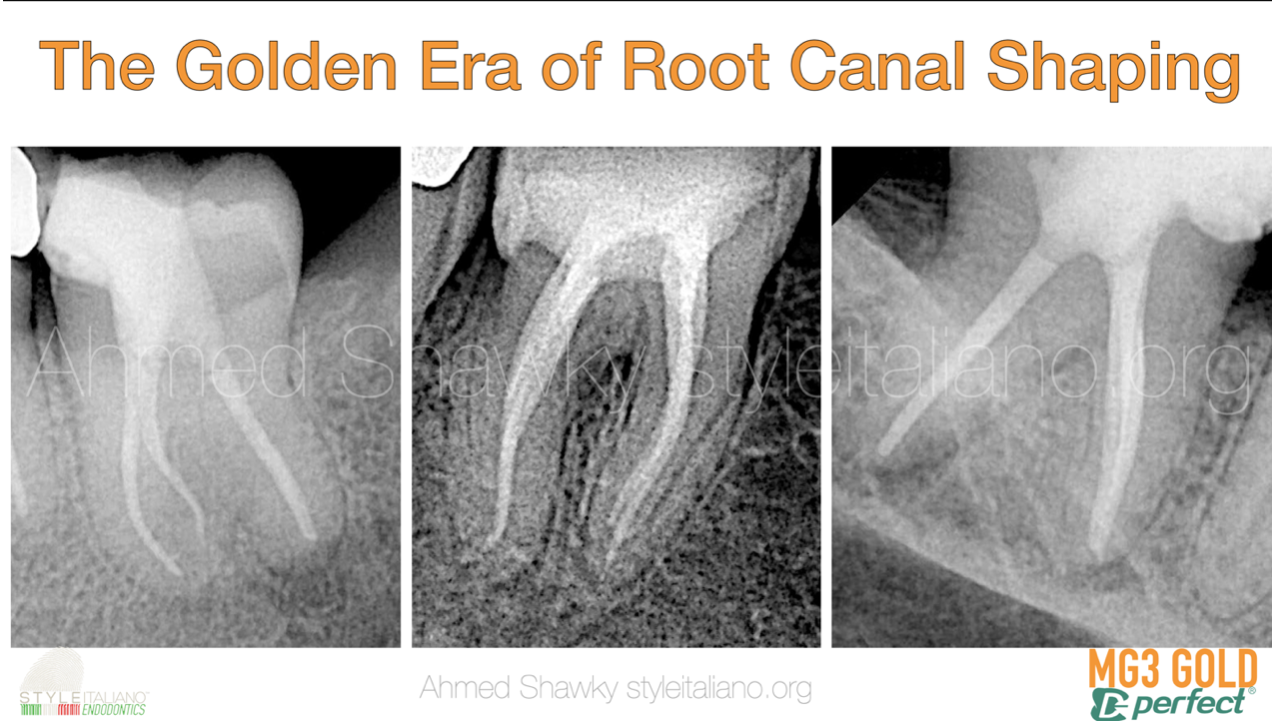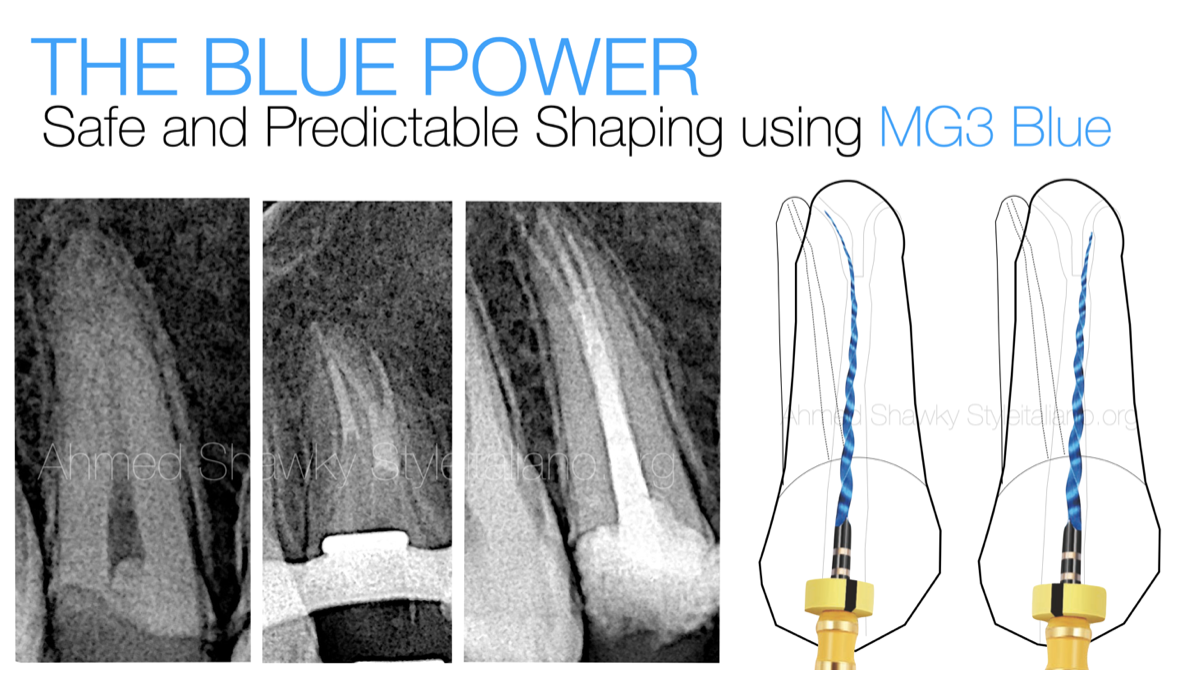
GOLD and BLUE: The Squad For Predictable Shaping
21/07/2022
Ahmed Shawky
Warning: Undefined variable $post in /home/styleendo/htdocs/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
Warning: Attempt to read property "ID" on null in /home/styleendo/htdocs/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
The primary objective of nonsurgical endodontic treatment is the healing of existing, as well as prevention of recurrence of, apical periodontitis. This objective can be fulfilled by disinfection of persistent residual microbes present in the root canal system. Shaping is an important step to fulfill the disinfection allowing delivery of the irrigating solutions as close as possible to the apical part. In many cases the operator needs to customize instrument sequence, mix two different alloys in the same case or even use different operation kinematics as dictated by the anatomy.
This article will demonstrate the use of MG3 Blue instruments in some cases of primary non-surgical endodontic treatments with moderate to high difficulty using different operation kinematics, customized sequence and incorporating MG3 Gold in the sequence.
The first case is mandibular first molar in a 17 years old female presented with previously restored coronal structure, yet having recurrence of decay. The diagnosis was irreversible pulpitis with Symptomatic apical periodontitis. On analyzing the pre-operative radiograph, the pulp space seemed to be narrow with appearance of an extra disto-lingual root “Radix Entomolaris”
Modified Kinematics: In this case I used the ZR Rap motor, to be able to adjust the kinematics of instrumentation from Continuous rotation to Interrupted Rotation “Rotation Reciprocation” with angles 170 FWD/50 REV, respecting the FWD direction of the MG3 files.
Mechanical Pre-Flaring: here I used the 25/.06 MG3 Gold as I needed high cutting efficiency to eliminate coronal interferences. It has been used in pressure-less maneuver.
Body Shaping/Apical Finishing: after Preflaring, shaping of the body of the curved root canals, required controlled memory behavior to avoid transportations or exceesive cutting on danger zones, especially in the radix Entomolaris which is well known of its double curvatures in the BL plane. Therefore, I used the MG3 Blue 25/.04, 30/.04 all in Reciprocation motion using The ZR Rap Motor.
In this way, the anatomy in this case was successfully and safely managed by modifying the operation kinematics, mixing MG3 GOLD with MG3 blue in the same case and in the same time very few instruments have been used (only 3 files)
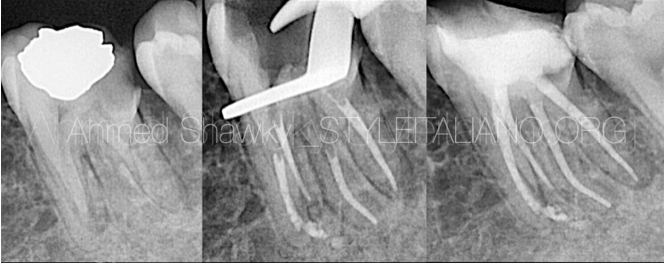
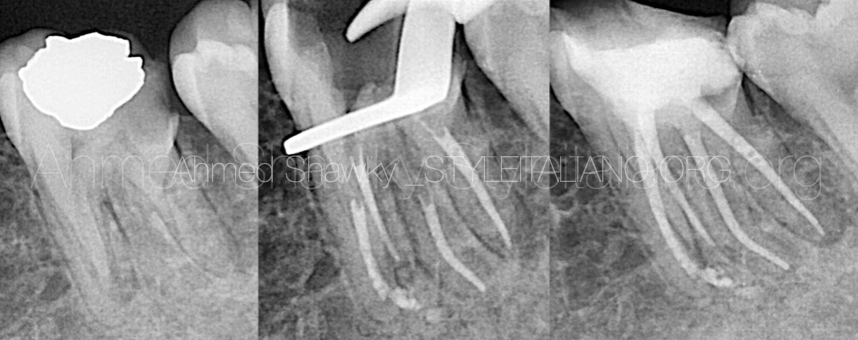
Fig. 1
In this way, the anatomy in this case was successfully and safely managed by modifying the operation kinematics, mixing MG3 GOLD with MG3 blue in the same case and in the same time very few instruments have been used (only 3 files)
The second case is a maxillary second molar with existing full coverage restoration (porcelain fused to metal crown). The patient presented with signs of apical periodontitis requiring endodontic treatment.
According to a recent article published by the author in the journal of endodontics, the criteria for retaining the restoration were followed and treatment was initiated across the restoration.
Removal of coronal interferences and cavity refinement was done using medium power ultrasonics
MB2 Management:
A pre-curved #10 k file was used to detect the location of the MB2.
Mechanical Pre-flaring was done using 25/.04 file
Due to the high cutting efficiency of MG3 GOLD, 15/.04 was used in reciprocation motion as a glide path file. Due to the limited accessibility to the tooth the file was inserted manually followed by attachment of the motor
Body shaping (2/3 of the WL) was done using MG3 Blue 20/.04, 25/.04
Full length shaping was done using MG3 Blue 25/.04
Palatal canal was done only with 30/.04 MG3 Blue in Reciprocation motion using ZR RAP motor
Disto-buccal and main mesio-buccal canals were instrumented only with 25/.04 also in interrupted rotation
Disto-buccal and main mesio-buccal canals were instrumented only with 25/.04 also in interrupted rotation
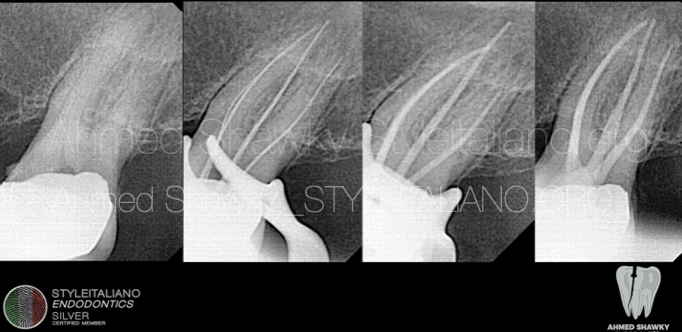
Fig. 2
X-rays of the case
Conclusions
The primary objective in Endodontics is the treatment/prevention of apical periodontitis
Shaping sequence must be determined based on case-by-case evaluation.
The clinician must have adequate knowledge about Kinematics, metallurgy and file design in order to be able to adapt his/her instruments to the anatomy
Bibliography
Outcome of Endodontic Treatment through Existing FCRs. https://doi.org/10.1016/ j.joen.2021.11.008
Schilder H. Cleaning and shaping the root canal. Dent Clin North Am. 1974; 18: 269-296
Schilder H. Filling root canals in three dimensions. Dent Clin North Am. 1967; : 723-744
Swati Srivastava, Current Strategies in Metallurgical Advances of Rotary NiTi Instruments: A Review J Dent Health Oral Disord Ther 2018, 9(1): 00333
Gao Y, Gutmann JL, Wilkinson K, Maxwell R, Ammon D (2012) Evaluation of the impact of raw materials on the fatigue and mechanical properties of ProFile Vortex rotary instruments 10.1016/j.joen.2011.11.004
Shen Y, Qian W, Abtin H, Gao Y, Haapasalo M (2011) Fatigue testing of controlled memory wire nickel-titanium rotary instruments J Endod 2011 Jul;37(7):997-1001. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2011.03.023.
Shen Y, Qian W, Abtin H, Gao Y, Haapasalo M (2012) Effect of Environment on Fatigue Failure of Controlled Memory Wire Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instruments https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2011.12.002
Shen Y, Zhou HM, Zheng YF, Peng B, Haapasalo M. Current challenges and concepts of the thermomechanical treatment of nickel-titanium instruments. J Endod. 2013 Feb;39(2):163-72. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2012.11.005. PMID: 23321225.
Peters OA, Gluskin AK, Weiss RA, Han JT. An in vitro assessment of the physical properties of novel Hyflex nickel-titanium rotary instruments. Int Endod J. 2012 Nov;45(11):1027-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2012.02067.x. Epub 2012 May 8. PMID: 22563821.