How to deal with EIAE? A case report
17/07/2023
Fellow
Warning: Undefined variable $post in /home/styleendo/htdocs/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
Warning: Attempt to read property "ID" on null in /home/styleendo/htdocs/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
EIAE (Endodontic interappointment emergencies) is a complication commences a few hours or days after root canal procedures and it is characterized by the development of pain and/or swelling.
Despite the advances in the endodontic field, the inter-appointment flare up remains a true nightmare that encounters every dentist.
This article will report a case of inter-appointment flare up.
A female patient, 16 year old, reported swelling and pain on the upper right molar for 7 days.
Present illness: chronic gingivitis. 5 days before the appointment the patient felt pain to the right upper molar and the gum was swollen. There was no pain during the night, but she was unable to chew on that tooth. The patient also referred nasal congestion lasting for nearly a week.
Past history:
Respiratory system: No history of respiratory disease.
Infectious history :No history of severe infectious disease.
Allergic history :She was not allergic to penicillin.
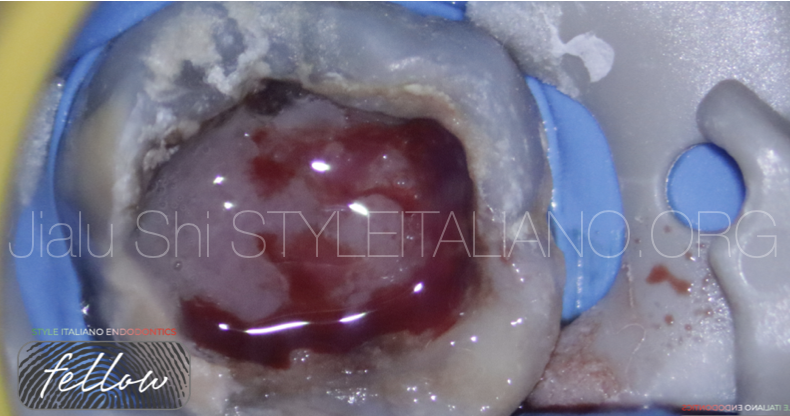
Fig. 1
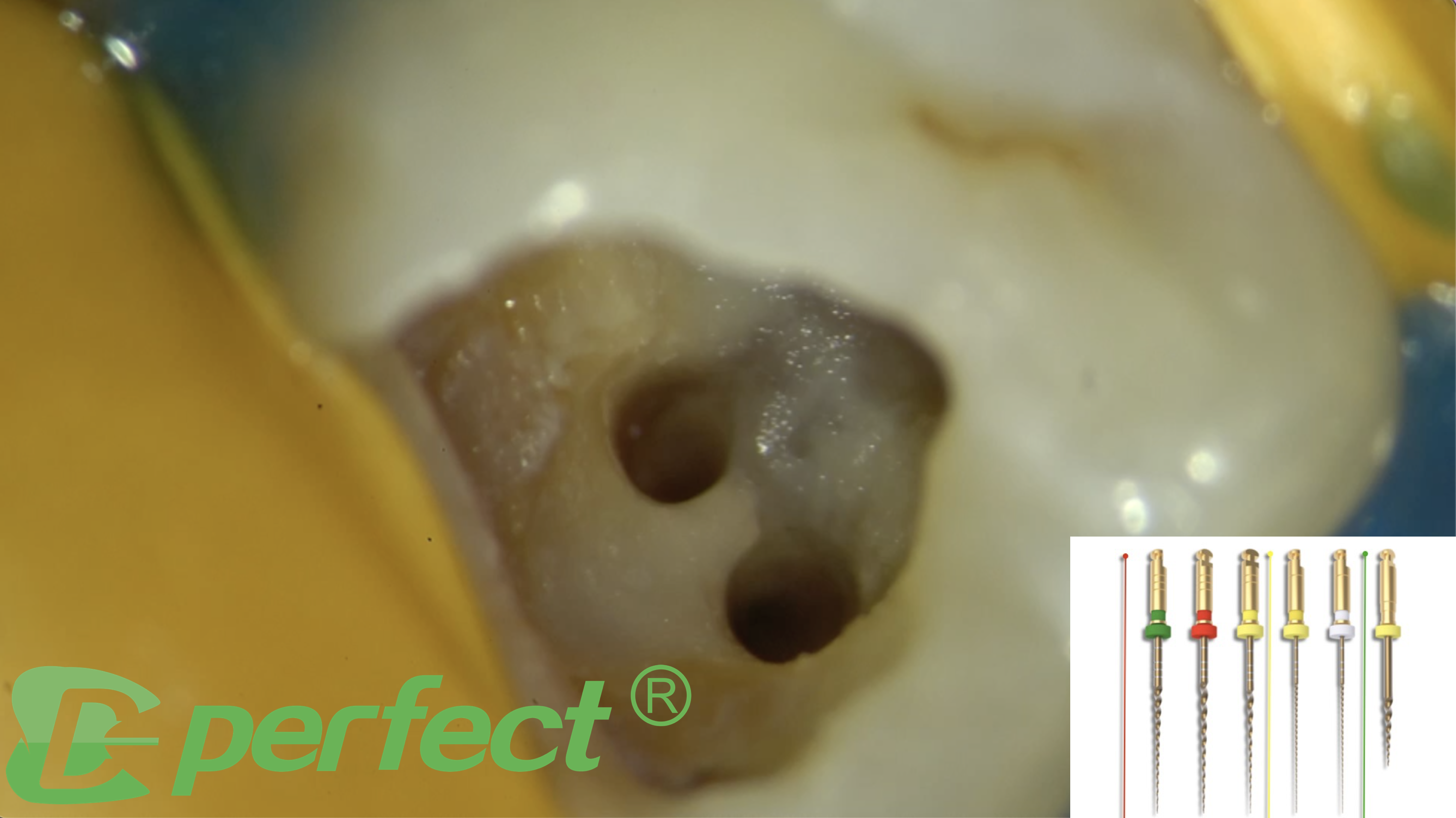
Upon examination, the 16 had large pulpal polyps.
Many dental calculus can be seen on the occlusal surface, moreover the tooth was not responsive to cold testing and was tender to pressure.
Not checked deep periodontal pocketing.
No excessive mobility and fluctuant buccal swelling.
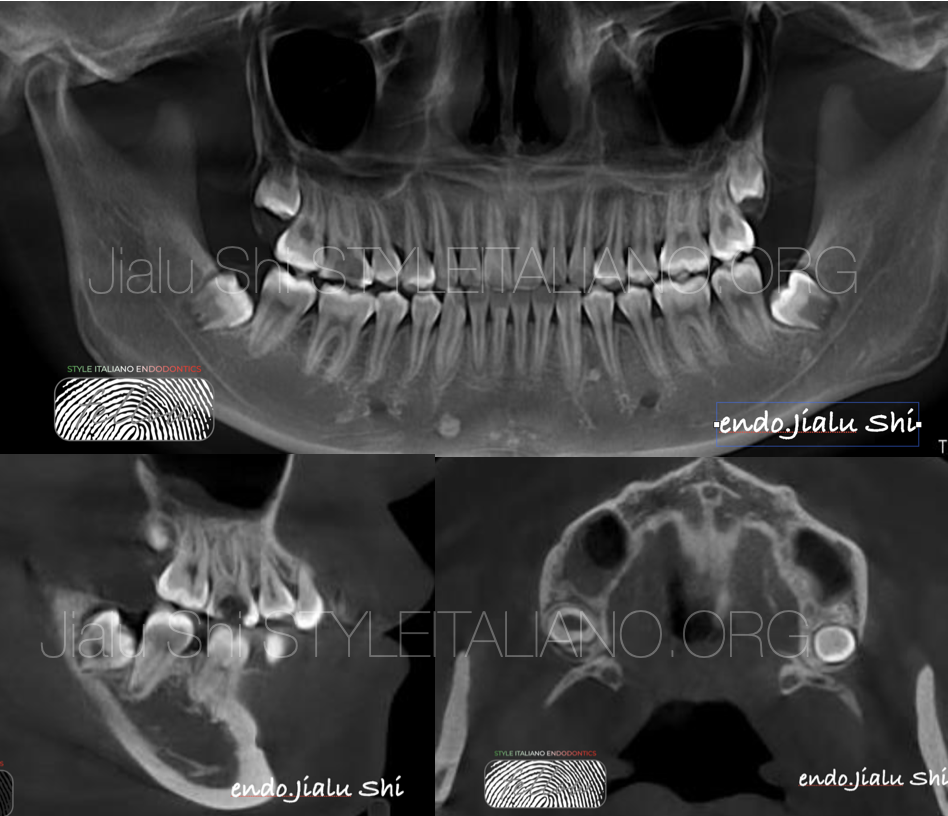
Fig. 2
Careful examination of pre-operative CBCT to determine the degree of difficulty:
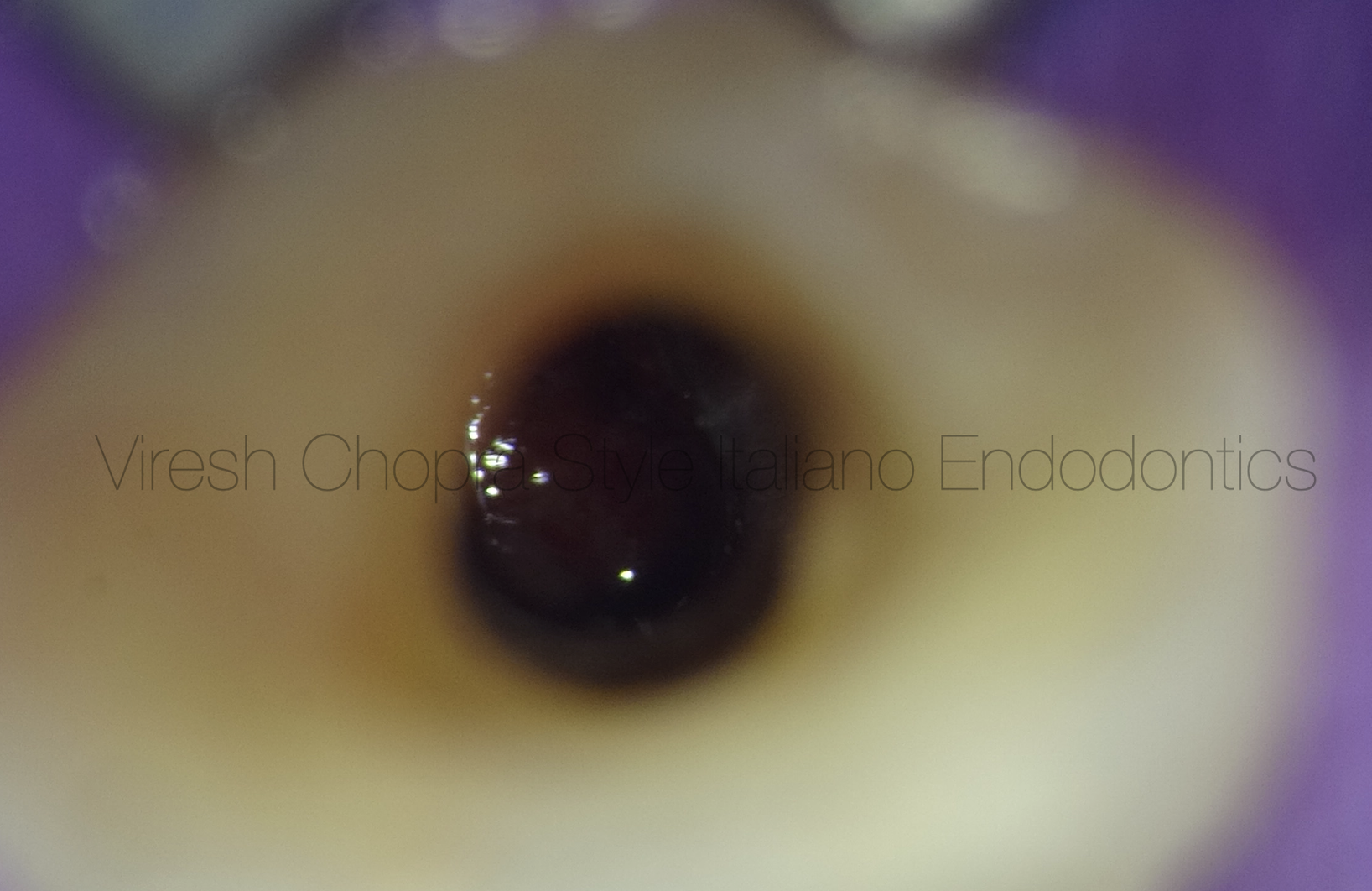
CBCT shows that the defect is deep into the pulp chamber and small periapical radiolucency around the apex of the mesial root and distal root of the first right upper molar.
No radiolucency around into the furcation.
The mucosa of the right maxillary sinus thickened.
The diagnosis of 16 Chronic pulpitis with pulp polyps and maxillary sinusitis.
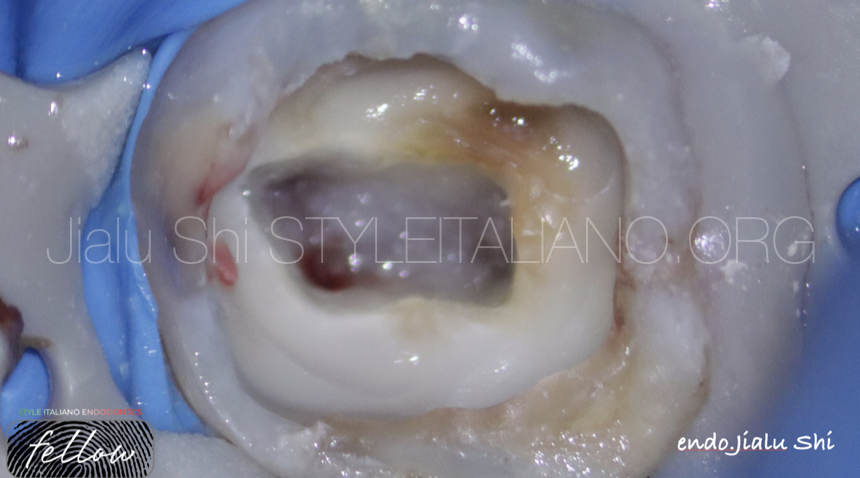
Fig. 3
Although there is very little remaining in this tooth, the patient is only 16 years old, and we need to help her retain her natural teeth.
The patient was informed regarding the guarded overall prognosis of this tooth. After adequate local anaesthesia and rubber dam placement, the pulp polyps,caries and dental calculus have been removed by ET 20 Ultrasonic Tip.
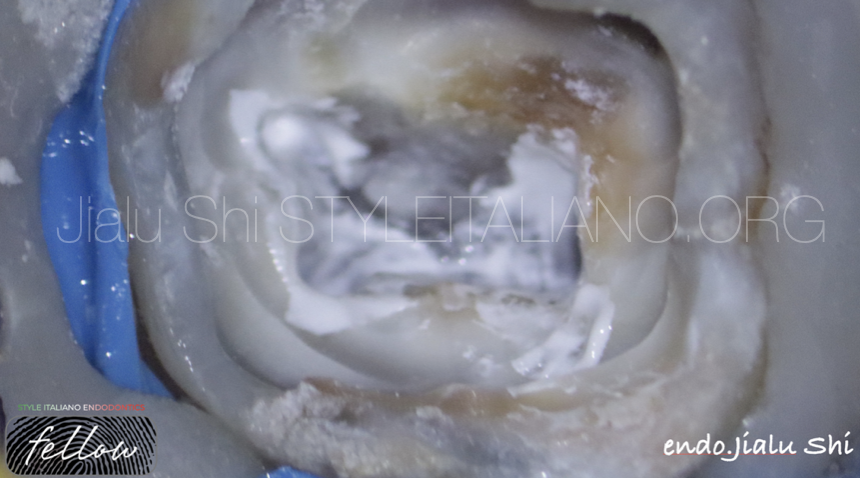
Fig. 4
Preparation 3 root canals by modified 30 Taper 6% rotary file and irrigation by 3% NaOCl.
Intracanal medication by calcium hydroxide.
Fig. 5
Only 2 days later, the patient's face was markedly swollen without any pain or discomfort.
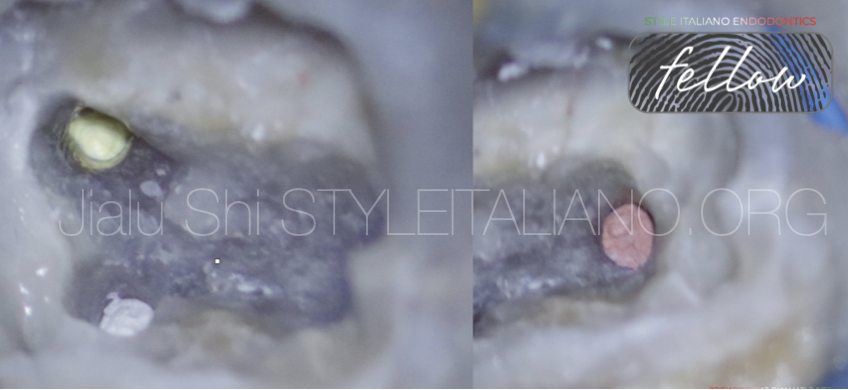
Fig. 6
So, I re-opened the root canal and enlarged the NITI file’s number to 40/.06 (MB,DB) and 50/.04(P)
Irrigation was carried out by using 5.25% NaOCl 5 min per root canal.
The swelling had subsided by the second day after this treatment.
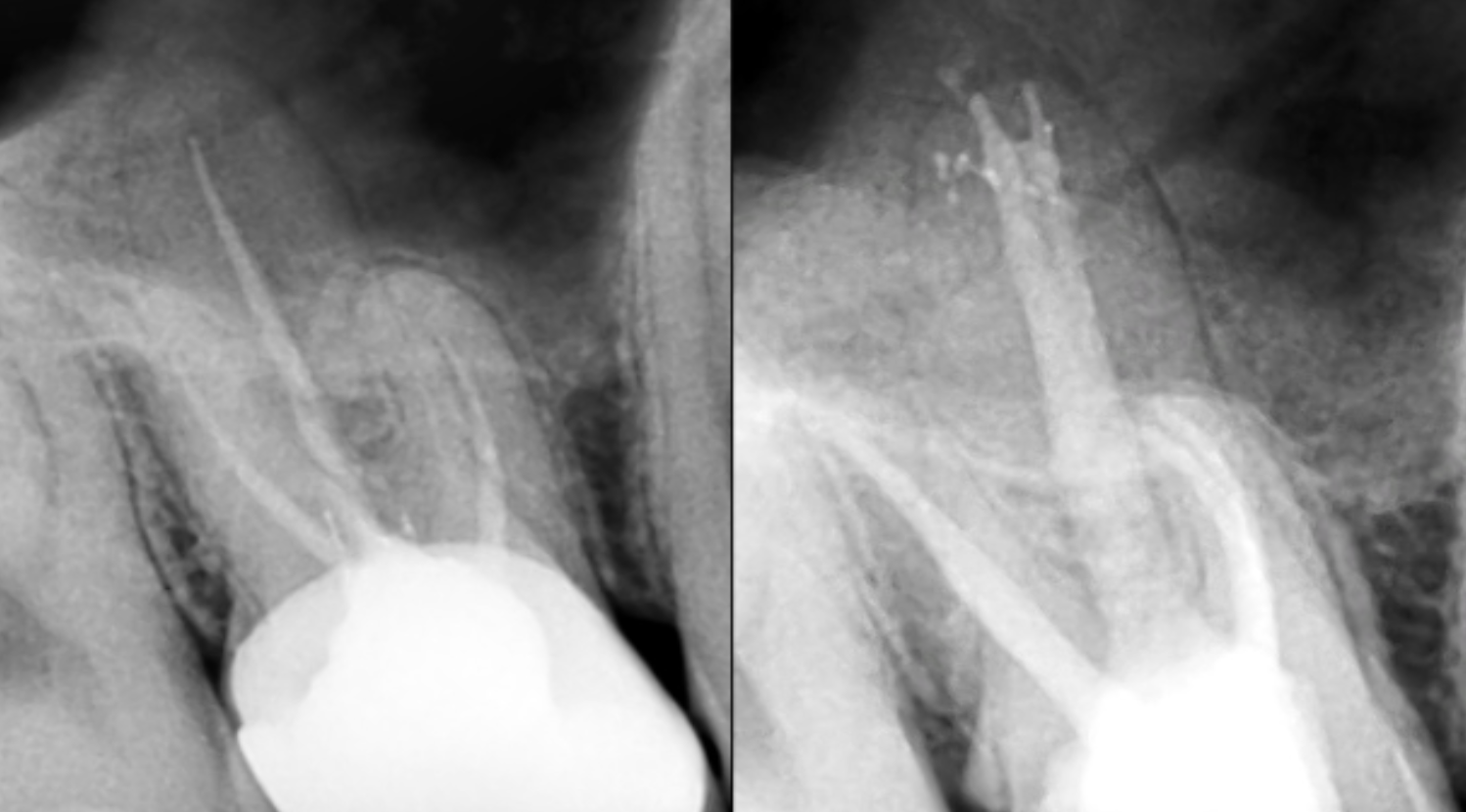
2 weeks later, I finished the root canals filling by GP+BC Sealer.
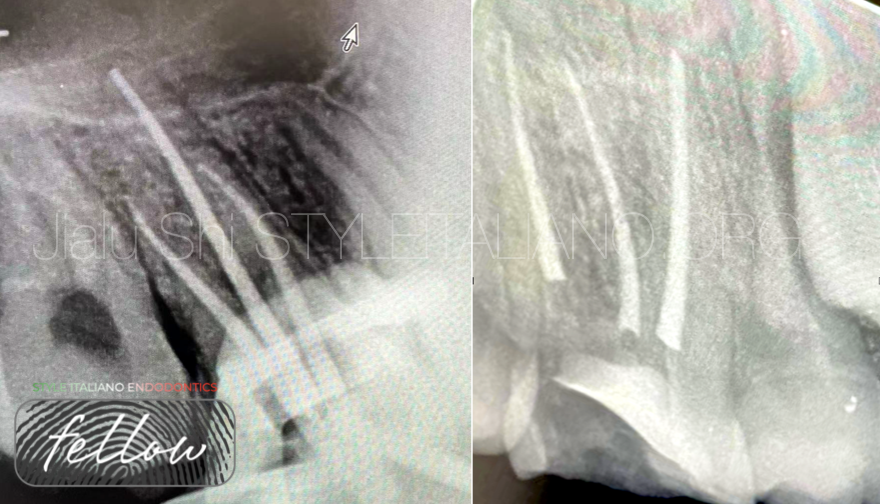
Fig. 7
Intra and post-operative X-rays
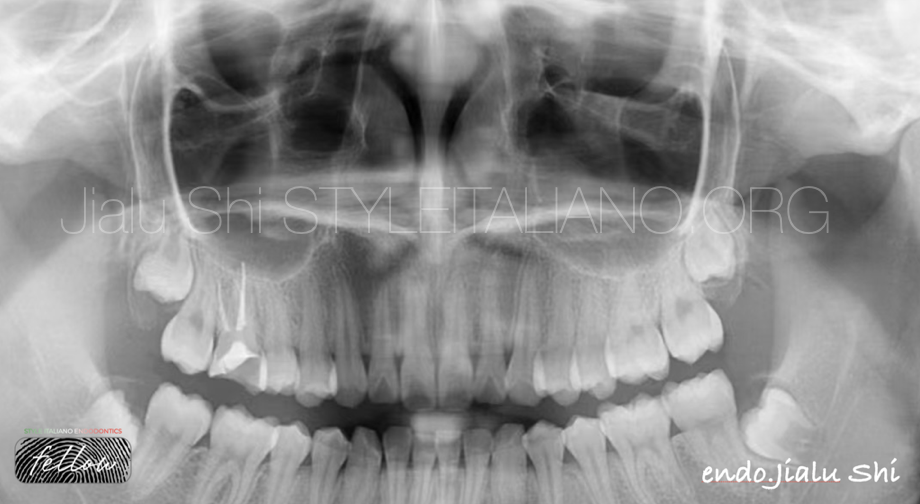
Fig. 8
11 months later, the tooth has been symptom free, the periapical lesion and maxillary sinusitis is healing.
(Since the patient was studying abroad, only panoramic X-rays were taken)
Conclusions
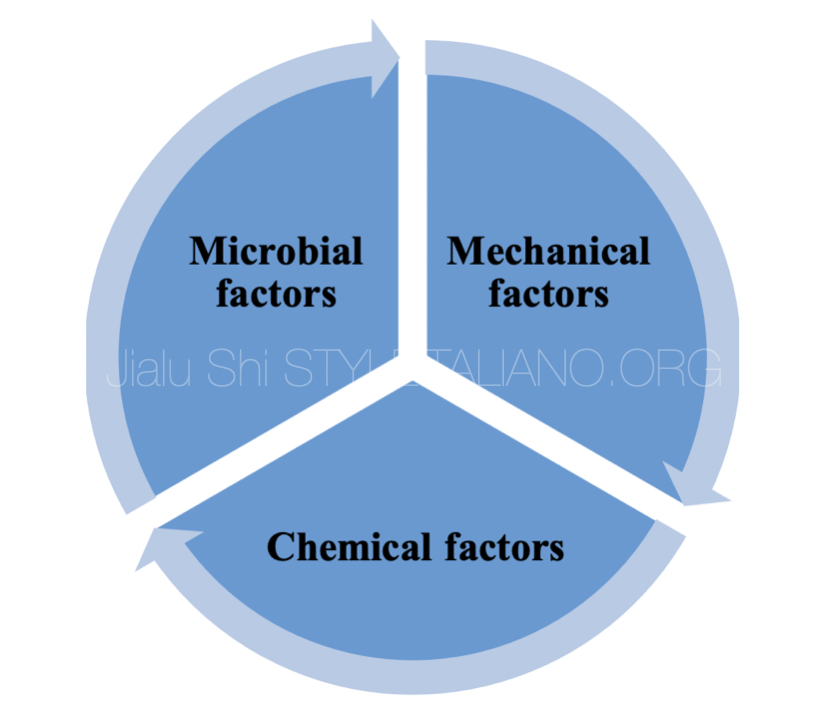
EIAE is a multifactorial phenomenon triggered by mechanical, chemical and microbial factors. Recent studies succeeded proving the efficency of some actions or guidelines in reducing its incidence.
The damage to periapical soft tissue was the main result of EIAE after root canal disinfection.
Reduce mechanical stimulation of apical area during root canal preparation, strictly control the working length of root canal and maintain apical barrier can reduce the incidence of EIAE and effectively improve the qualification rate of root canal filling.
Bibliography
Bassam S, El-Ahmar R, Salloum S, Ayoub S. Endodontic postoperative flare-up: An update. Saudi Dent J. 2021 Nov;33(7):386-394. doi: 10.1016/j.sdentj.2021.05.005. Epub 2021 Jun 3. PMID: 34803278; PMCID: PMC8589595.
Jia L, Zhang X, Shi H, Li T, Lv B, Xie M. The Clinical Effectiveness of Calcium Hydroxide in Root Canal Disinfection of Primary Teeth: A Meta-Analysis. Med Sci Monit. 2019 Apr 20;25:2908-2916. doi: 10.12659/MSM.913256. PMID: 31004424; PMCID: PMC6487674.
Hu YP, Qian Y. [The influence of different preparation methods on interappointment emergency and filling effect of root canal therapy]. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2022 Apr;31(2):198-200. Chinese. PMID: 36110080.
Yaylali, I.E., Kurnaz, S., Tunca, Y.M., 2018. Maintaining Apical Patency Does Not Increase Postoperative Pain in Molars with 860 Necrotic Pulp and Apical Periodontitis: A Randomized Controlled 861 Trial. J. Endod. 44, 335–340.
Vieyra, J.P., Enriquez, F.J.J., Acosta, F.O., Guardado, J.A., 2019. Reduction of postendodontic pain after one-visit root canal 853 treatment using three irrigating regimens with different tempera- 854 ture. Niger J. Clin. Pract. 22, 34–40.