How to improve ergonomics in endodontics
11/05/2023
Fellow
Warning: Undefined variable $post in /home/styleendo/htdocs/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
Warning: Attempt to read property "ID" on null in /home/styleendo/htdocs/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
Ergonomics in endodontics refers to designing tools, equipment, and workspaces to reduce health risks for operators and patients while improving posture and movement.
Ergonomics in endodontics is extremely important to ensure effective and safe execution of the treatment. It refers to the design of tools, equipment and workspaces in order to minimize risks to the health of operators and patients, by improving their posture and movement.
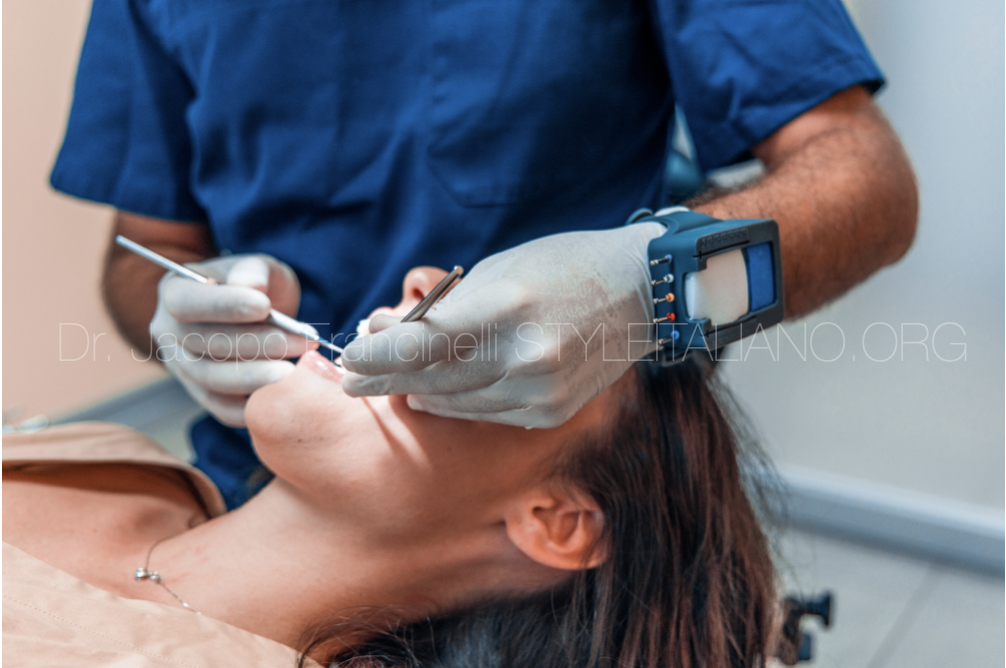
As for the tools, it is important that they are ergonomic and designed to reduce muscle fatigue and the risk of injuries, such as tendonitis and carpal tunnel syndrome. For example, endodontic files should be shaped and diameter appropriate for the operator's hand to reduce pressure on the wrist and hand.
The equipment must also be ergonomically designed. The operating table should be adjustable in height and angle to allow the operator to work in a comfortable and natural position. The operator's chair should also be height adjustable and have lumbar support to reduce fatigue and the risk of back injury.
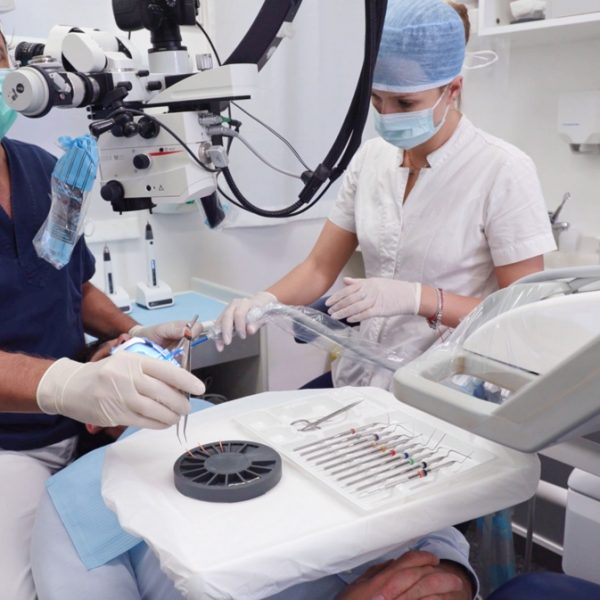
Organization is a highly sought-after skill among dentists. An organized work environment can improve efficiency, productivity, and treatment quality, reducing the risk of errors and enhancing patient safety. Additionally, organization can also improve the professional's image, creating a sense of professionalism and attention to detail. Therefore, dentists are encouraged to develop effective organizational skills and implement time and space management systems to optimize their professional activities.
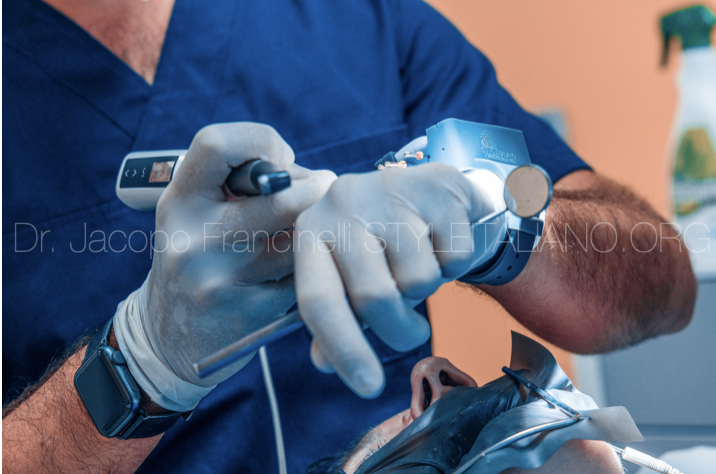
Fig. 1
Having everything organized in endodontics is useful for several reasons. It can increase efficiency, reduce stress, improve patient safety and enhance the overall quality of care.
Using ERGO, the ultimate tool to organize the endodontic workflow in daily practice, one can clean the instruments after use, simplify the organization of rotary and hand files, and have everything at one's fingertips.
Detail of how the use of rotating instruments is facilitated by wearing ERGO, allowing them to be catch in rotation and cleaned in the best possible way.
Ergo is divided into two sections that are used to accommodate two different foams. The smaller blue foam is useful for organizing manual endodontic instruments. The grey foam, on the other hand, is used to clean rotary instruments by positioning them in motion above or inside it.
On the side of Ergo there are 5 holes that are used to hold the operator's preferred sequence of rotary instruments. The holes are very useful for connecting and disconnecting the instruments from the endodontic motor head without touching them with one's fingers.
Above Ergo there are two millimeter scales for measuring endodontic instruments.
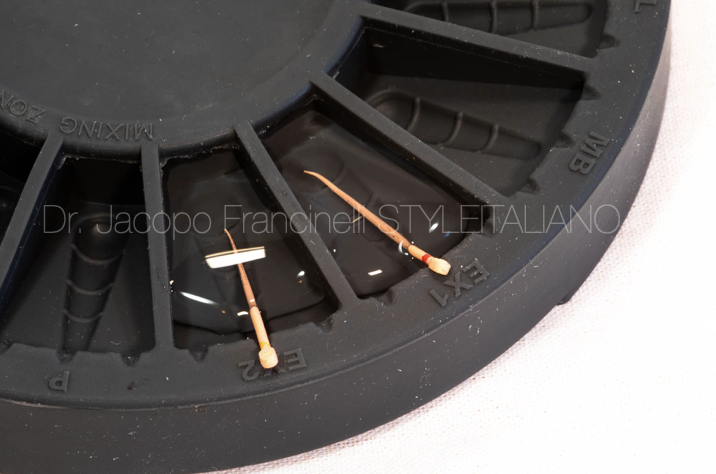

Fig. 2
Additionally, an organized workspace can reduce stress and fatigue for the operator, leading to better outcomes and increased job satisfaction.
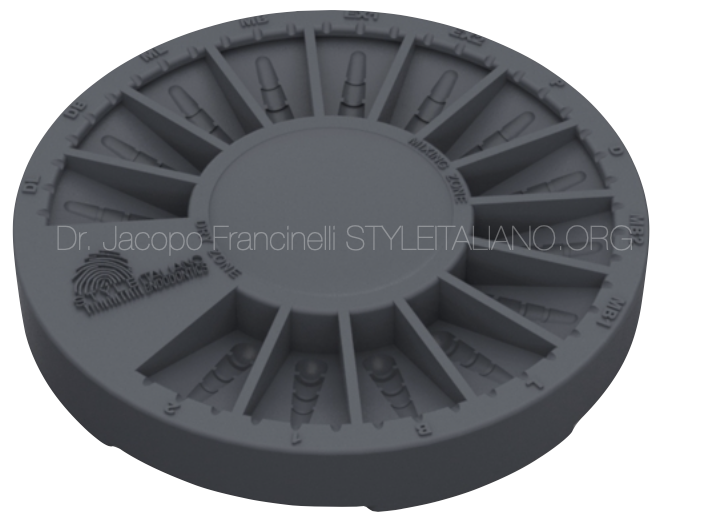
Fig. 3
Plano is an accessory designed to improve the organization of multiple endodontic materials used during the canal filling phase.
With Plano, it is possible to:
- Disinfect and insert gutta-percha points in dedicated spaces for each canal
- Mix and collect endodontic cement
- Dry gutta-percha points before inserting them into the root canals
- Place paper points.
Conclusions
By having a well-organized workspace, it's easier to find the necessary instruments and materials, minimizing the risk of error or delay during the procedure. Moreover, it creates a more professional environment, which can increase patient confidence and trust.
Bibliography
-Gopinadh A, Devi KN, Chiramana S, Manne P, Sampath A, Babu MS. Ergonomics and musculoskeletal disorder: as an occupational hazard in dentistry. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2013 Mar 1;14(2):299-303. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1317. PMID: 23811663.
-Caux Y, Husson R, Maquin M. Ergonomie et endodontie: rationalisation de l'acte endodontique [Ergonomics and endodontics: rationalization of the endodontic procedure]. Rev Odontostomatol (Paris). 1984 Sep-Oct;13(5):352-64. French. PMID: 6597508.
-Ehrmann EH. Ergonomics in endodontics. Quintessence Int Dent Dig. 1979 Jan;10(1):53-61. PMID: 297900.
-Kumar M, Mishra G, Vaibhav R, Priyadarshini S, Simran, Turagam N. Assessment of Knowledge about Ergonomics and Determining Musculoskeletal Disorders in Dentists: An Original Research. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2021 Jun;13(Suppl 1):S391-S394. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.JPBS_591_20. Epub 2021 Jun 5. PMID: 34447117; PMCID: PMC8375953.