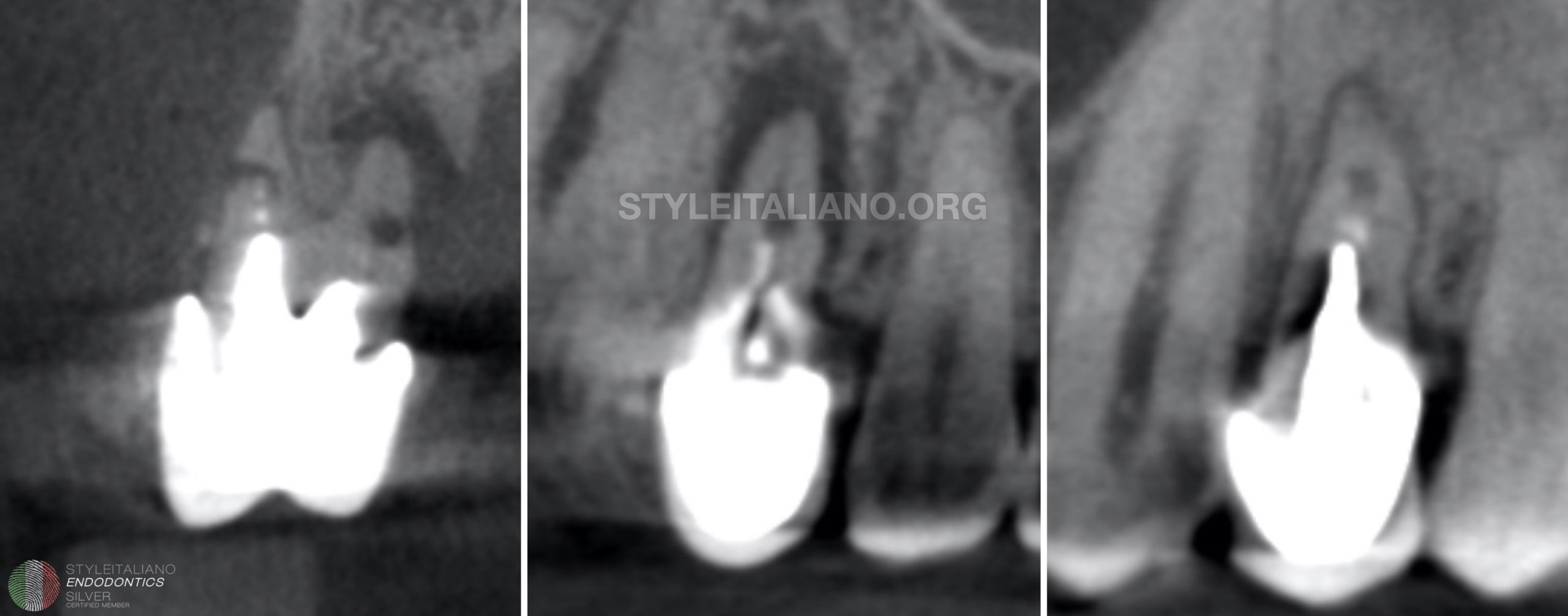
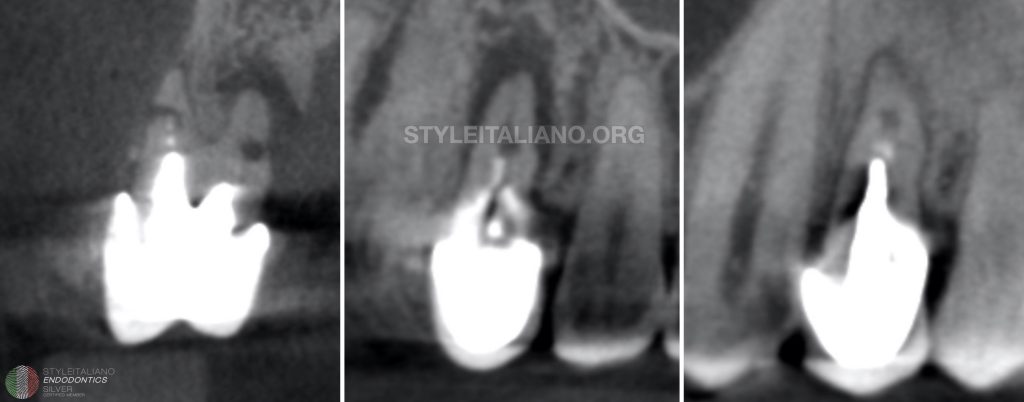
Fig. 1
The patient was referred to my office to estimate the possibility of the RCT. The most important tool during the diagnostic protocol was the CBCT imagining. 3D image allowed me to estimate all the difficulties of the treatment:
- huge lesion around the palatal root
- internal resorption of the palatal root with the perforation
- resorption or crack of the vestibular root
I gave two options for the treatment. Extraction and implantoprothetic treatment or small experiment with surgical and nonsurgical pretreatment which I called a „necrodontics”.
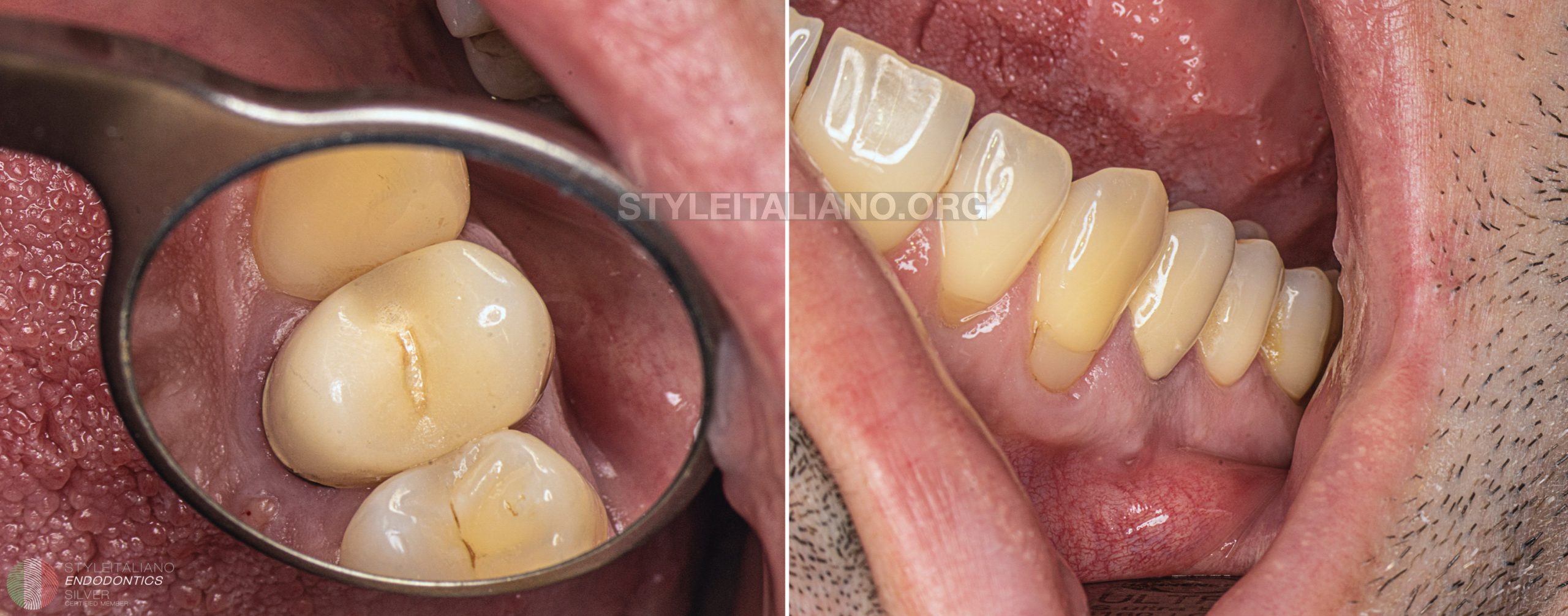
Fig. 2
Necrodontic procedure was developed to give a chance to a hopeless teeth. In this particular case I had to perform:
- removal of the crown and cast post
- restore the tooth
- remove the endomethasone
- shape the palatal canal
- clean the resorption chamber
- fill the apex with guttapercha (sandwich technique) and clean the resorption chamber
- fill the resorption and palatal root with MTA
- restore the tooth
- make a flap
- perform the apicectomy of the vestibular root
- place sutures
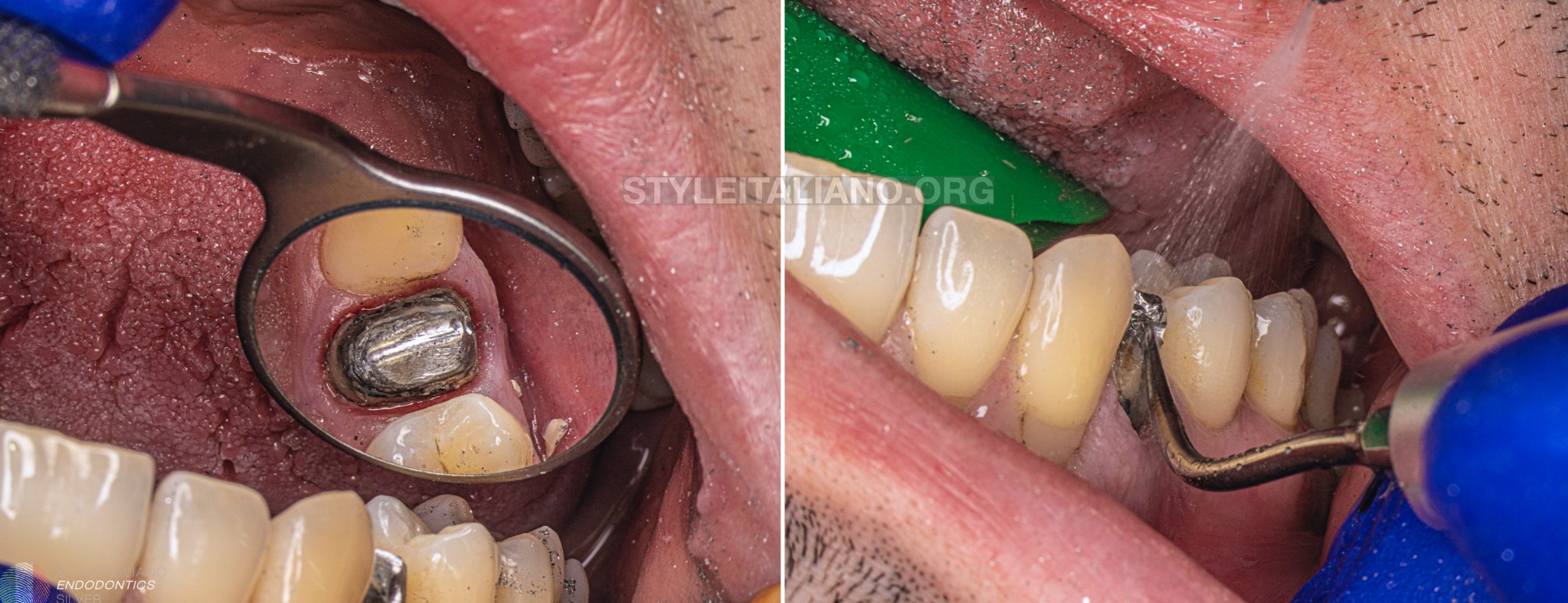
Fig. 3
In the beginning the crown was cut and the cast post was removed with ultrasonic tips
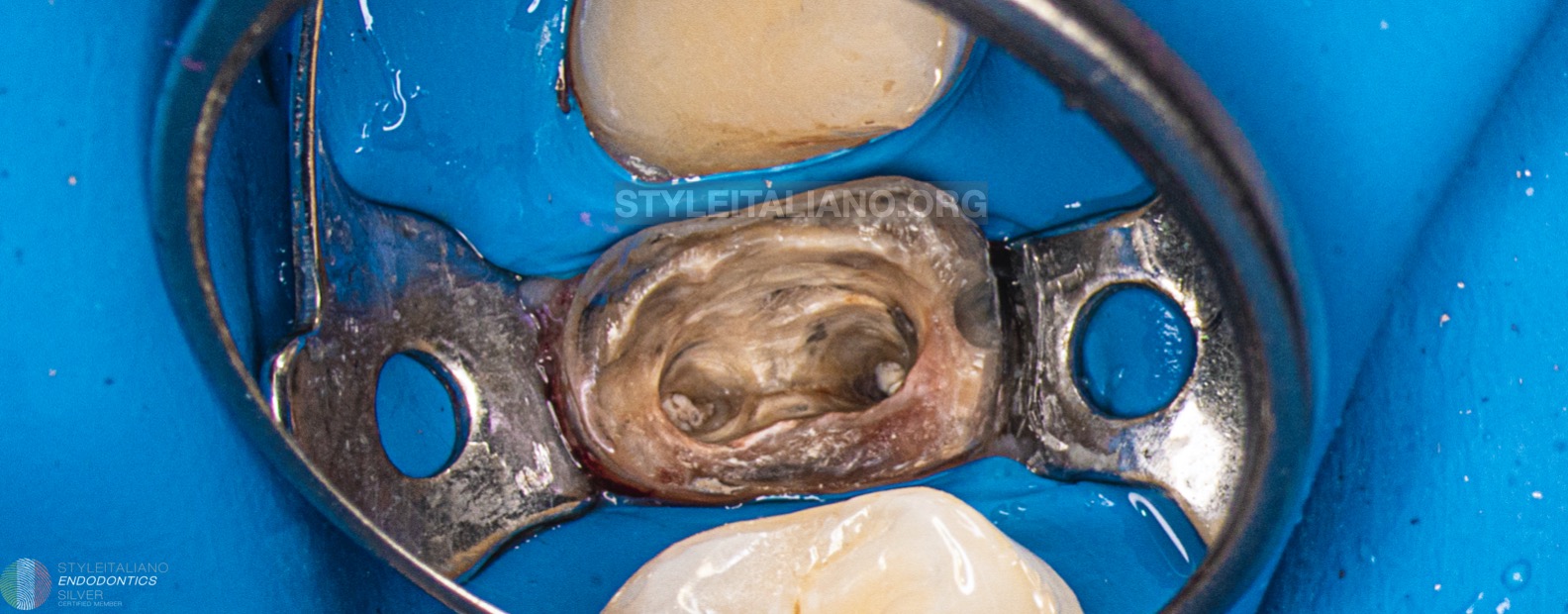
Fig. 4
After removing the cast post the tooth was isolated with the rubber dam with a single clamp
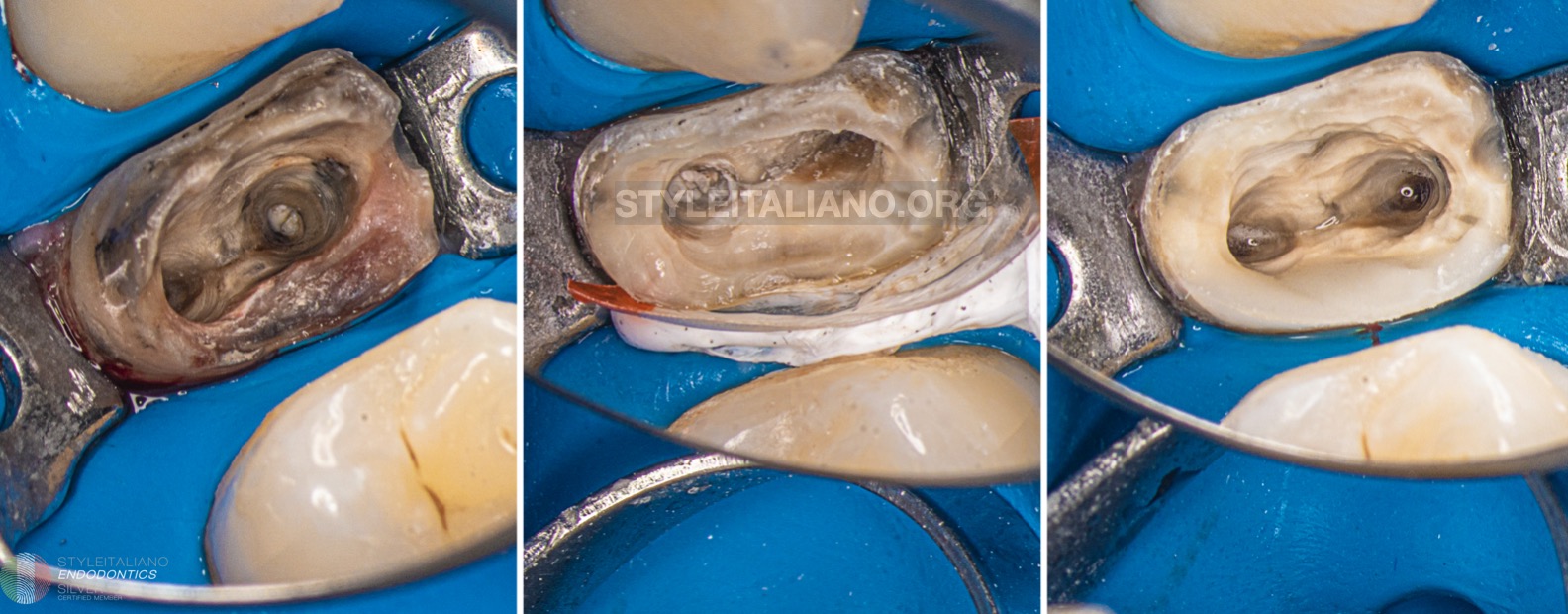
Fig. 5
distal wall was restored with additional isolation of the teflon tape and matrix
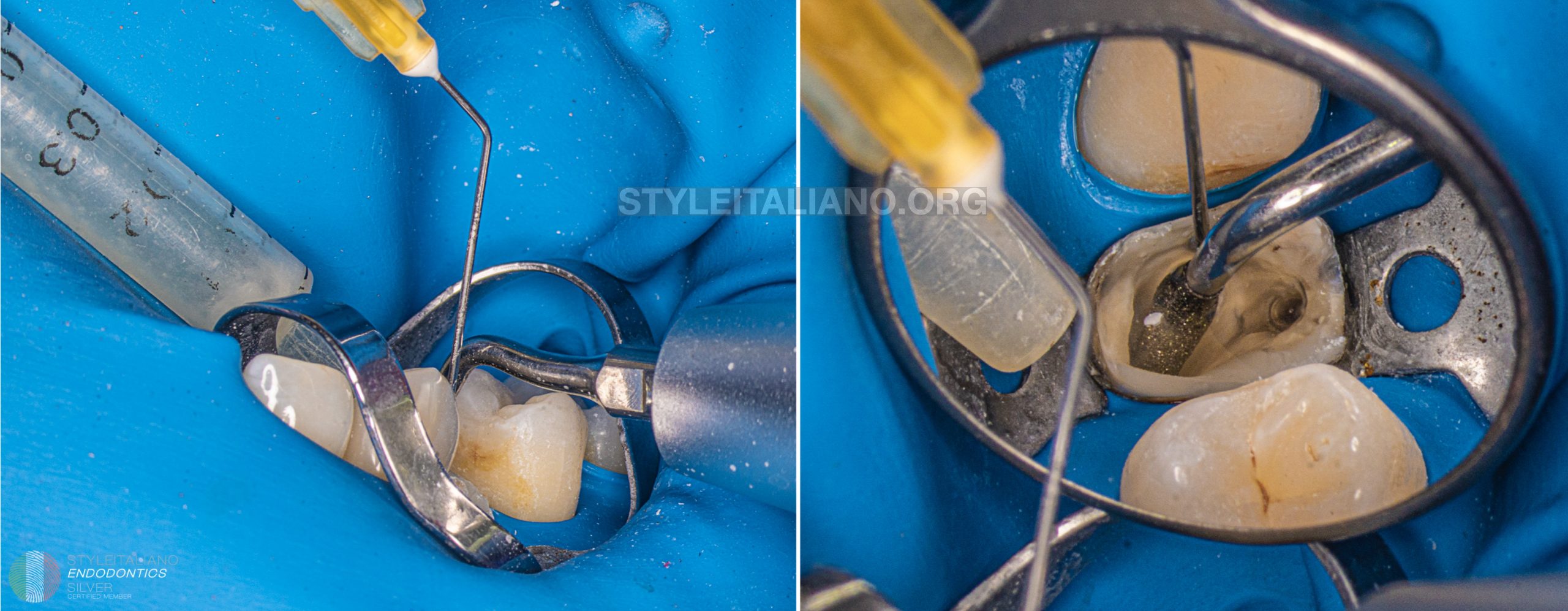
Fig. 6
Cleaning of the chamber and canals were performed with sodium hypo and US tips
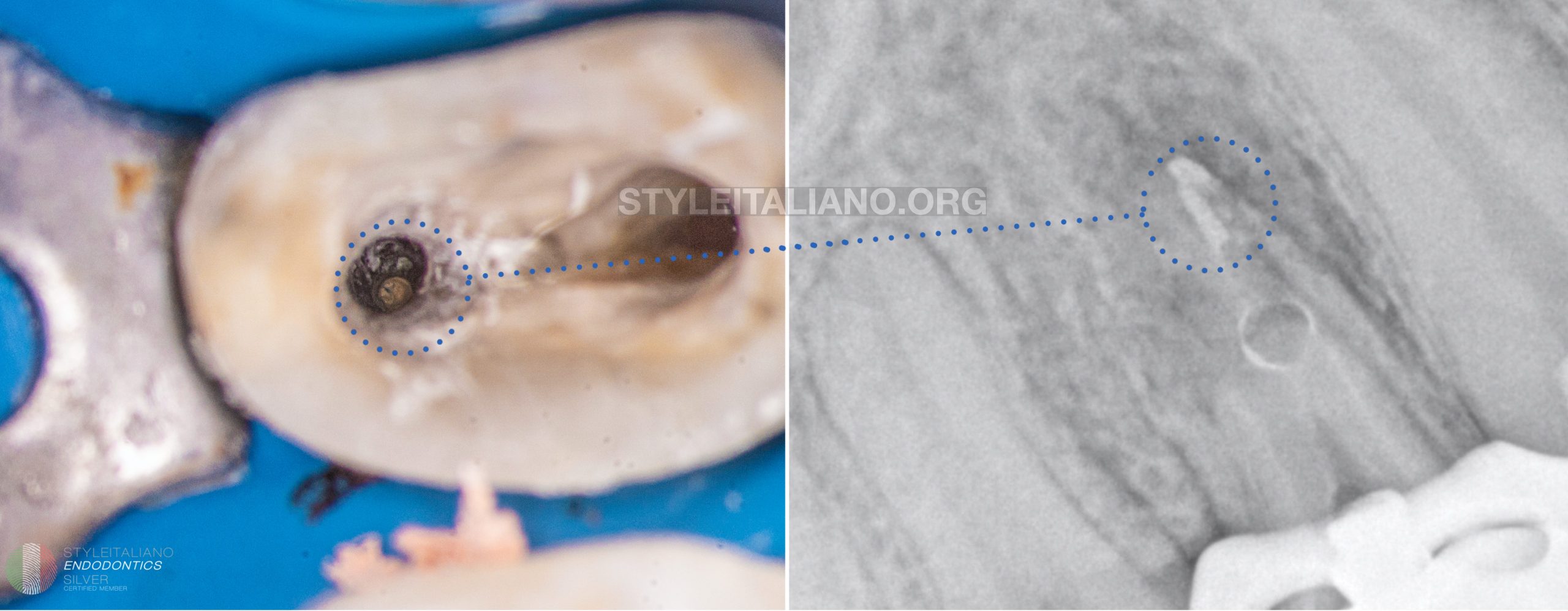
Fig. 7
First stage of the obturation was to fill the apex of the palatal canal with guttapercha and bioceramic sealer. As we can see on the Xray some part of the sealer remain in the resorption chamber and I had to clear it before placing the MTA. In fact both materials have quite similar composition but I wanted to have good compaction of the MTA so I removed and dried the chamber.
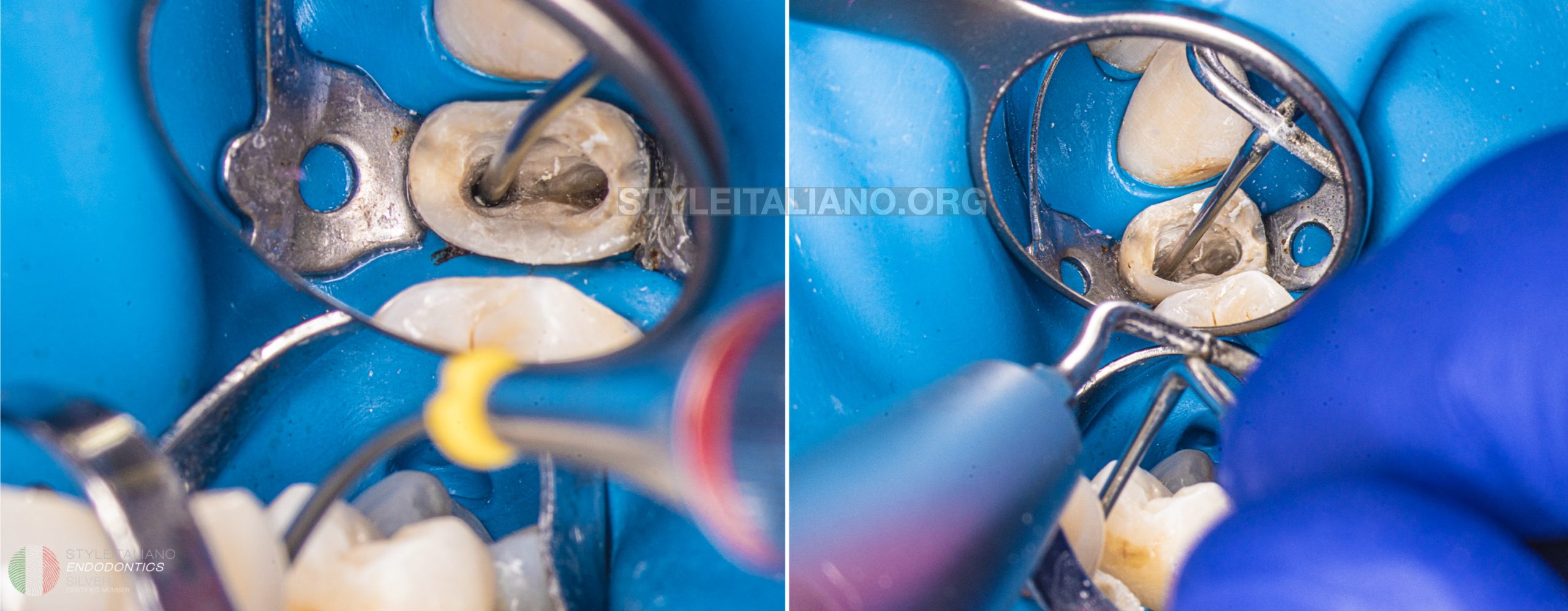
Fig. 8
MTA was placed in both canals with the MAP One system and compacted with US tip and hand plugger
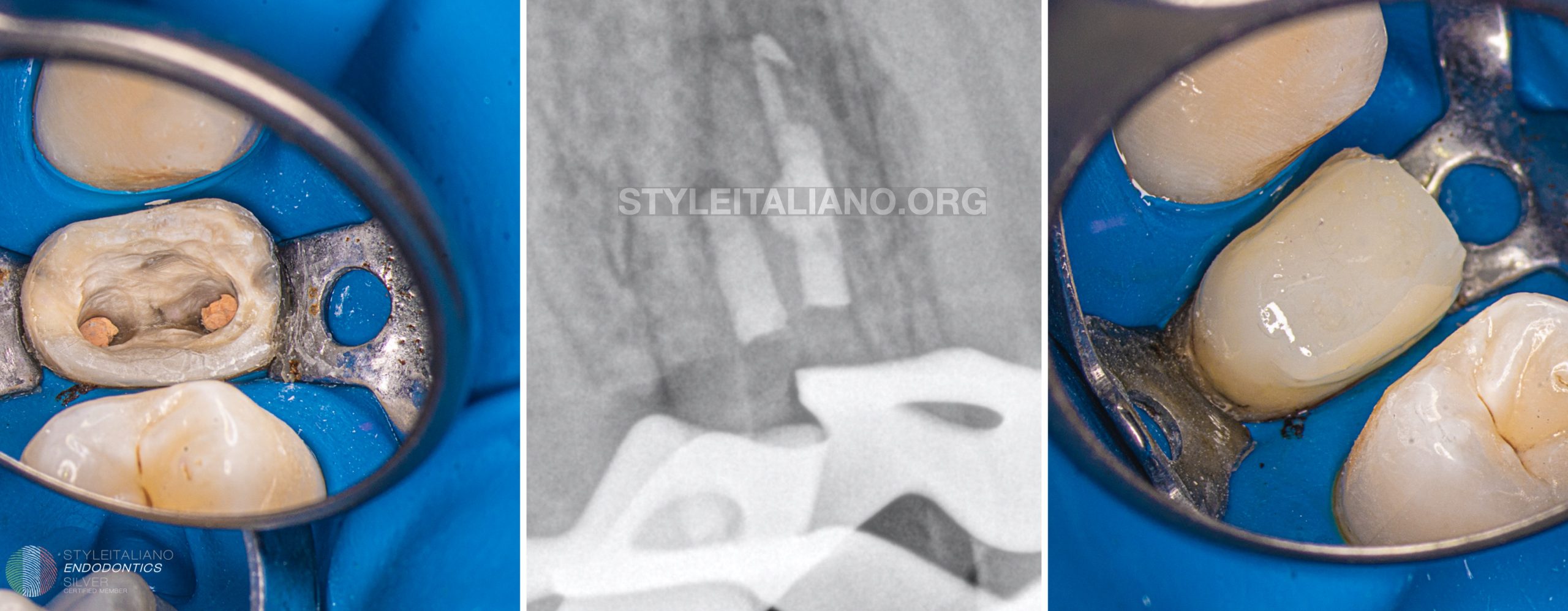
Fig. 9
Coronal part of the roots was filled with guttapercha plug
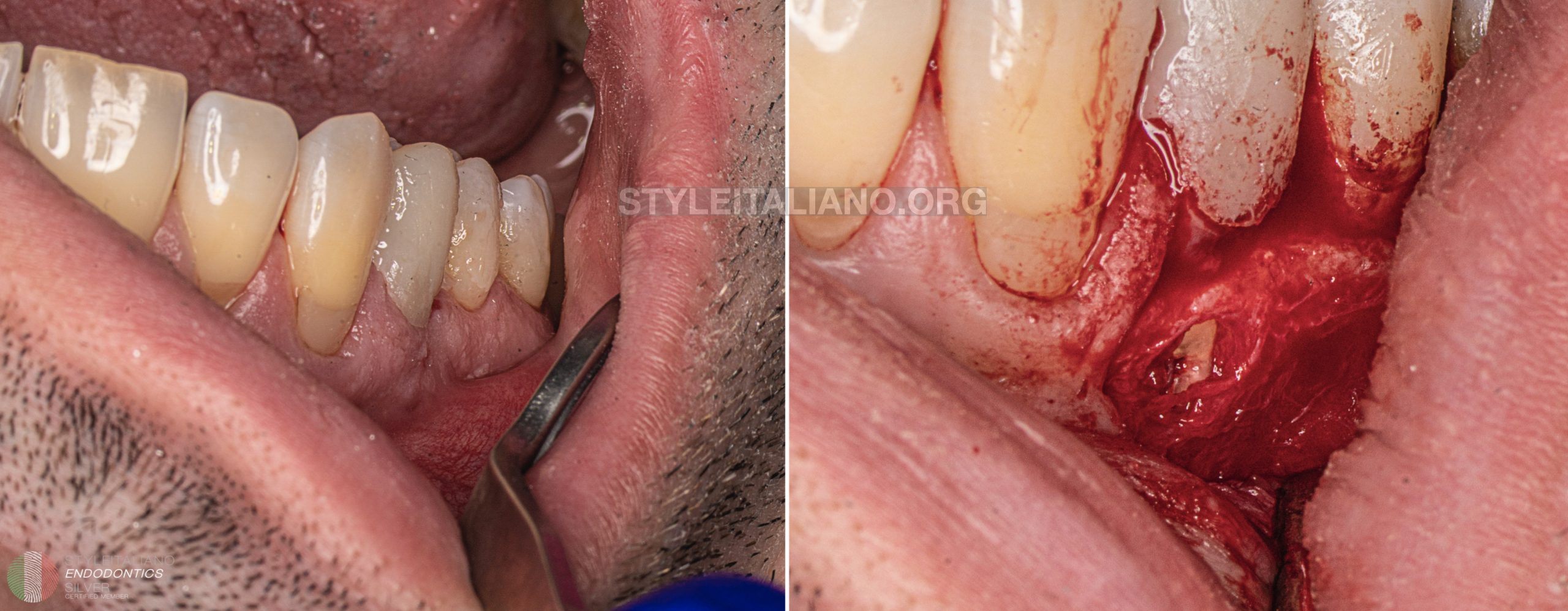
Fig. 10
The flap and surgical procedure of apicectomy was performed
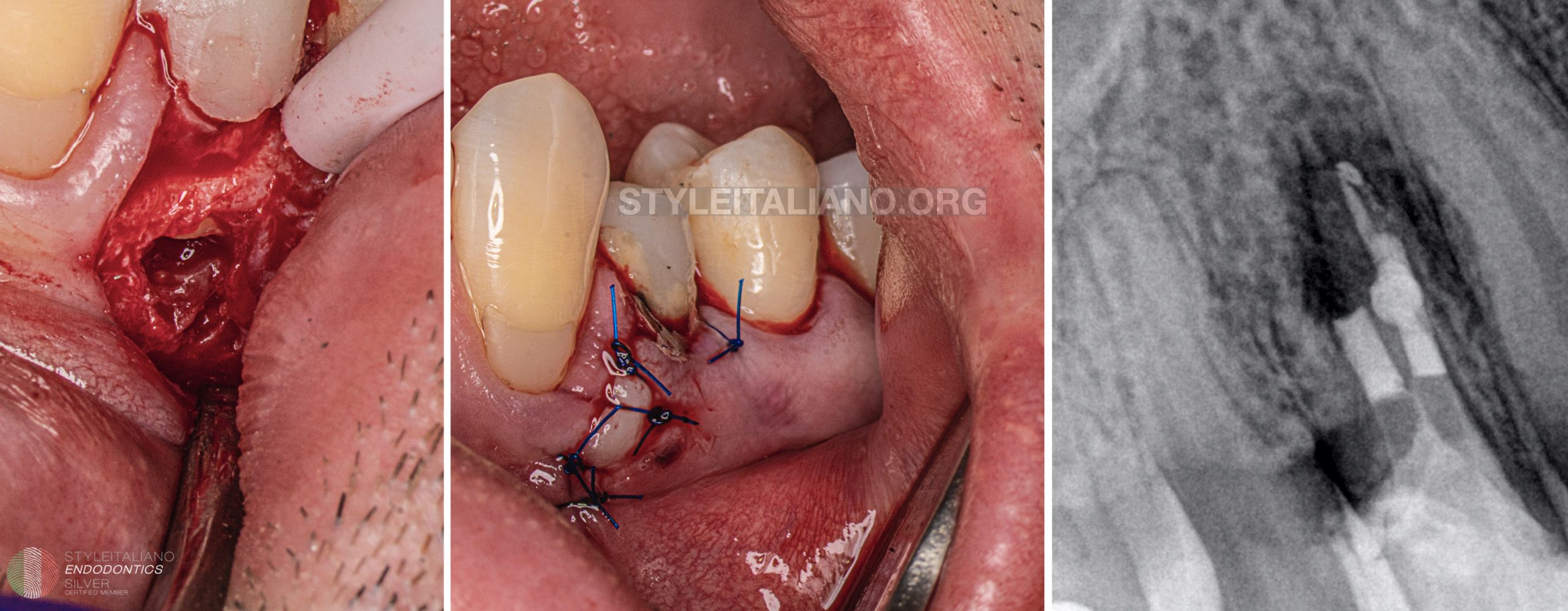
Fig. 11
Sutures were placed and the control Xray was performed.
Conclusions
In the end of this case report I would like to remind that this kind of treatment is an alternative approach. We need to understand and explain to the patient that the longevity of the tooth is limited and one of the most important values of the treatment is the healed bone for further implantoprothetic procedures
Bibliography
Estrela Carlos, Decurcio Daniel de Almeida, Rossi-Fedele Giampiero, Silva Julio Almeida, Guedes Orlando Aguirre, Borges Álvaro Henrique. Root perforations: a review of diagnosis, prognosis and materials. Braz. oral res. Epub Oct 18, 2018.
M Torabinejad, N Chivian. Clinical applications of mineral trioxide aggregate. J Endod. 1999 Mar;25(3):197-205.
Patel S,Ricucci D, Durak C, BDSc, Tay F. Internal Root Resorption: A Review. JOE, Volume 36, Number 7, July 2010