Management of Missed Canal Part 1: Lower First Molar
31/10/2020
Marc Habib
Warning: Undefined variable $post in /var/www/vhosts/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/endodontics.styleitaliano.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
Warning: Attempt to read property "ID" on null in /var/www/vhosts/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/endodontics.styleitaliano.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
It is reported that almost 40% of retreatment with chronic apical periodontitis or symptomatic apical periodontitis are due to missed canals.
Karabucak & all reported in 2016 an overall incidence of missed canals in treated teeth to be 23.04% and 41 to 46% in maxillary first molars. Teeth with a missed canal were 4.38 times more likely to be associated with a lesion.
Baruwa & al in 2019, reported as well overall incidence of missed canals in treated teeth to be 12% and 62% in maxillary first molars. Teeth with a missed canal were 3.1 times more likely to be associated with a lesion.The focus is always on maxillary molars due to the high frequency of the MB2 canal and the difficulty of locating it in most of the cases.
Witherspoon & all 2013, found In the mandibular first molars, 86% of missed canals in the distal root and 14% were identified in the mesial root.
The following case report, confirms the findings sited in the literature.
A lower first molar treated endodonticaly due to deep caries on the distal aspect , was then restored with a Crown.The patient comes back after only 4 months with acute pain and tenderness on his first lower first molar tooth #46.
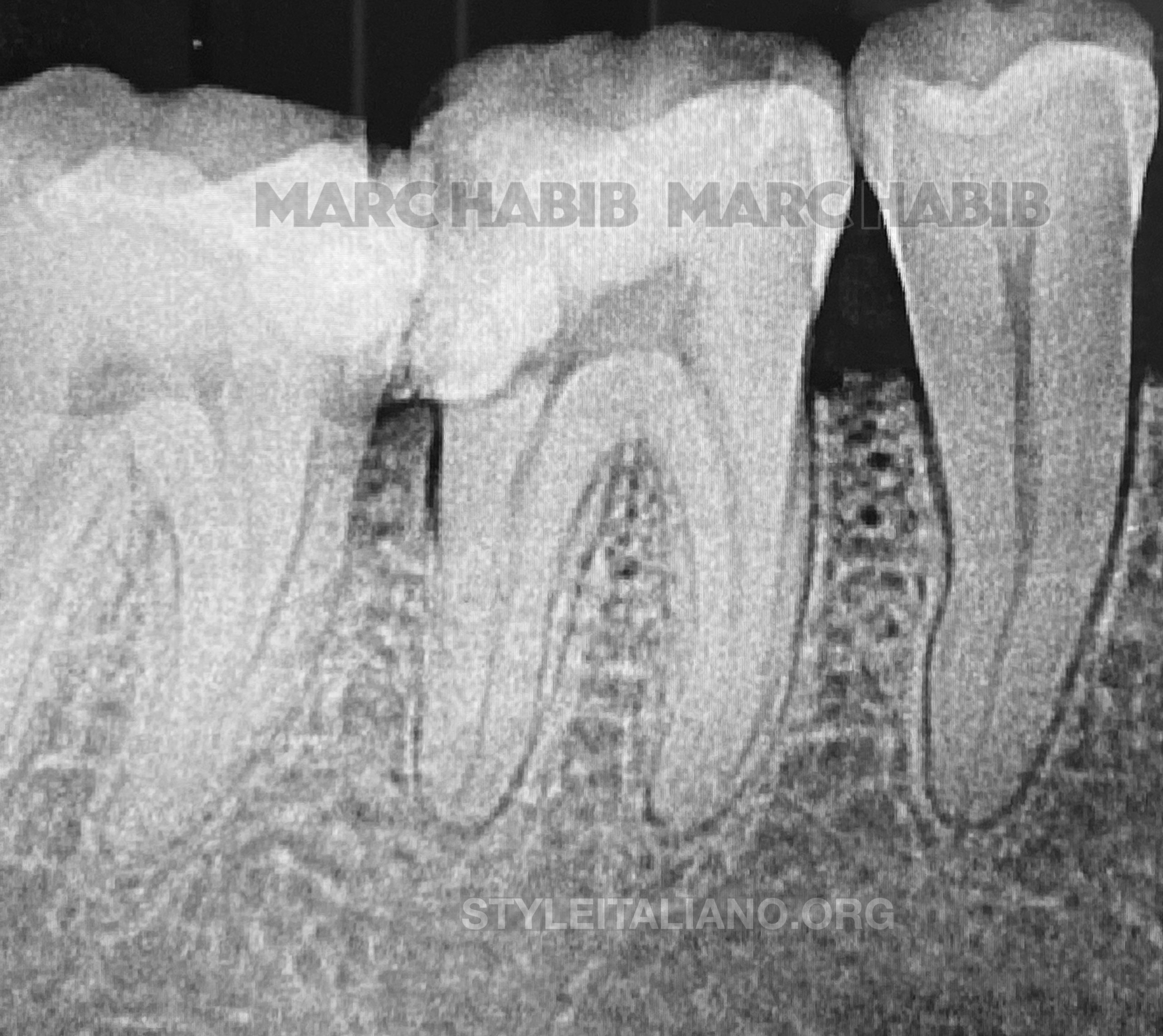
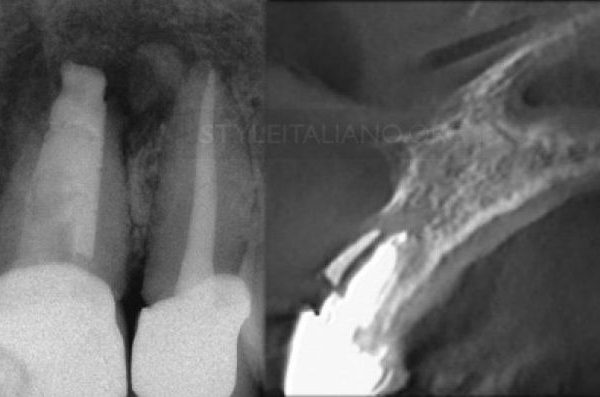
Fig. 1
Pre operative X ray before the primary treatment of tooth number 46 showing deep carious lesion reaching the pulp chamber
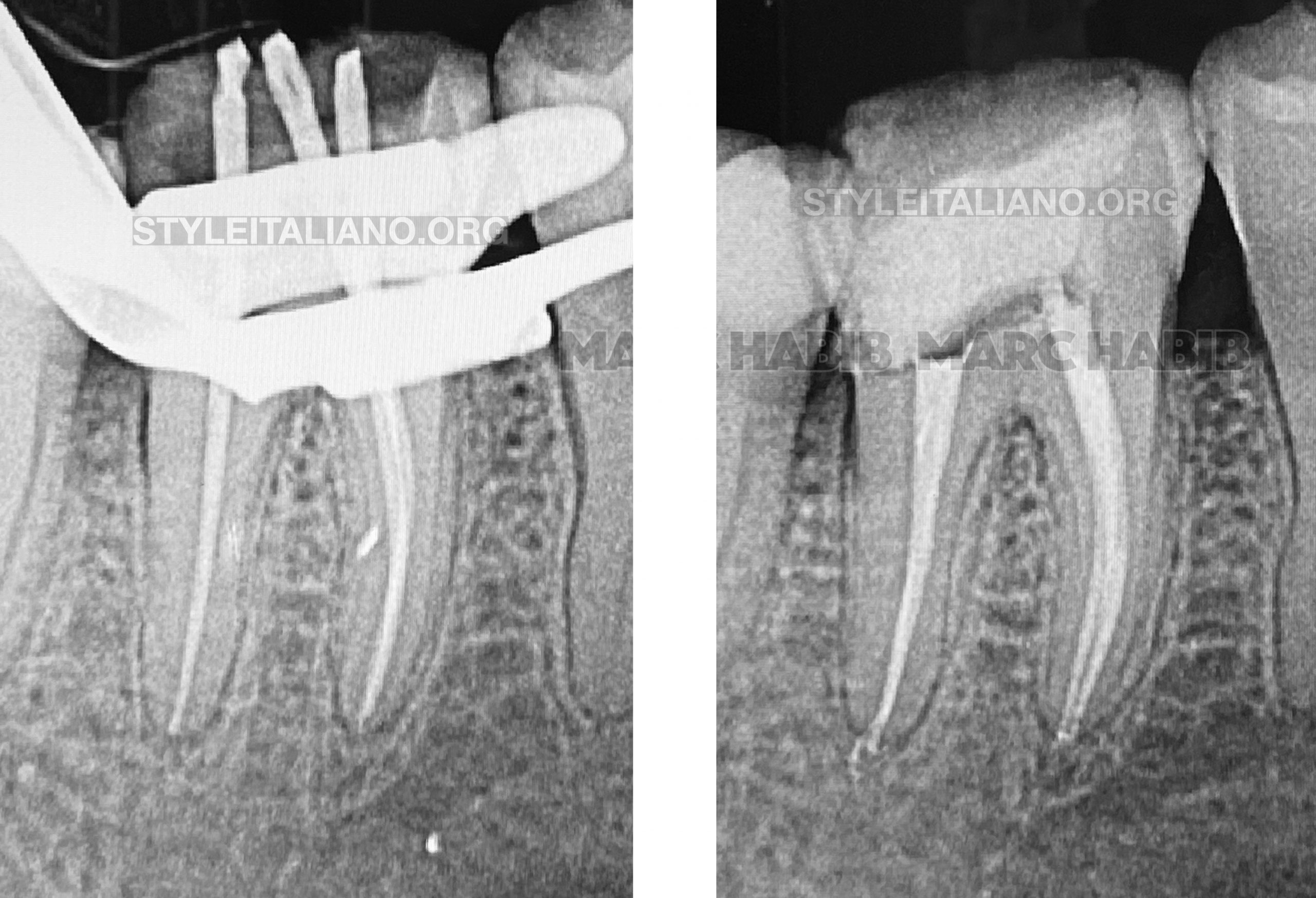
Fig. 2
Cone Fit and post operative X-rays during the primary treatment.
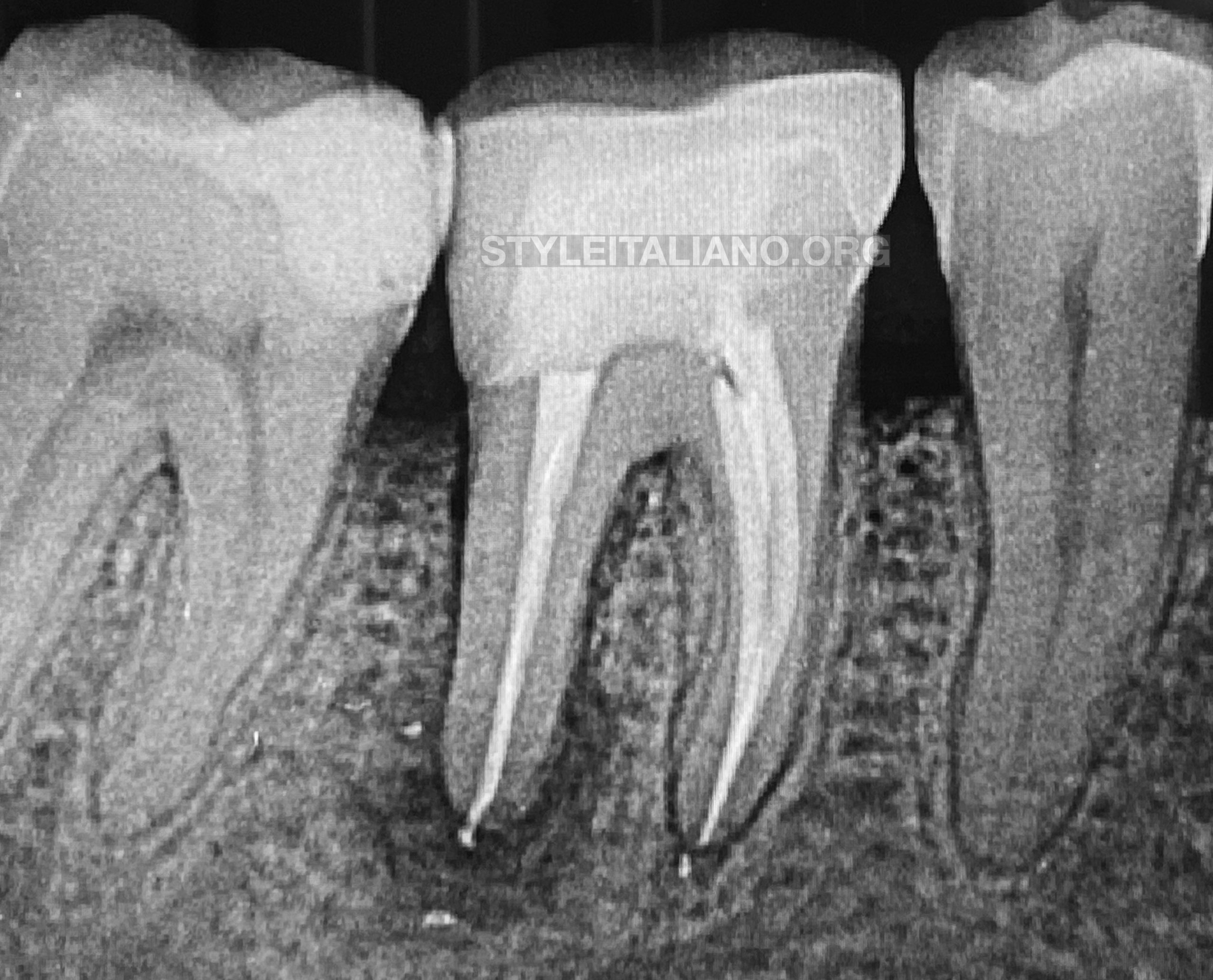
Fig. 3
After 4 months.
The patient is experiencing pain with very high tenderness to percussion on the fist lower right molar, clinical examination and X-rays shows an Acute Apical Periodontist.
A missed second distal canal was suspected since the treatment on the X-rays are satisfactory and reaching the entire working lenght and also that the lesion was observed in a very short period of time after the primary treatment.
A CBCT study was examined and confirms the diagnoses of a missed disco-buccal canal.
After mandibular block anesthesia and a buccal infiltration were performed, rubber dam was put in place along with liquid dam.
Once the access cavity was redefined DB canal was located under microscope. After scouting pus was found extruding from the orifice due to pressure build up inside the canal space.
Then preflaring was achieved with the orifice modifier from the TruNatomy system Dentsply Sirona.
The shaping was finalized with the Protaper Gold F1 to working length in all 4 canals.
Special care was taken while cleaning and shaping both distal canals specially isthmus cleaning with ultrasonic tips, irrigation with IrriFlex from Products Dentaires (Vevey, Switzerland ) and irrigant sonic activation using EDDY from VDW(Germany).

Fig. 4
Retreatment stages with cone fit of 4 canals and post operative X-rays showing final result of the obturation
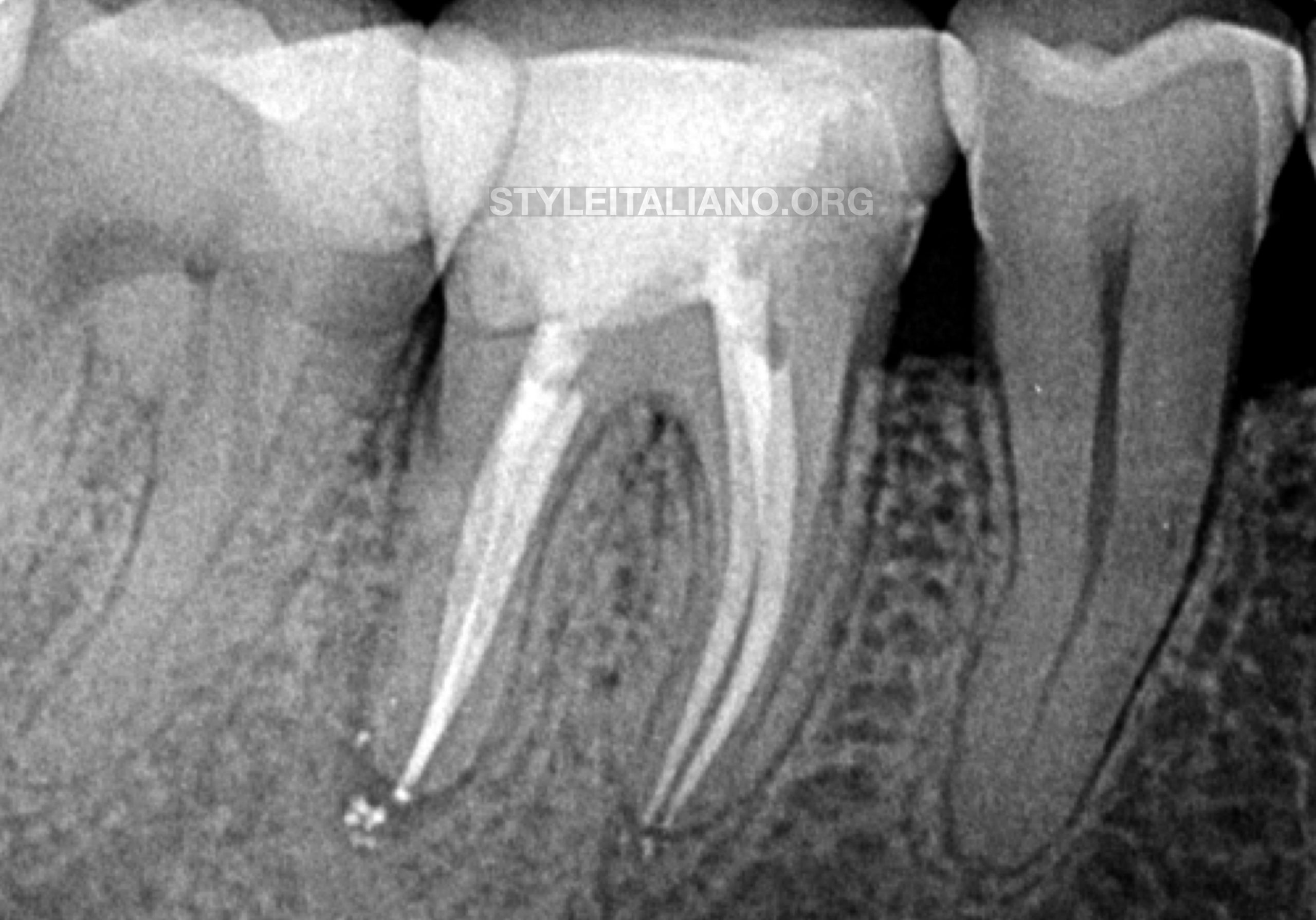
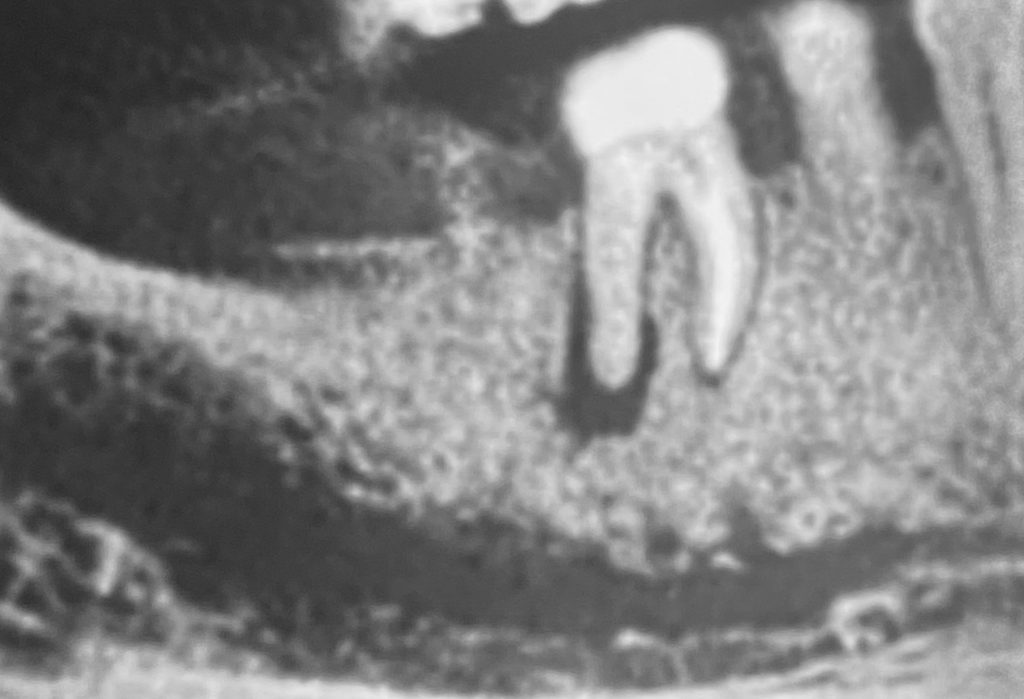
Fig. 5
6 months follow up X-ray showing partial and undergoing healing.
Conclusions
It is not always easy to detect all canals on the PA, it is essential to take many angulation like mesial or distal shift x-rays.
In fact, periapical X-rays alone can never be enough to decipher the internal anatomy of some teeth nor give us a clear idea about the periapical status. This is why it is mandatory when indicated to prescribe a Cone Beam CT before performing the root canal treatment or when needed for any periapical diagnoses.
On another note, the use of magnification will help enormously the clinician to locate extra canal orifices during the access cavity preparation and interpretation.
Untreated space and remains of pulp tissue will lead in the majority of the cases to root canal failure. Once the entire root canal tissue is eliminated and cleaning is achieved, prognosis will be positive leading to a healing and a favorable outcome.
This case report shows that missed canals have a significant impact on treatment prognosis. This is why the clinician should be aware of all measures available and equipped with specific tools to maximize canal identification.
Bibliography
- Baruwa AO, Martins JNR, Meirinhos J, Pereira B, Gouveia J, Quaresma SA, Monroe A, Ginjeira A. The Influence of Missed Canals on the Prevalence of Periapical Lesions in Endodontically Treated Teeth: A Cross-sectional Study. J Endod. 2020 Jan;46 (1) 34-39.
- Karabucak B., Bunes A., Chehoud C., Koli MR, Setzer F. Prevalence of Apical Periodontitis in Endodontically Treated Premolars and Molars with Untreated Canal: A Cone Beam Computed Tomography Study.J Endod. 2016 Apr;42 (4) 538-541.
- Witherspoon DE, Small JC, Regan JD. Missed canal system are the most likely basis for Endodontics pretreatment of molars.Tex Dent J. 2013 Feb;130(2):127-39.