Pulpotomy in mature permanent teeth
16/06/2022
Fitim Shabani
Warning: Undefined variable $post in /var/www/vhosts/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/endodontics.styleitaliano.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
Warning: Attempt to read property "ID" on null in /var/www/vhosts/styleitaliano-endodontics.org/endodontics.styleitaliano.org/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/code-block.class.php(133) : eval()'d code on line 2
Irreversible pulpitis is an inflammatory condition of the dental pulp that is characterized by spontaneous, lingering pain that persists for minutes to hours and can lead the pulp tissue to a state where it is incapable of self-healing. In an era of minimally invasive dentistry, where the paradigm of dental care is shifting toward conservative dentistry and selecting biologic options, pulpotomy is now increasingly being considered as a minimally invasive approach for the management of teeth with irreversible pulpitis.
With better understanding of pulp biology and the development of bioactive materials, pulpotomy has now been reinvestigated as a definitive treatment option for mature permanent teeth presented with irreversible pulpitis.
In this clinical case we will present all the pulpotomy procedures, which has been successful as a definitive treatment.
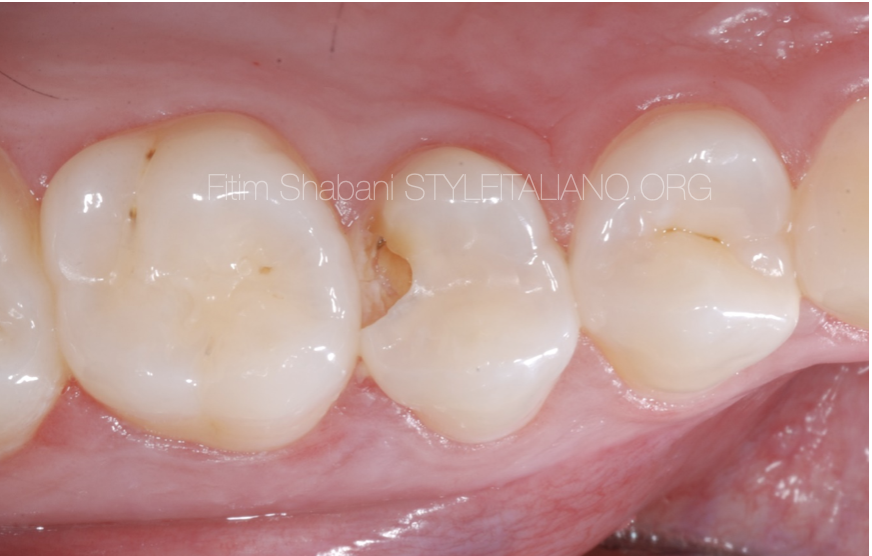
Fig. 1
Age : 15y
Tooth : Second maxillary right premolar
Dg : Irreversible pulpitis
Treatment plan : Pulpotomy
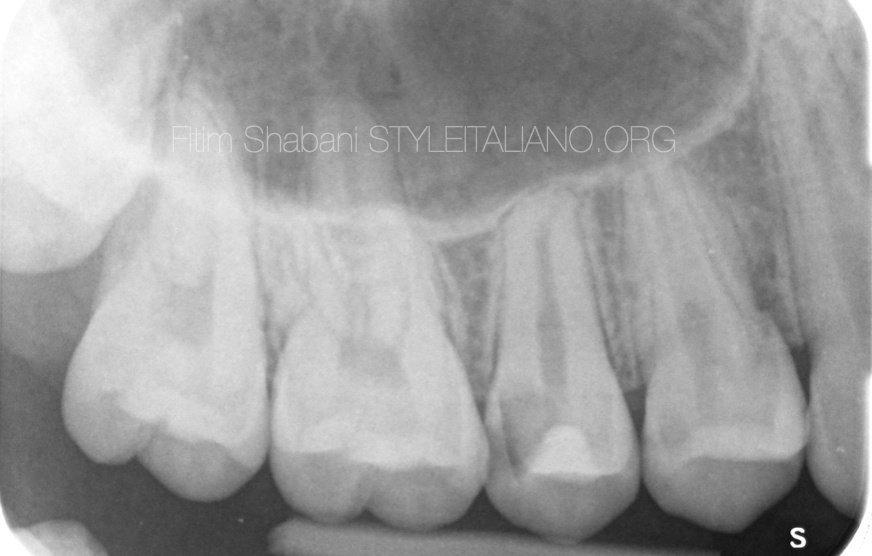
Fig. 2
Pre operative X-ray
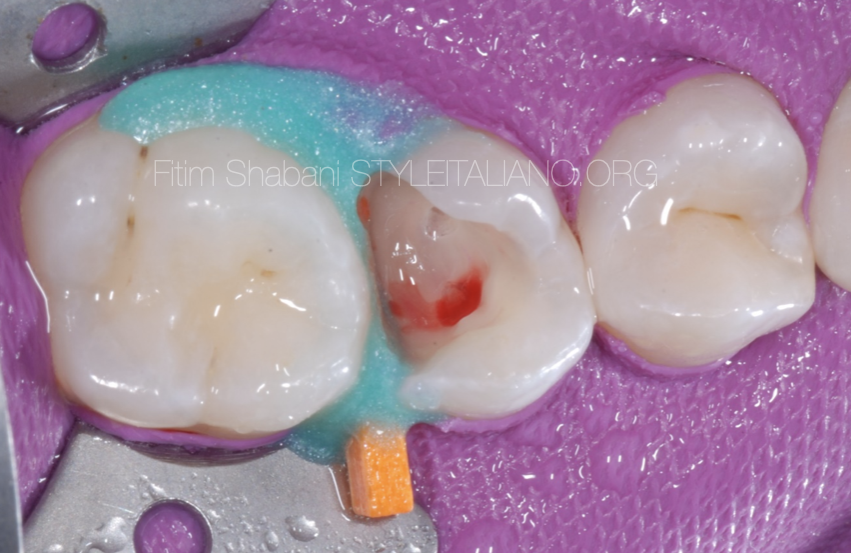
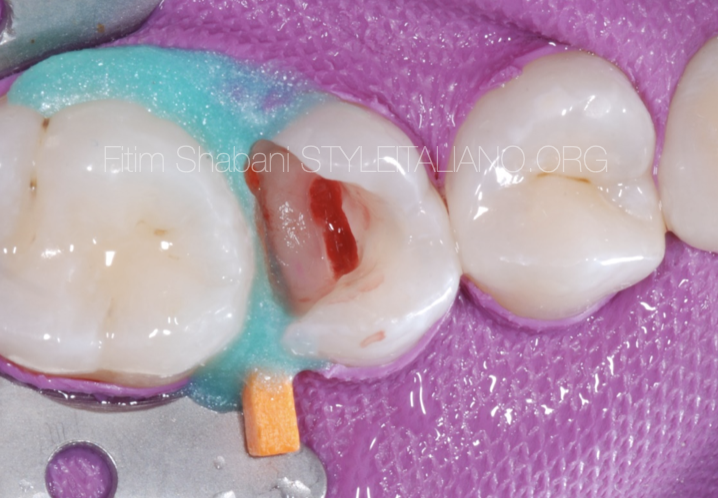
Fig. 3
Isolation, initial preparation which has resulted in pulp opening.
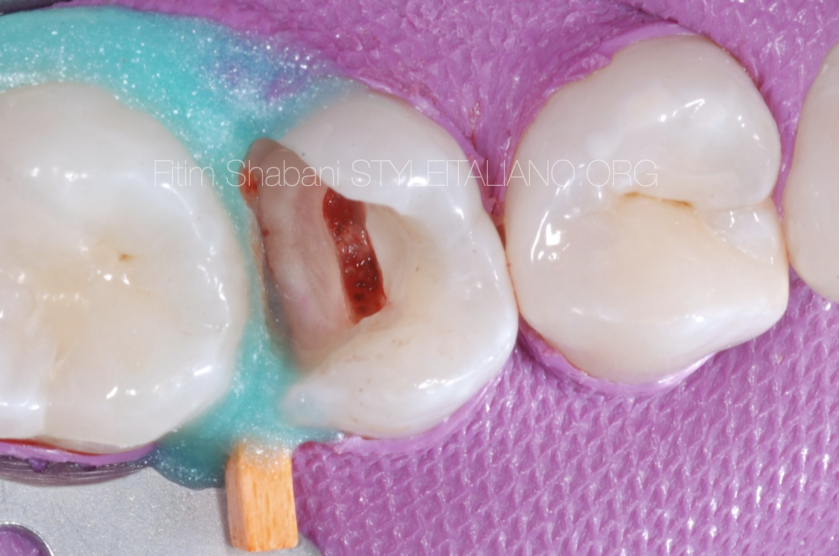
Fig. 4
Caries removal prior to pulpal access is required to reduce the bacterial load.
Hemostasis – cotton pellet within 3min.
video of the procedure
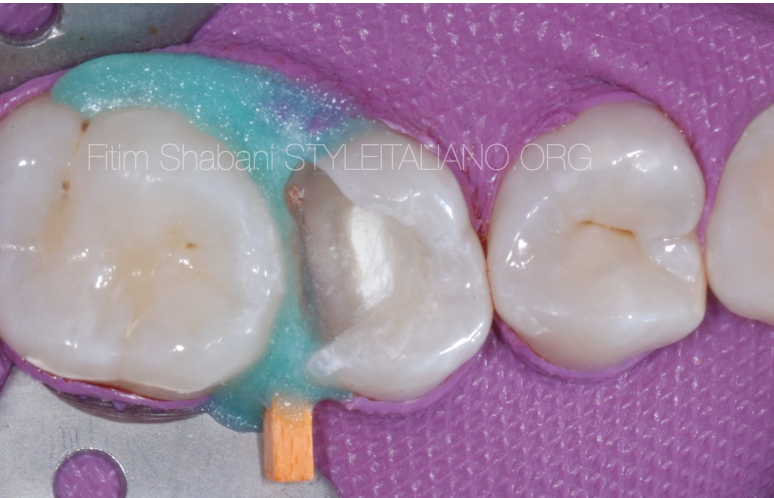
Fig. 5
MTA (mineral trioxide aggregate) was placed against the wound.
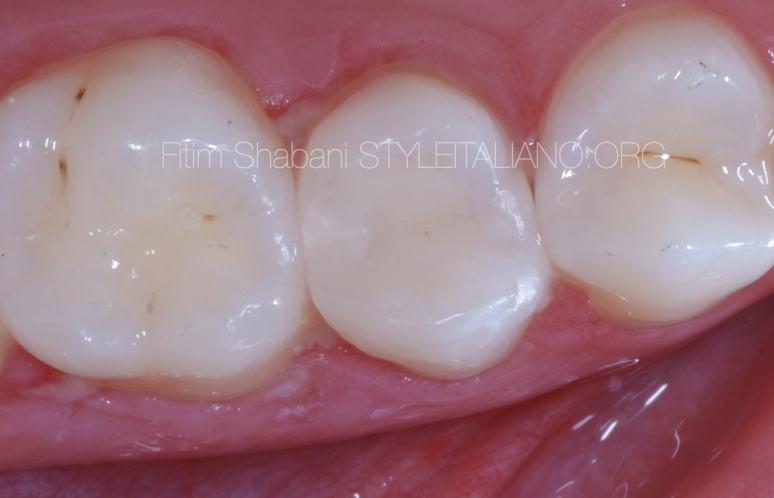
Fig. 6
Composite restoration
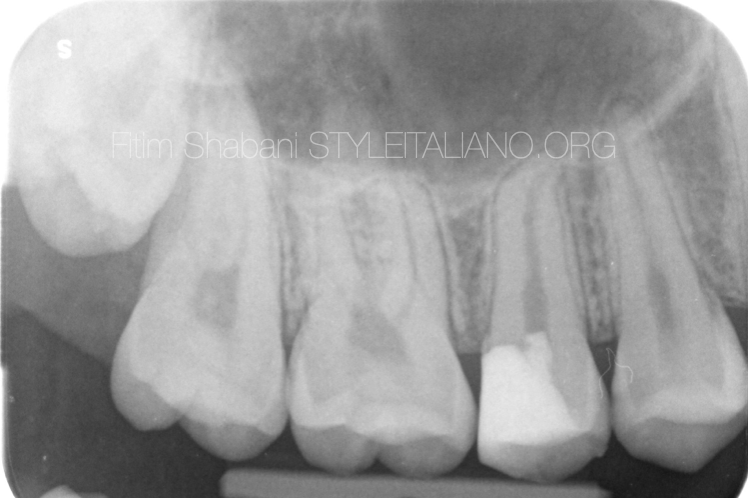
Fig. 7
X-ray after 1 treatment
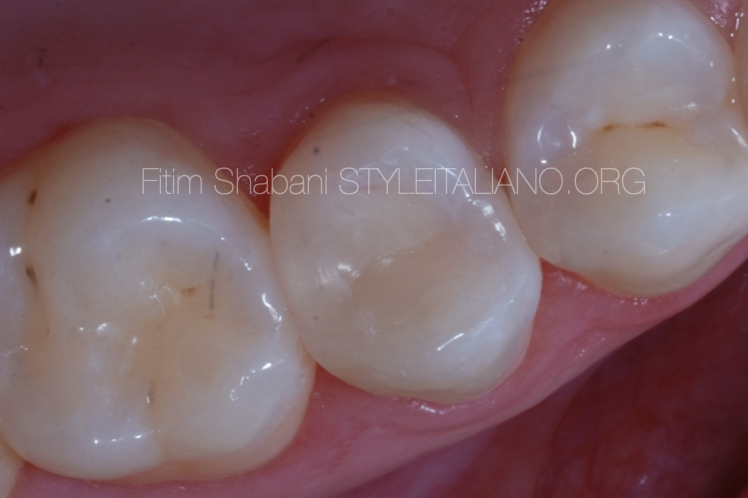
Fig. 8
Intraoral picture after 1.5 year
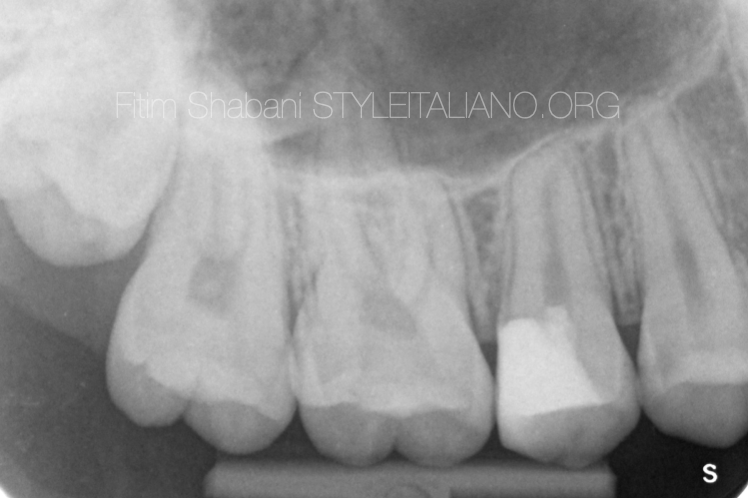
Fig. 9
X-ray after 1.5 year
The patient has no complaints
The vitality test is positive delayed
Conclusions
Pulpotomy is a prospective substitute for root canal treatment in managing permanent teeth with carious pulp exposures, even in permanent teeth with irreversible pulpitis. Large, well-designed trials comparing pulpotomy with other treatments in terms of cost-effectiveness should be informative.
Bibliography
1. Endodontists A. Glossary of Endodontic Terms. Chicago: American Association of Endodontists; 2012.
2. Taha NA, Abdelkhader SZ. Outcome of full pulpotomy using Biodentine in adult patients with symptoms indicative of irreversible pulpitis. Int Endod J. 2018;51:819–28.
3. Qudeimat MA, Alyahya A, Hasan AA. Mineral trioxide aggregate pulpotomy for permanent molars with clinical signs indicative of irreversible pulpitis: A preliminary study. Int Endod J. 2017;50:126–34.
4. McDonald RE, Avery DR, Dean JA. Treatment of deep caries, vital pulp exposure and pulpless teeth. In: Dentistry for the Child and Adolescent. 8th ed. St. Louis: Mosby: 2004. pp. 389–412.
5. Linsuwanont P, Wimonsutthikul K, Pothimoke U, Santiwong B. Treatment outcomes of mineral trioxide aggregate pulpotomy in vital permanent teeth with carious pulp exposure: The retrospective study. J Endod. 2017;43:225–30.
6. Yuanyuan Li 1, Bingdong Sui 2, Christian Dahl 3, Brian Bergeron 3, Peter Shipman 4, Lina Niu 5, Jihua Chen 6, Franklin R Tay 7 Pulpotomy for carious pulp exposures in permanent teeth: A systematic review and meta-analysis. In : J Dent, May 2019

