Internal root resorption in permanent mandibular molar: A rare entity
20/03/2025
Leena Rawal
Warning: Undefined variable $post in /home/styleendo/htdocs/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
Warning: Attempt to read property "ID" on null in /home/styleendo/htdocs/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
Internal resorption is usually uncommon thing which starts from the root canal & destroy the tooth structure. It usually occurs as a result of a continuous chronic inflammatory process . Patient might come with a dull pain in that area .
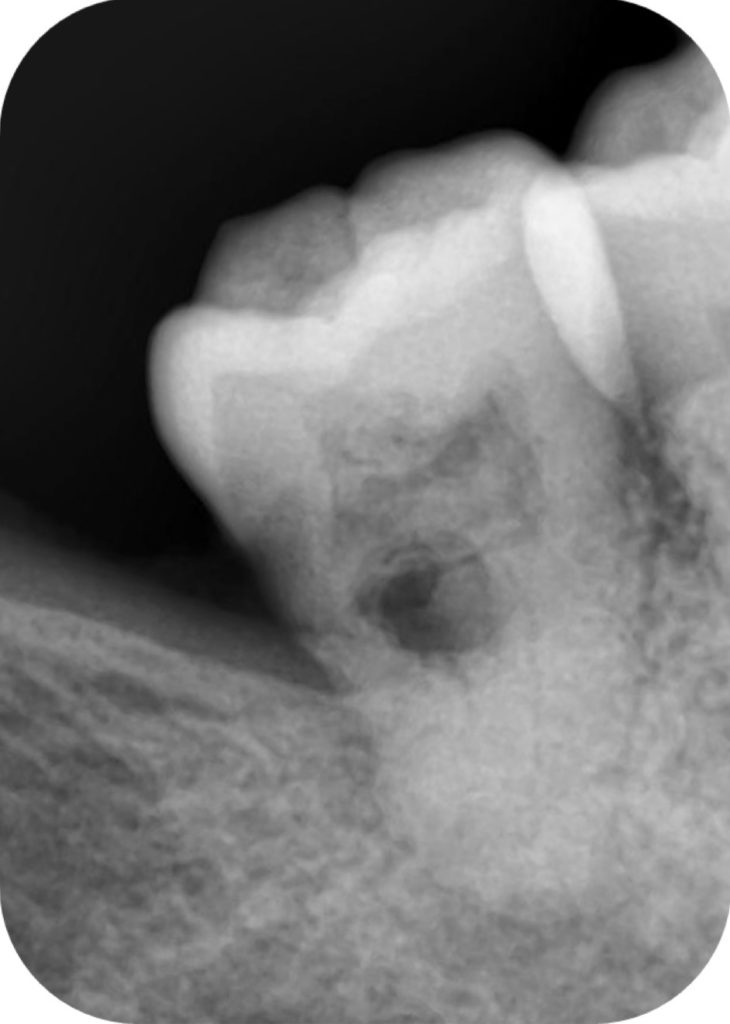
Fig. 1
Pre-operative IOPA of mandibular right second molar showing distal caries approaching to pulp( which is partially calcified) ,also showing an internal resorption & periodical lesion confirms an irreversible pulpitis suggesting a root canal treatment for the same.
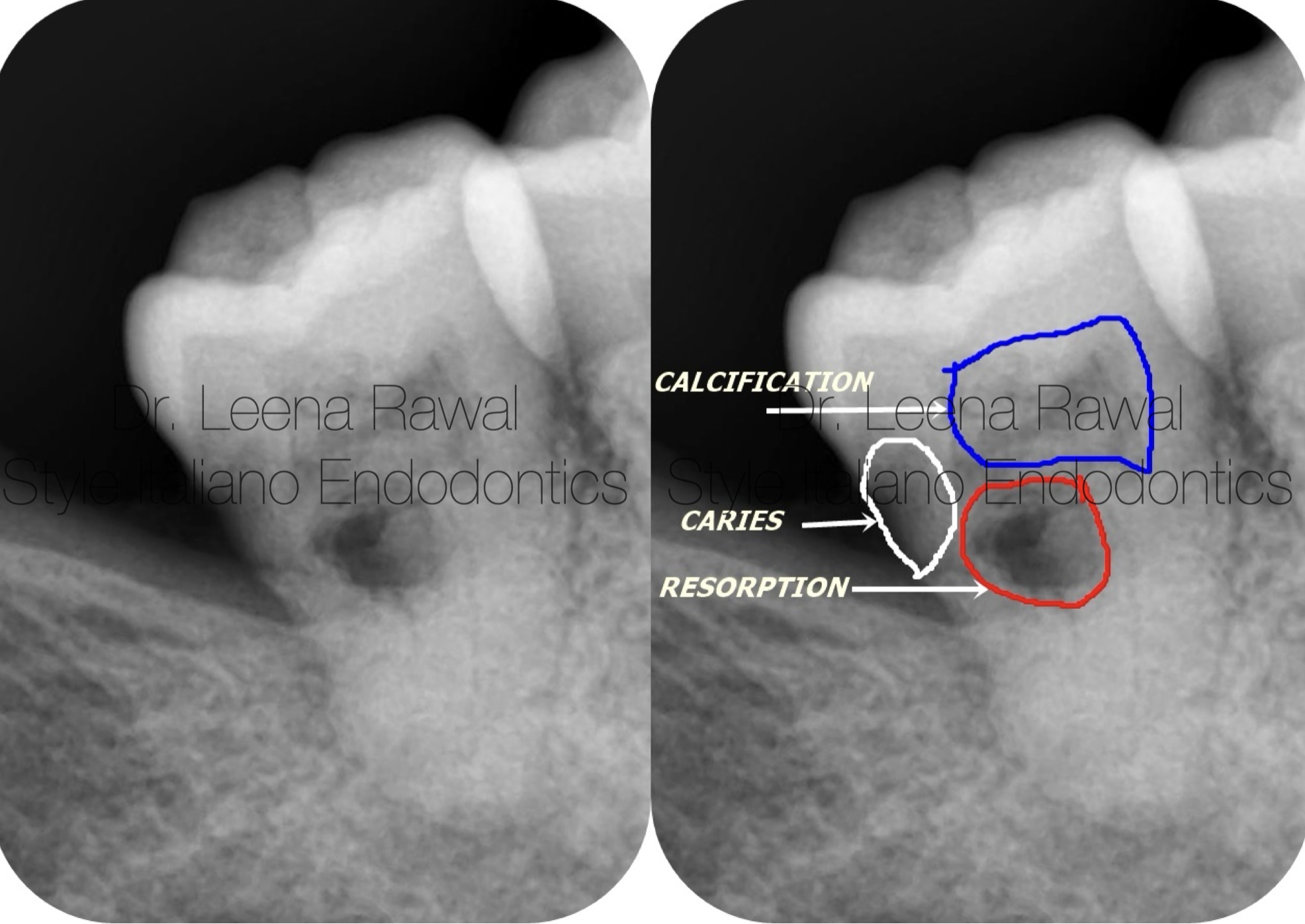
Fig. 2
Preoperative visualizzation
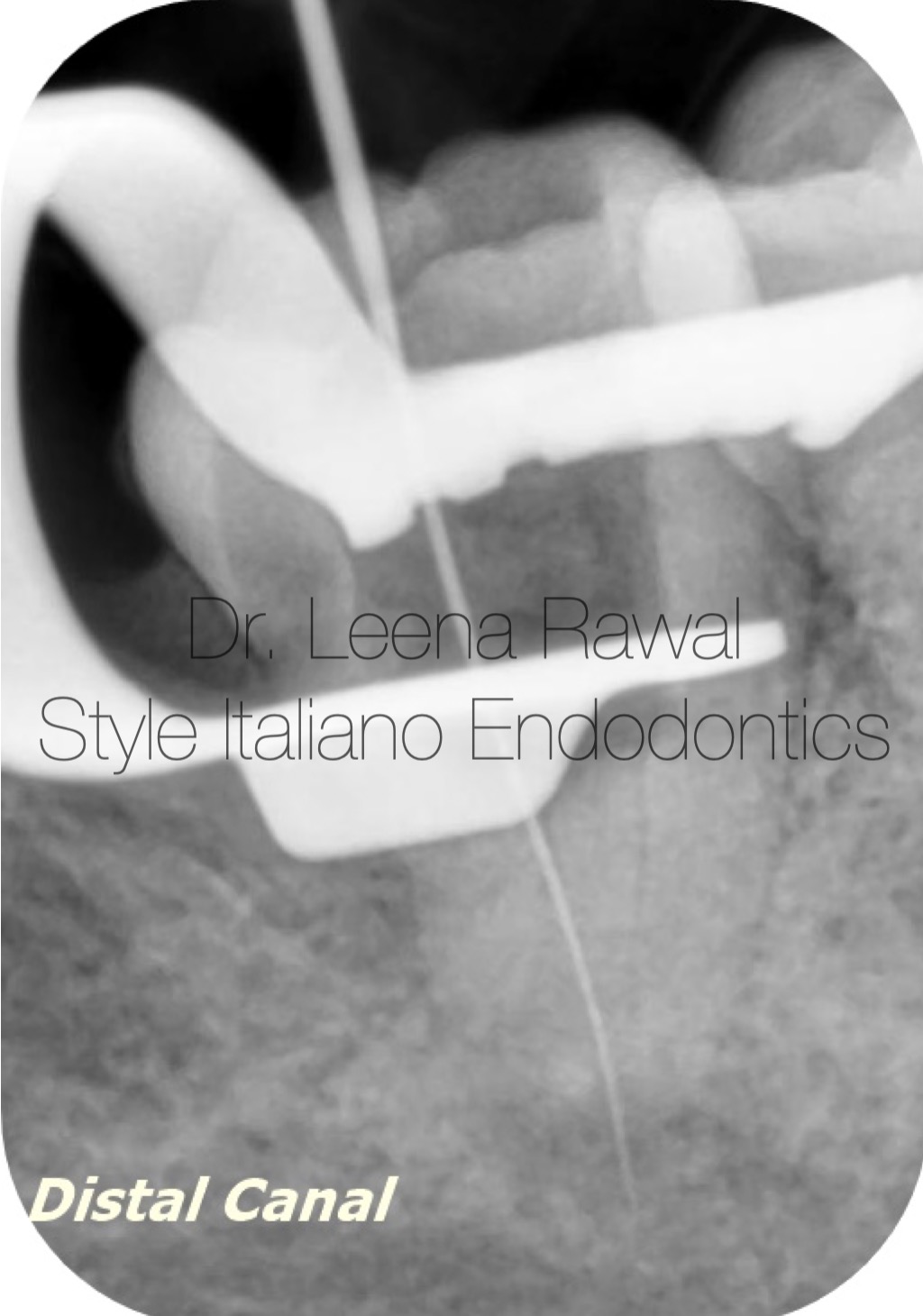
Fig. 3
Distal canal is found easily

Fig. 4
Mesial canal was a bit difficult to locate because of calcification of chamber .But after an hour of handwork finally got the mesial canal.
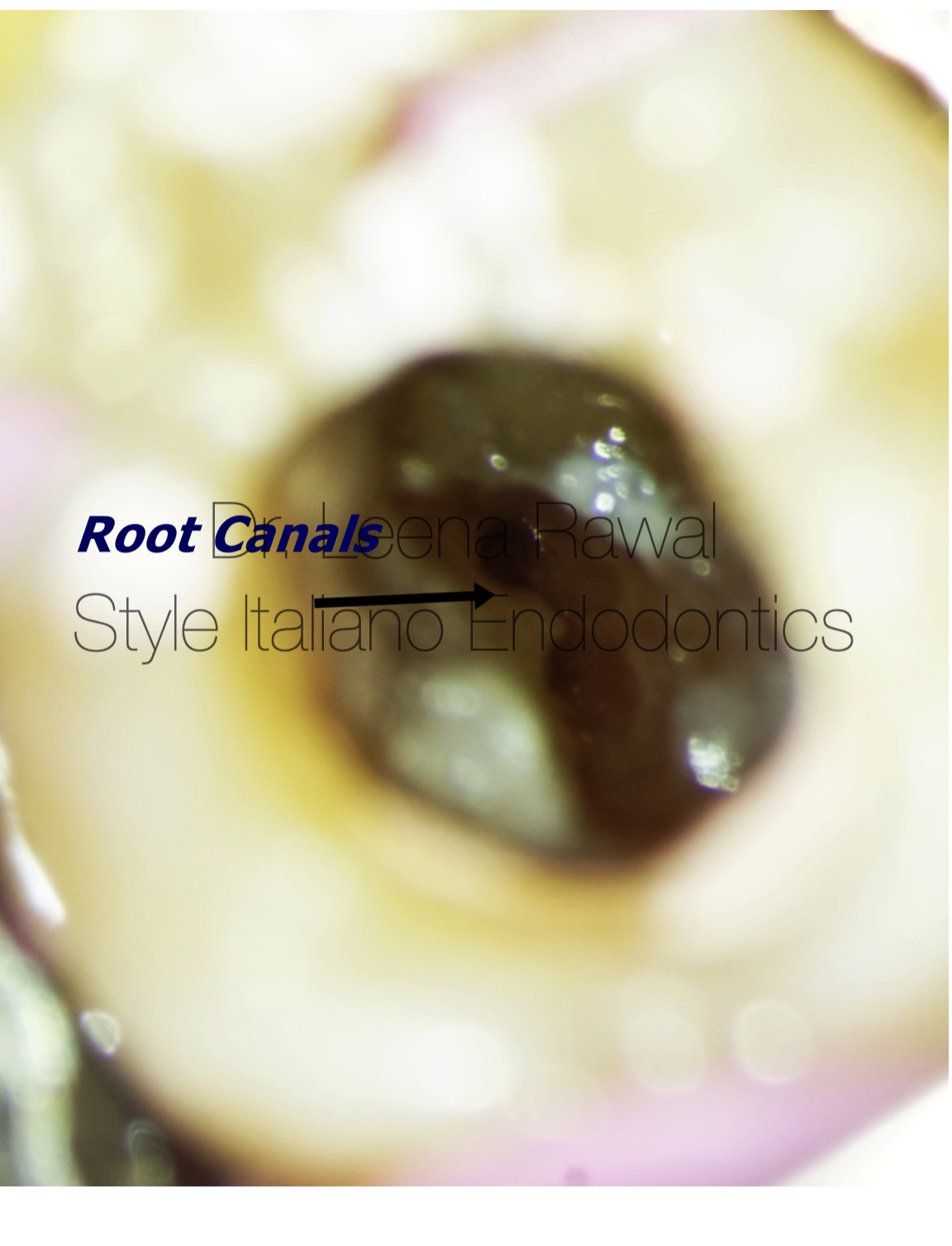
Fig. 5
In this picture the orifices of mesial & distal canals are clearly seen after cleaning & shaping till 30 4%.
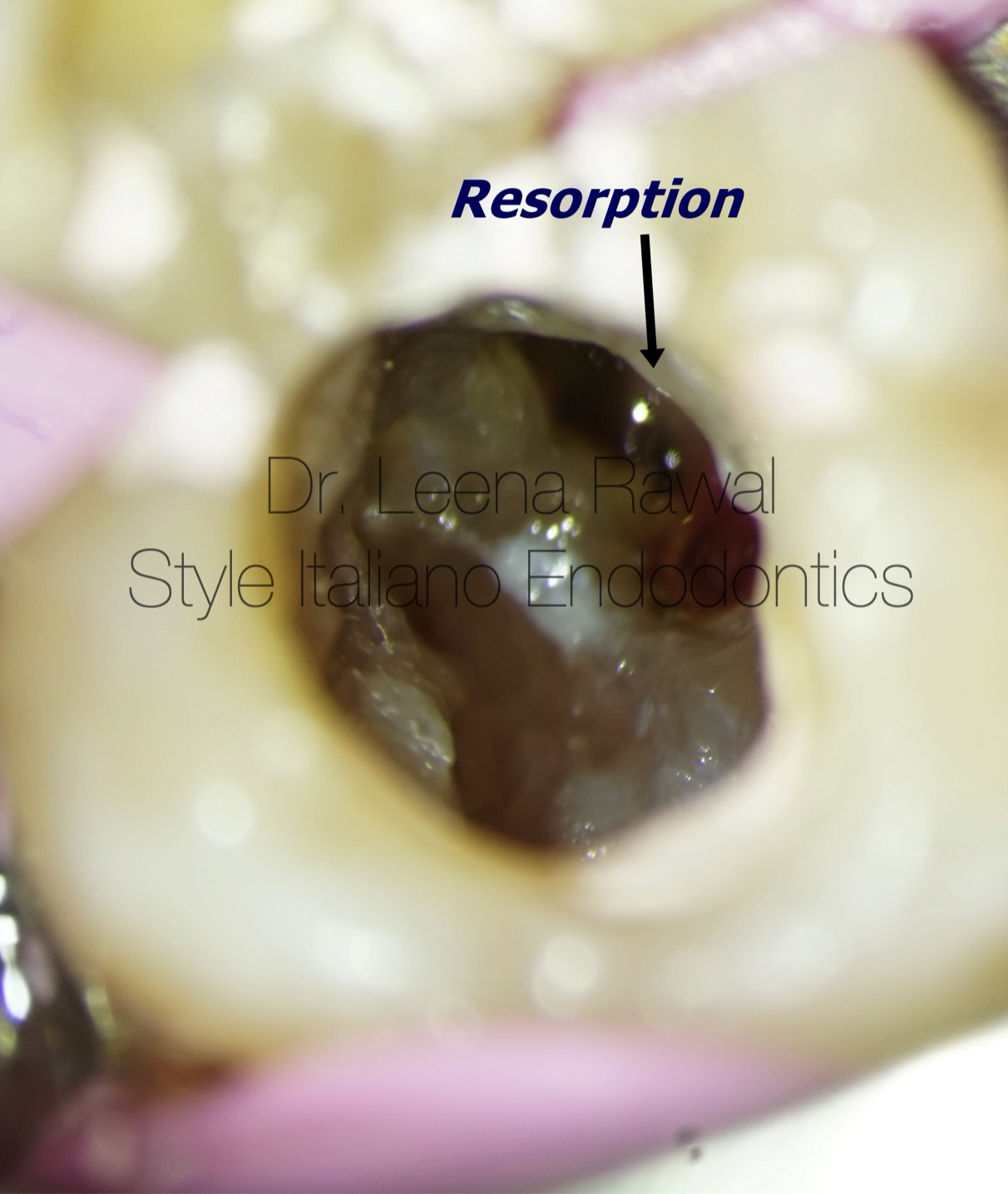
Fig. 6
This picture is showing internal resorption on distal portion of tooth

Fig. 7
This picture is showing internal resorption & prepared canal orifices in the same shot

Fig. 8
Master cone IOPA
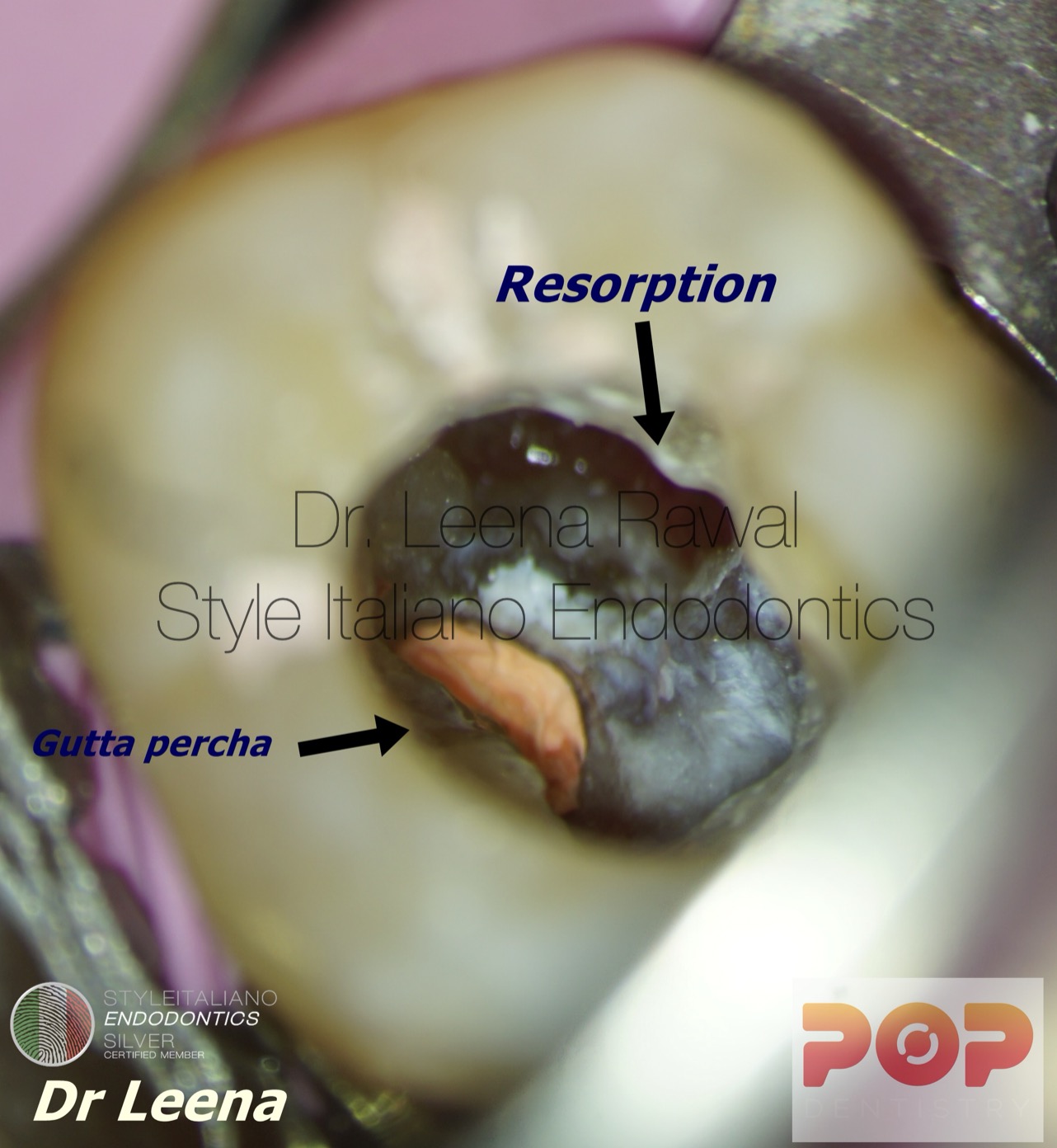
Fig. 9
Obturation was done before sealing the resorption area just to prevent blocking of canals by MTA.
Video of the procedure.
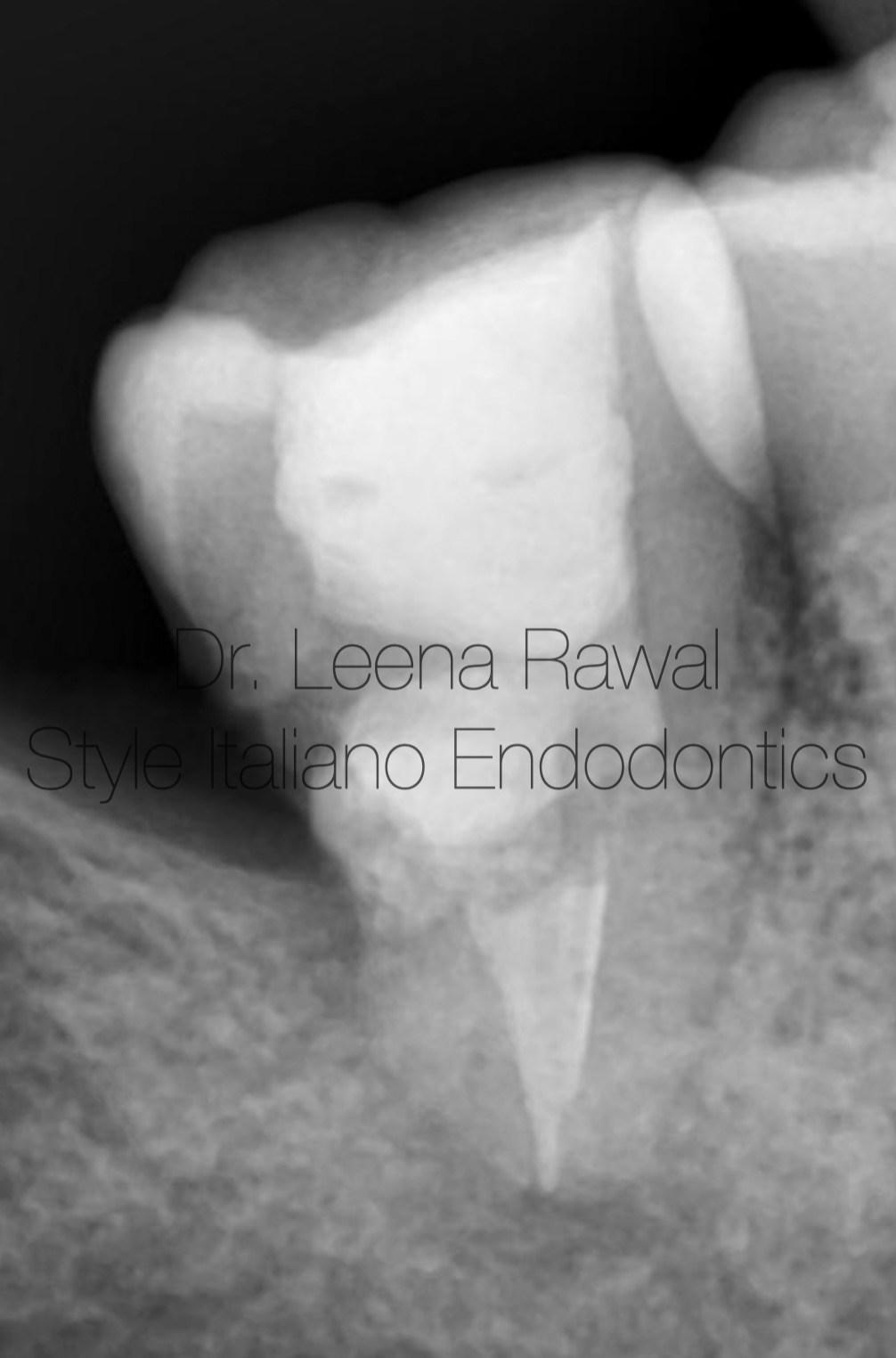
Fig. 10
Post-op IOPA showing gutta percha in the canals ,MTA putty in resorption area & Direct composite build-up of distal caries followed by occlusal build up with the same .
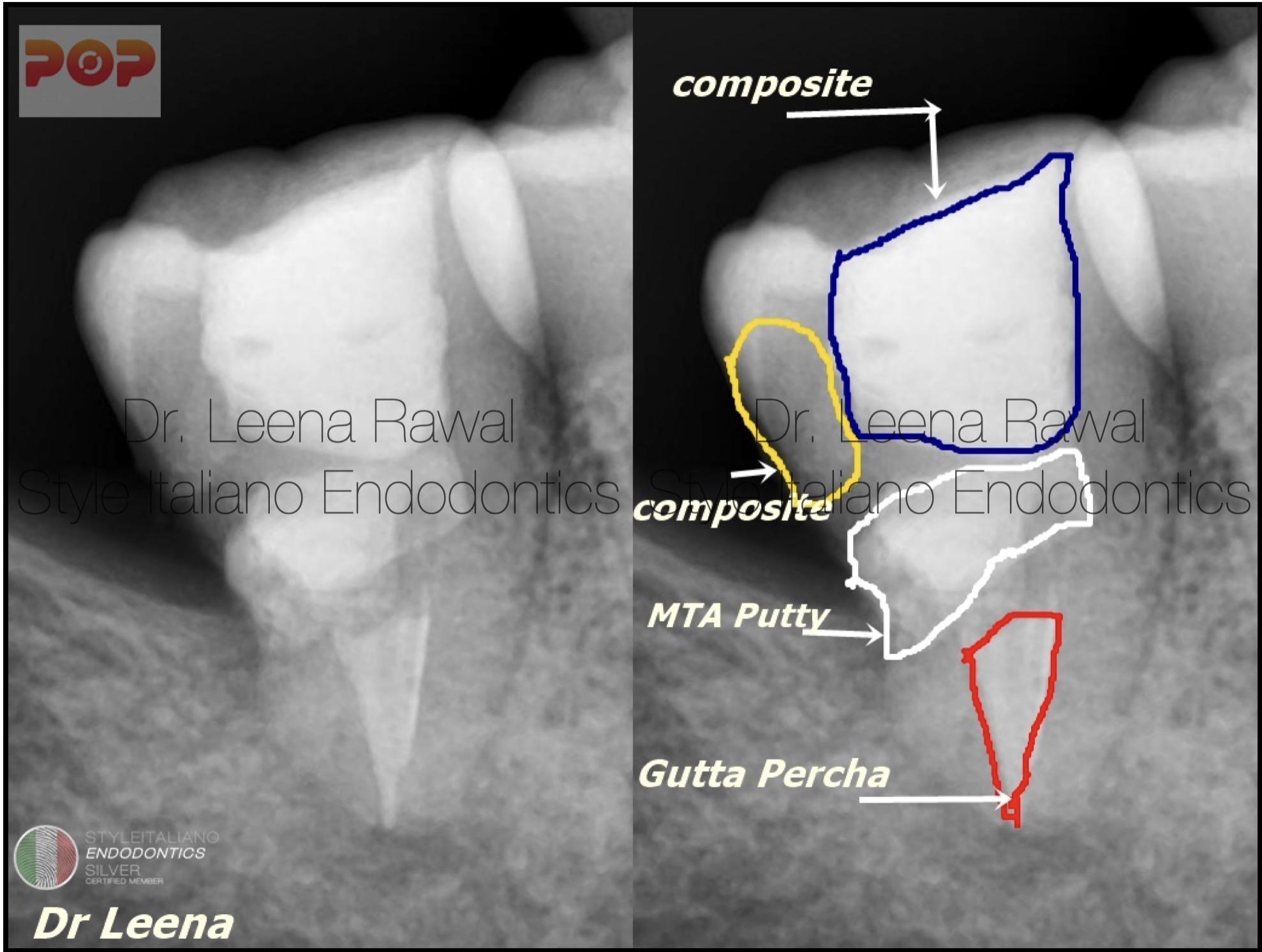
Fig. 11
Comparison of Pre-op & Post-op IOPA
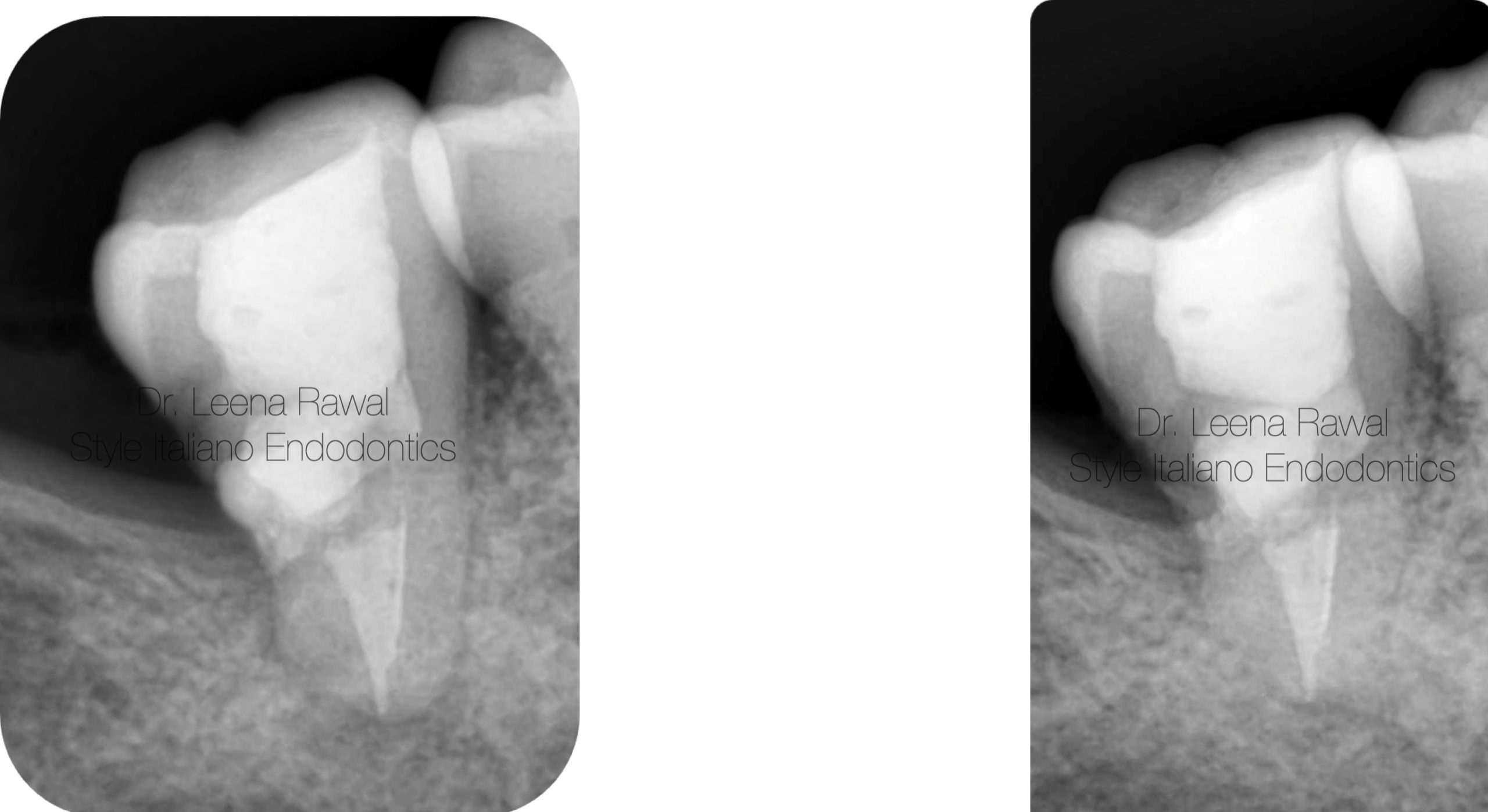
Fig. 12
Healing is evident in IOPA
After 1 month of recall of the patient
Conclusions
Early diagnosis, removal of the cause, proper treatment of the resorbed root is mandatory for the successful outcome .It is easy to control the process of internal root resorption via serving the blood supply top the resorbed tissue with conventional root canal therapy. Regular recalls are important to see the prognosis and healing of the tooth.
Bibliography
1.Ne RF, Witherspoon DE, Gutmann JL. Tooth resorption. Quintessence Int. 1999;30:9–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
2.Tronstad L. Root resorption-etiology, terminology and clinical manifestations. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1988;4:241–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-9657.1988.tb00642.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
3.Patel S, Ricucci D, Durak C, Tay F. Internal root resorption: A review. J Endod. 2010;36:1107–21. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2010.03.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
4.Silveira FF, Nunes E, Soares JA, Ferreira CL, Rotstein I. Double ‘pink tooth’ associated with extensive internal root resorption after orthodontic treatment: A case report. Dent Traumatol. 2009;25:e43–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-9657.2008.00755.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
5.Bhaskar SN. 10th ed. St. Louis: C. V. Mosby; 1986. Orban's oral histology and embryology; pp. 206–8. [Google Scholar]

