Endodontic management of a tooth with large pulp stone
23/07/2020
Khalid Jamal Attar
Warning: Undefined variable $post in /home/styleendo/htdocs/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
Warning: Attempt to read property "ID" on null in /home/styleendo/htdocs/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
Pulp stones are discrete calcifications found in the pulp chamber of the tooth which may undergo changes to become diffuse pulp calcifications such as dystrophic calcification.[1]
The number of pulp stones in a single tooth may vary from 1 to 12 or more, with varying sizes from minute particles to large masses which tend to occlude the pulpal space. It is reported that pulp stones are more commonly found in the coronal region of pulp, also found in the radicular pulp.[1]
Etiological factors for pulp stone formation are not well understood, although some factors that have been implicated in stone formation include pulp degeneration, inductive interactions between epithelium and pulp tissue, age, circulatory disturbances in pulp, orthodontic tooth movement, idiopathic factors, and genetic predisposition.[1]
The large size of pulp stones in the pulp chamber may block access to canal orifices and alter the internal anatomy. Attached stones may deflect or engage the tip of exploring instruments, preventing their easy passage down the canal.[2]
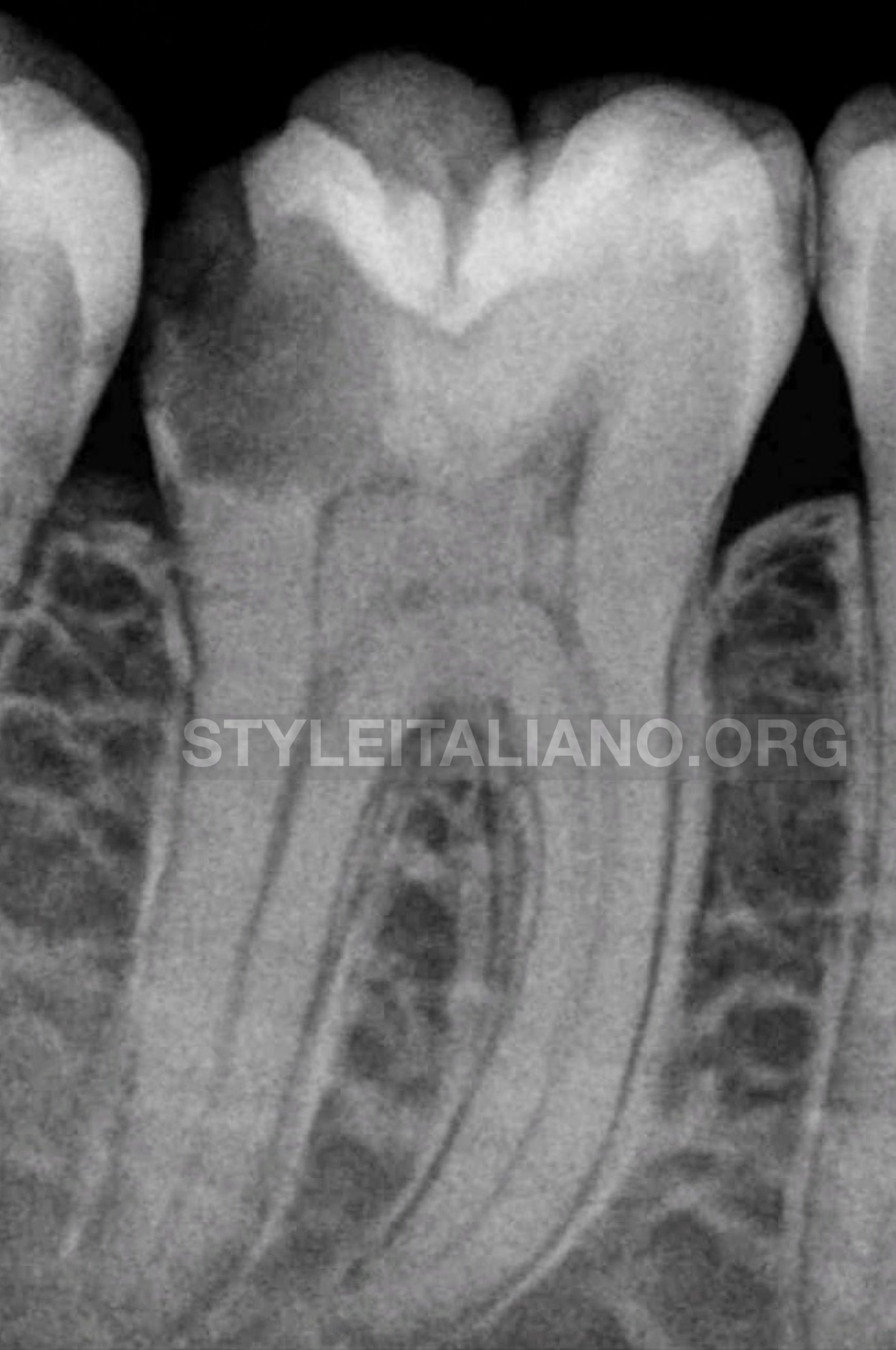
Fig. 1
A 42-year-old male came to our dental clinic , with a chief complaint of food impaction and awaked at night with sever pain in the right lower molar region for 3 weeks .
Clinical examination: it was observed that the mandibular right first molar had a deep distally caries with an exposed pulp.
The tooth was severely tender on percussion and had moderate pain on palpation.
Radiographically revealed diffused radio-opacities throughout the pulp chamber, the canal outlines for the mesial and distal roots were quite clear and traceable till the apex.
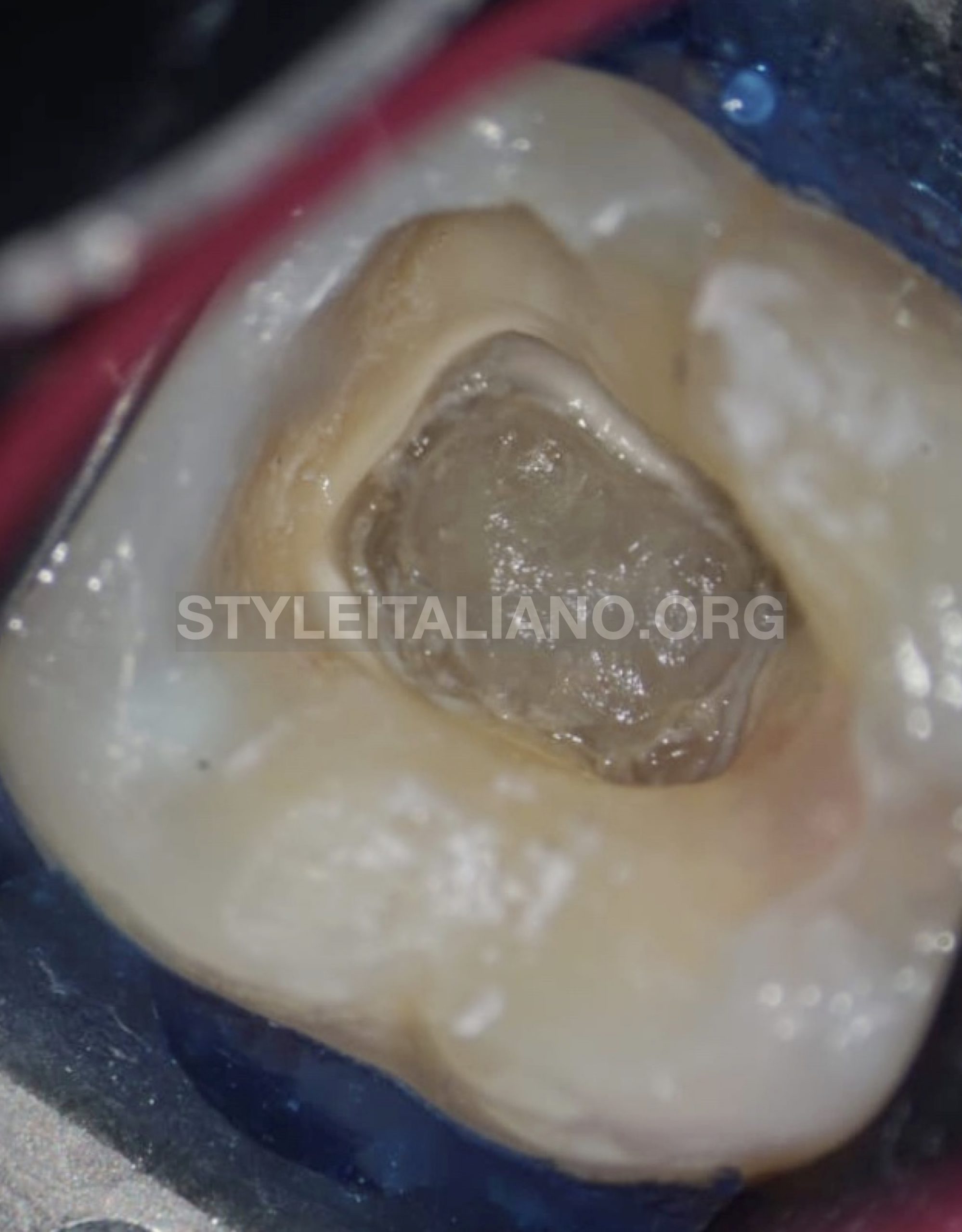
Fig. 2
Access was gained to the pulp chamber after administration of local anesthesia (2% lignocaine with 1:100,000 epinephrine) under rubber dam isolation.
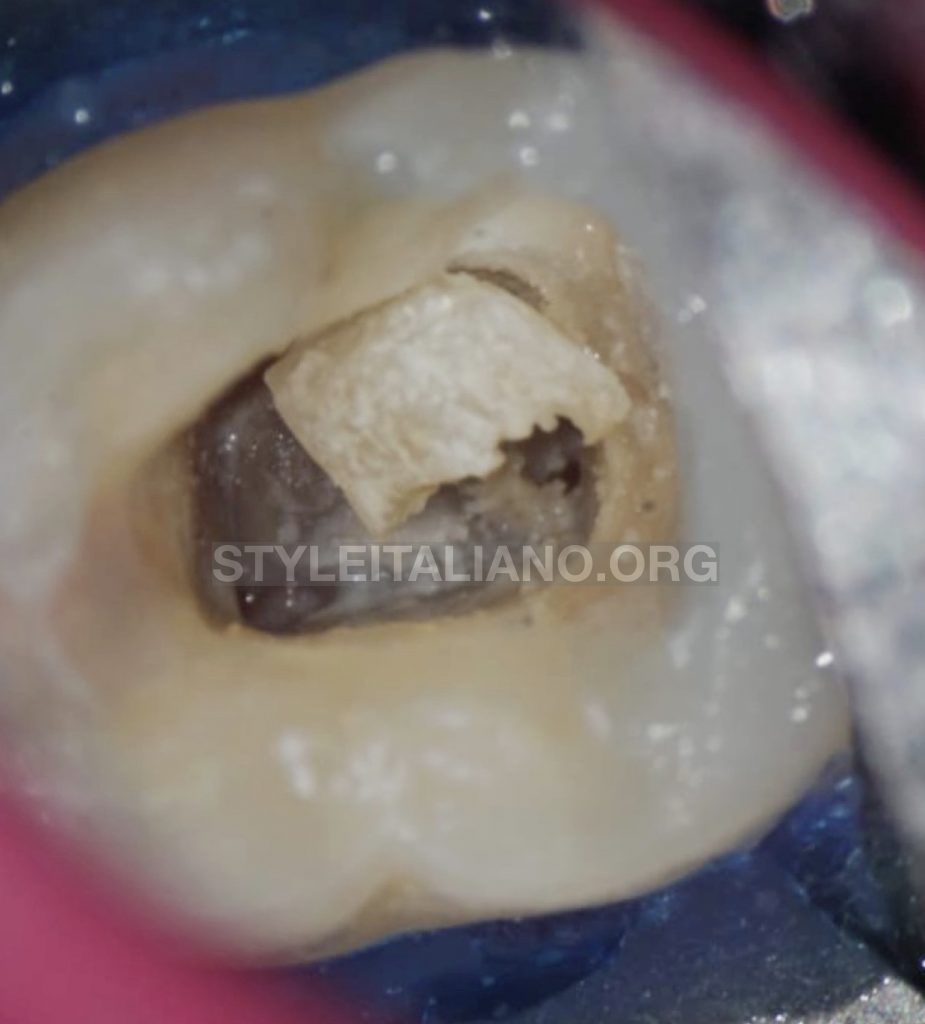
No drop was felt in the pulp chamber since it was completely obliterated.
The calcified mass was clinically visible under microscopical magnification, it was an irregular large mass attached to the walls and the floor of the pulp chamber.
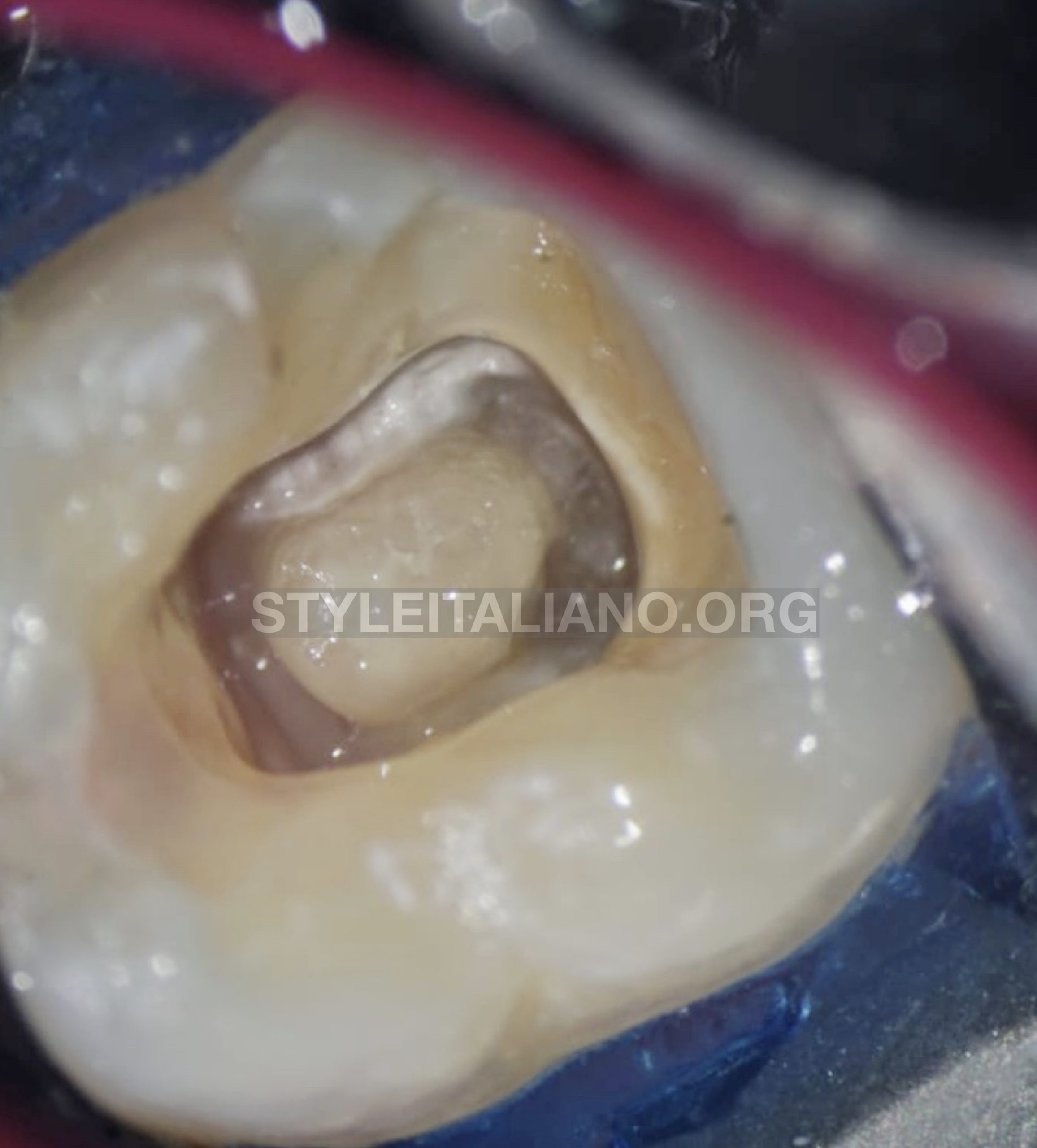
Fig. 3
After careful extensions of the access cavity, I used ultrasonic tips BUC1and BUC1A(Obtura Spartan) with newtron P5 BLED (Acteon, France) for further refinement of access cavity walls, also to dissect and displacement of the calcified mass (pulp stone).
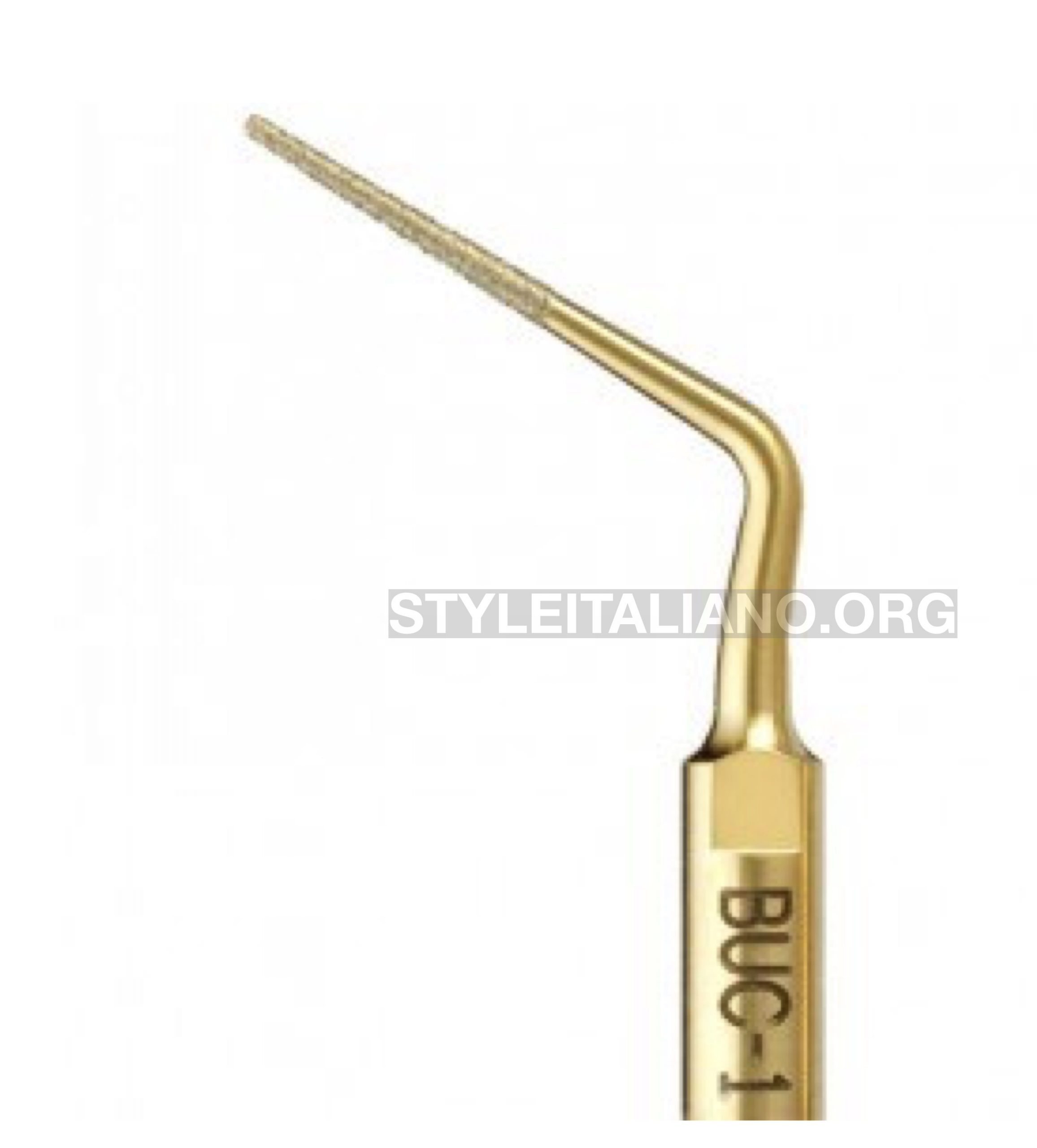

Fig. 4
Rounded tip with diamond coated used for smoothing access walls and cashing the calcification .
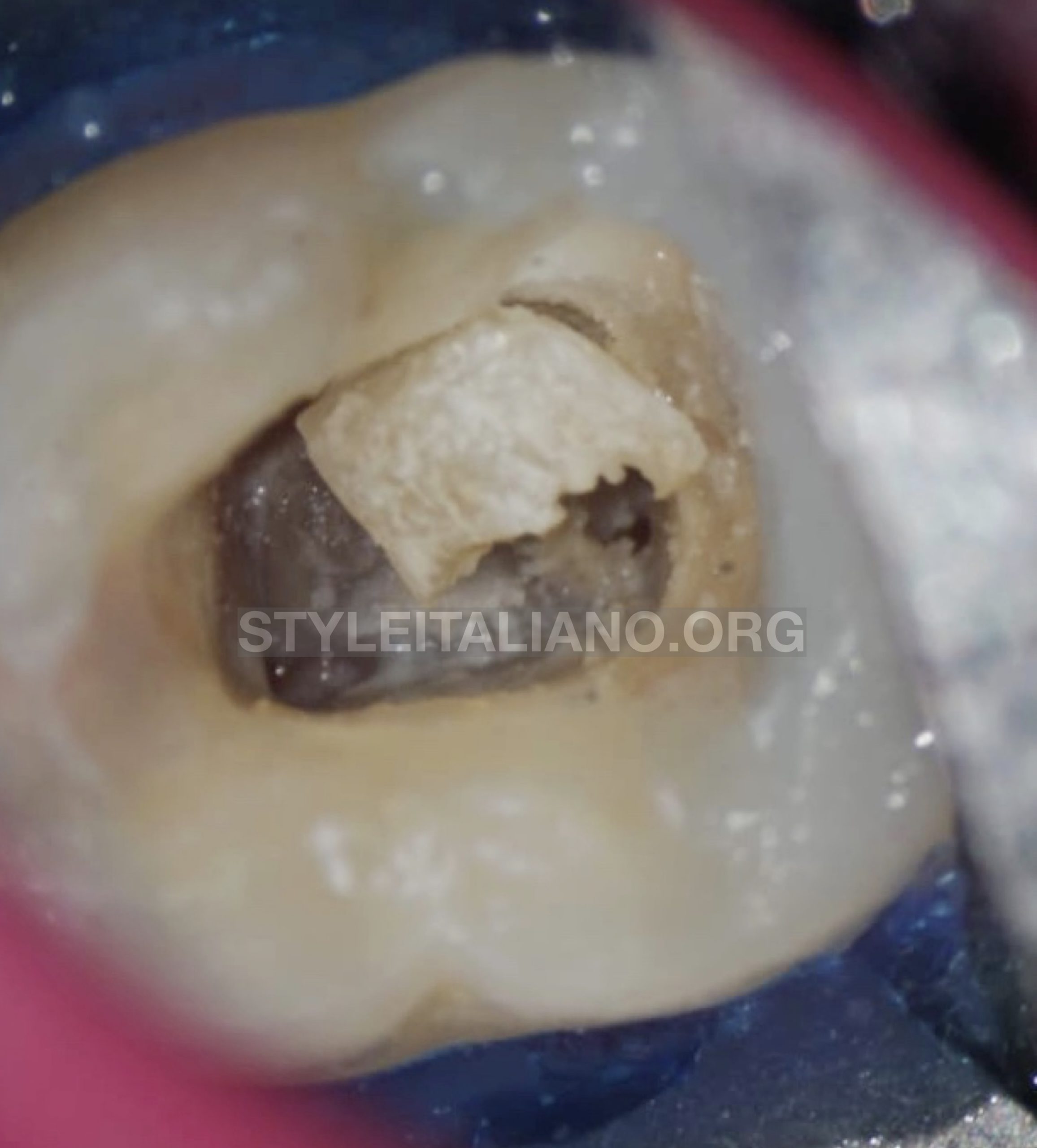
Fig. 5
Finally the entire mass (pulp stone) was dislodged from the walls and floor of the pulp chamber with ultrasonic tip BUC 2 (Obtura Spartan Endodontic), the root canal orifices were located .
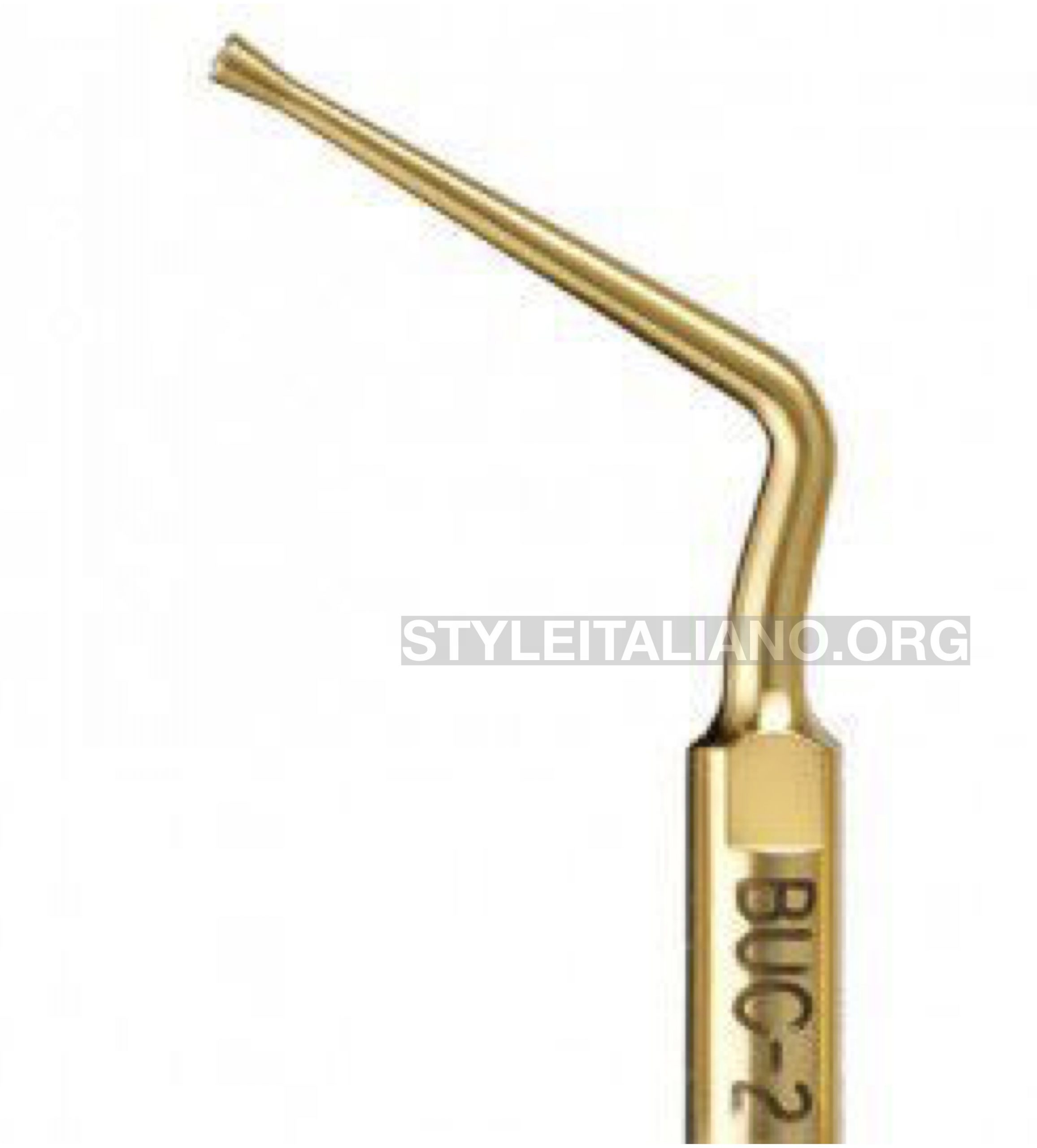

Fig. 6
Disk-like tip allows you to horizontally smooth pulp chamber floors,safety dislodgment the pulp stone and because the unique design prevents cutting of the chamber floor .
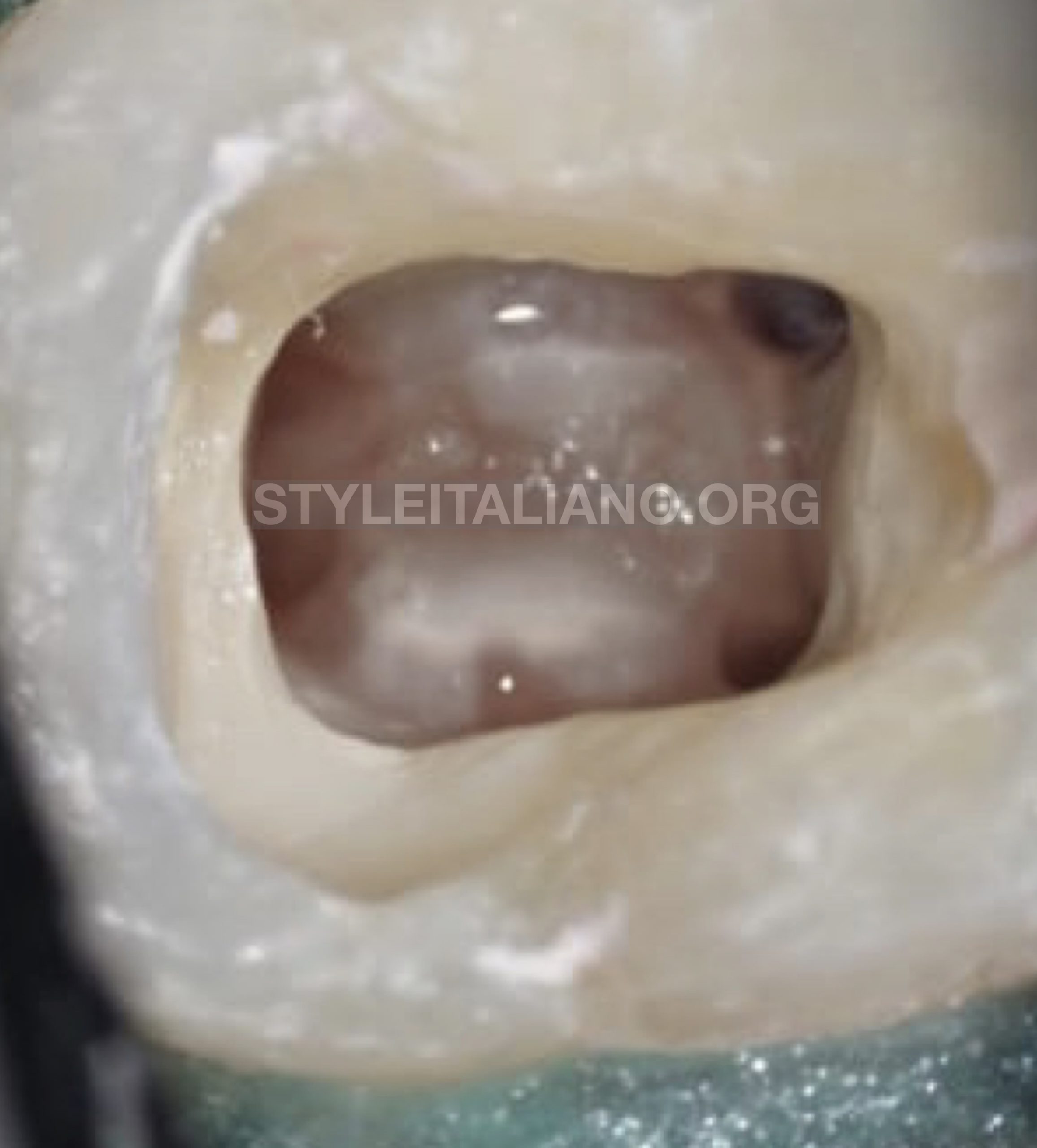
Fig. 7
After root canal orifices were located , the patency of all the root canals was checked with #10 K file.
The working length was determined by Root ZX II (J. Morita, Kyoto, Japan) apex locator for all the four root canals (ML, MD) were joined and also (DB ,DL) .
The root canals were cleaned and shaped by rotary Fanta files(Shanghai Fanta Dental Materials Co., Ltd ) .
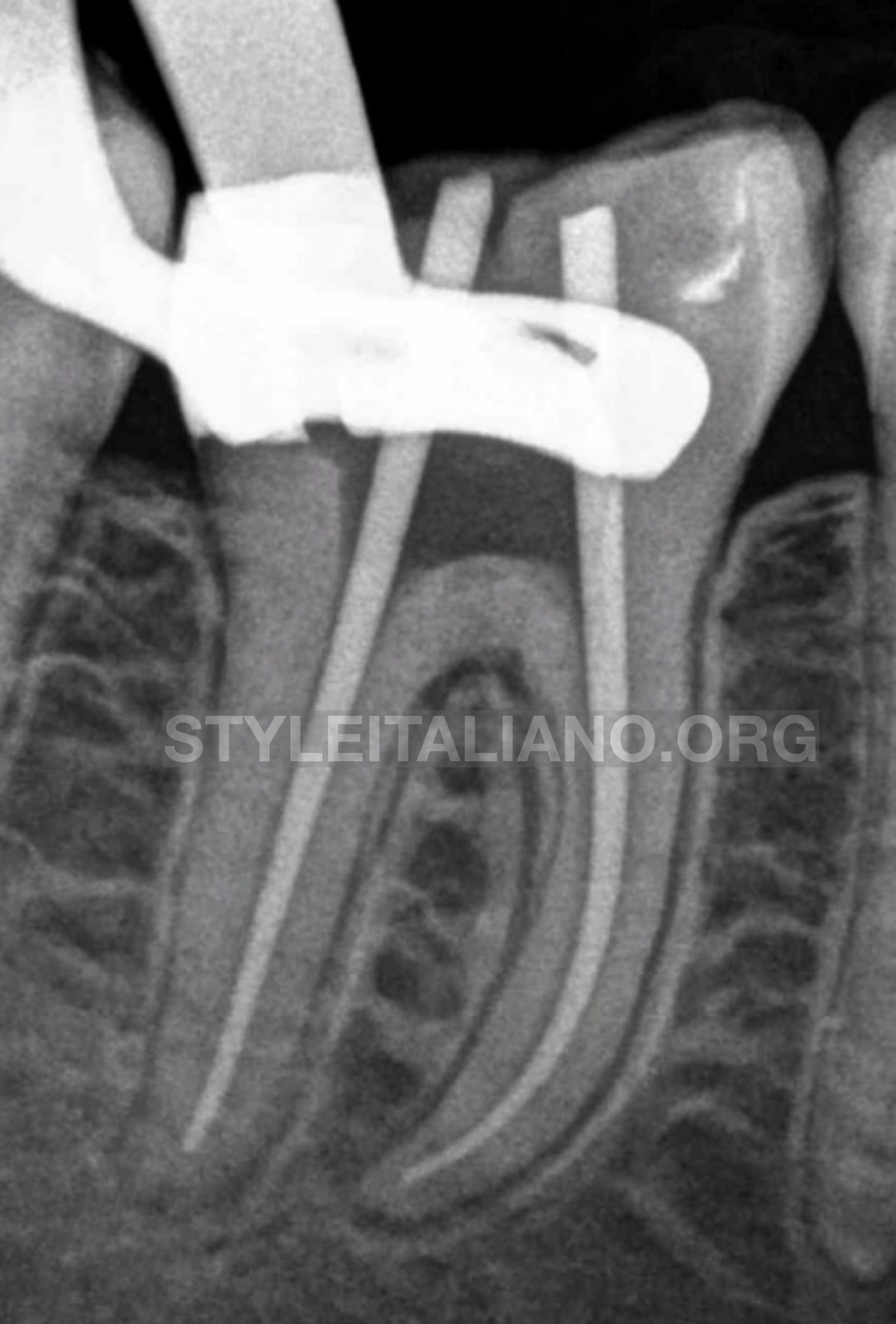
Fig. 8
The canals were sequentially irrigated using 5.2% sodium hypochlorite and 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) during the cleaning and shaping procedure with 2-side vents irrigation tip IrriFlex (Produits dentaires SA) ,final rinse activated with ultrasonic device UltraX eighteeth (Changzhou Sifary Medical Technology Co., Ltd) and the working length confirmed radiographically with gutta percha cone.
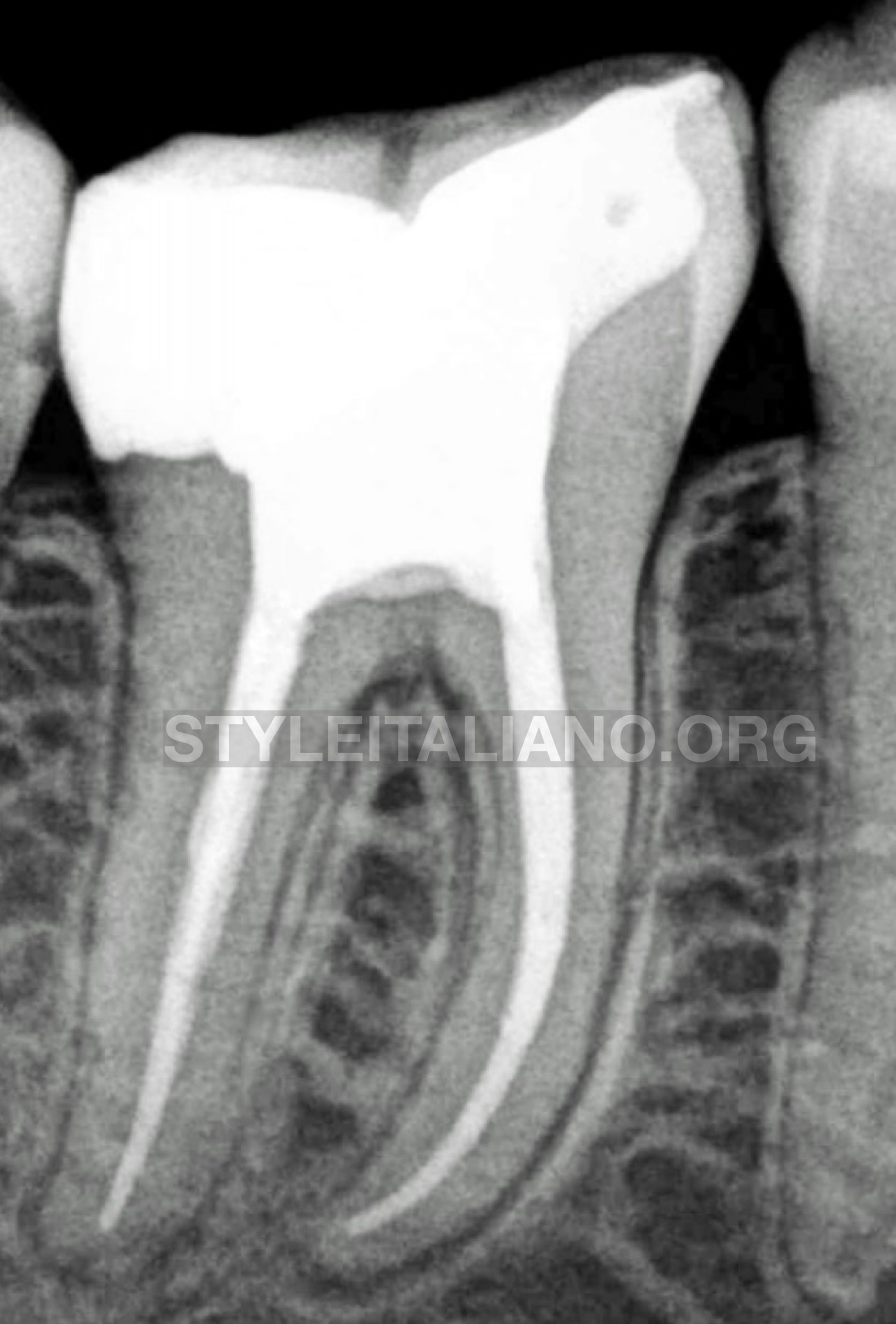
Fig. 9
-The canals were thoroughly dried and all the root canals were coated with AH-plus resin based sealer (Dentsply Maillefer).
-Obturation was carried out using the warm vertical compaction technique, then the access cavity was filled with composite resin.
-post-operative radiograph was taken which showed well-obturated root canals.
Conclusions
The removal of pulp calcification (pulp stones) is present another challenge in endodontic treatment, as they block the access to the root canals. The best treatment for this condition is the combination of magnification and ultrasonic tips. The improved visualization and the conservative wear of the ultrasonic tip result in fewer iatrogenic errors.
Bibliography
[1] Goga R, Chandler NP, Oginni AO (June 2008).pulp stone review PDF). International Endodontic Journal. 41 (6): 457–68.
[2].Pashley DH, Walton RE, Slavkin HC (2002) Histology and physiology of the dental pulp. In: Ingle JI, Bakland LK, eds. Endodontics, 5th edn. Hamilton, ON, Canada: BC Decker Inc, pp. 43–5.

